Abstract
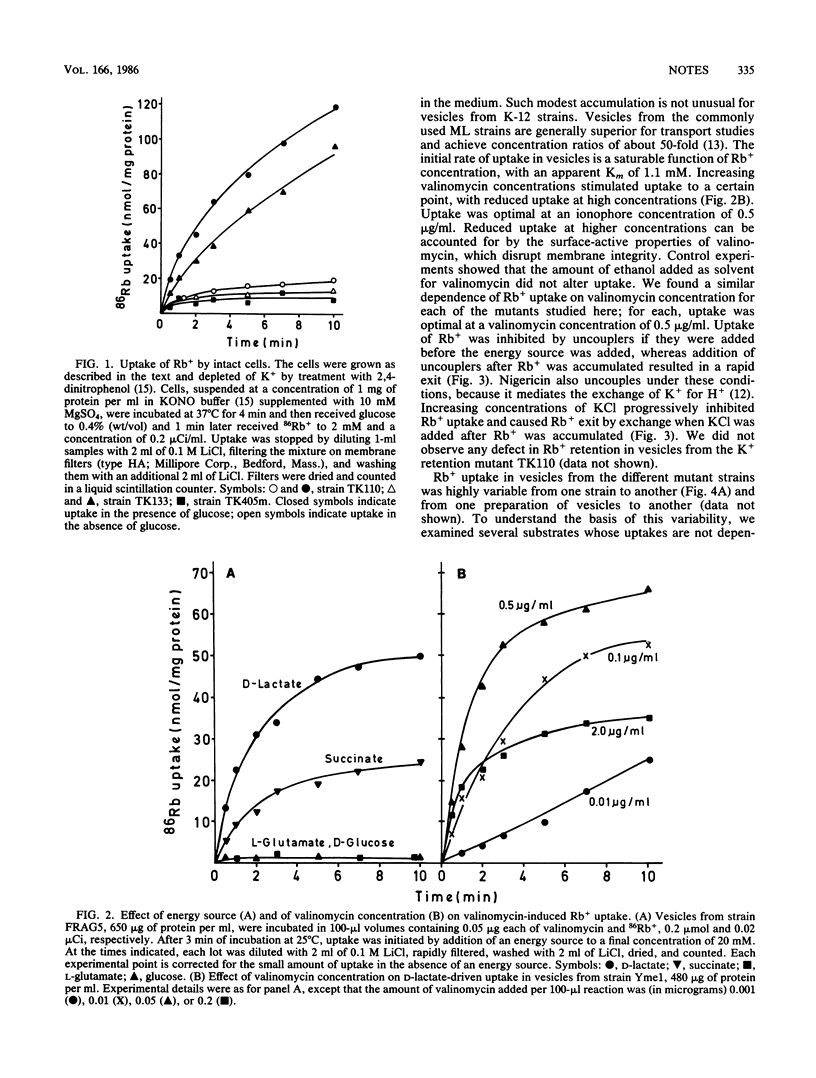
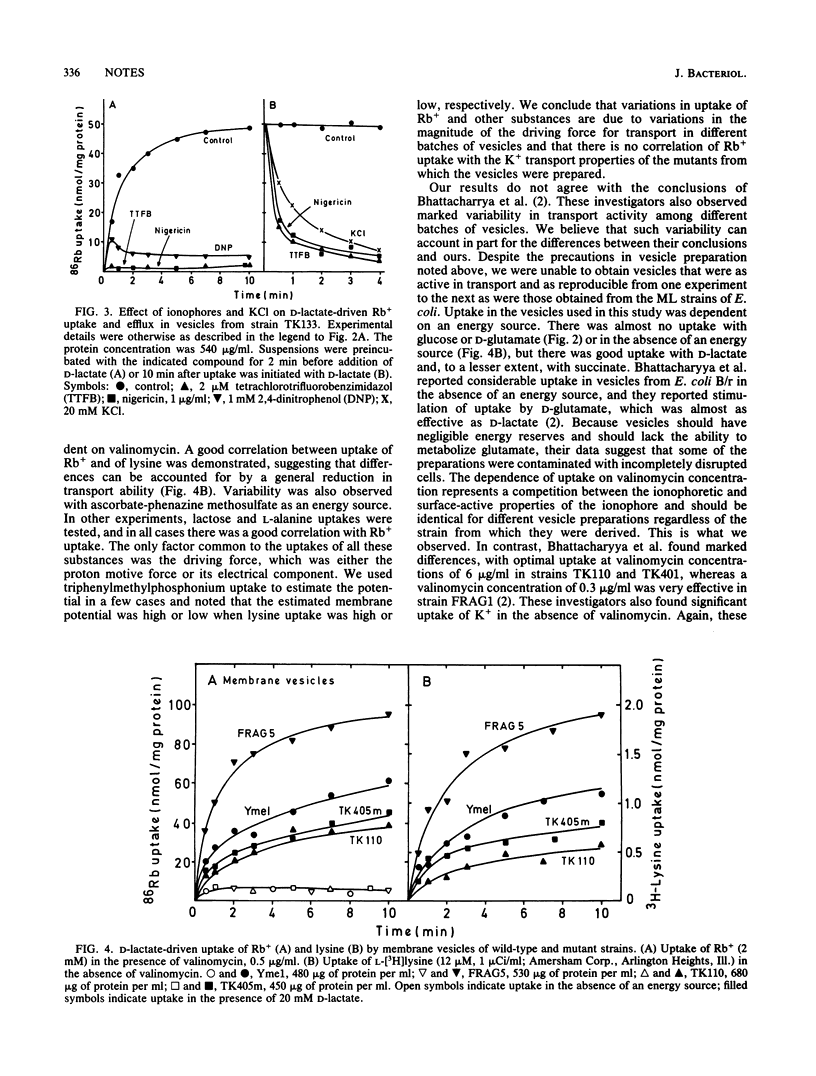
Transport systems for K+ in Escherichia coli are not detectable in membrane vesicles, but vesicles will take up K+ (and Rb+) in the presence of valinomycin. It is generally believed that valinomycin acts as a lipid-soluble cation carrier and that it does not interact with or activate cation transport systems. This view is challenged by Bhattacharyya et al. (Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 68:1448-1492, 1971), who reported reduced uptake in vesicles from E. coli mutants with K+ transport defects. We reexamined this question with some of the same mutants and were unable to confirm a correlation of valinomycin-induced vesicle transport with transport properties in intact cells. We found great variability in transport activity of vesicles from these E. coli K-12 strains and believe such variability as well as possible contamination with intact cells accounts for the earlier report. Our data do not support the idea that valinomycin-mediated transport in vesicles is related to physiological K+ transport systems.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altendorf K., Hirata H., Harold F. M. Accumulation of lipid-soluble ions and of rubidium as indicators of the electrical potential in membrane vesicles of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1975 Feb 25;250(4):1405–1412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharyya P., Epstein W., Silver S. Valinomycin-induced uptake of potassium in membrane vesicles from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jul;68(7):1488–1492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.7.1488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boos W. Bacterial transport. Annu Rev Biochem. 1974;43(0):123–146. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.43.070174.001011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein W., Kim B. S. Potassium transport loci in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1971 Nov;108(2):639–644. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.2.639-644.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson P. J. Ion transport by energy-conserving biological membranes. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1971;25:393–428. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.25.100171.002141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson P. J., McGivan J. D., Chappell J. B. The action of certain antibiotics on mitochondrial, erythrocyte and artificial phospholipid membranes. The role of induced proton permeability. Biochem J. 1969 Feb;111(4):521–535. doi: 10.1042/bj1110521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata H., Altendorf K., Harold F. M. Role of an electrical potential in the coupling of metabolic energy to active transport by membrane vesicles of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jun;70(6):1804–1808. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.6.1804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaback H. R., Barnes E. M., Jr Mechanisms of active transport in isolated membrane vesicles. II. The mechanism of energy coupling between D-lactic dehydrogenase and beta-galactoside transport in membrane preparations from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1971 Sep 10;246(17):5523–5531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lombardi F. J., Reeves J. P., Kaback H. R. Mechanisms of active transport in isolated bacterial membrane vesicles. 8. Valinomycin-induced rubidium transport. J Biol Chem. 1973 May 25;248(10):3551–3565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Läuger P. Carrier-mediated ion transport. Science. 1972 Oct 6;178(4056):24–30. doi: 10.1126/science.178.4056.24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. Proton-translocation phosphorylation in mitochondria, chloroplasts and bacteria: natural fuel cells and solar cells. Fed Proc. 1967 Sep;26(5):1370–1379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhoads D. B., Waters F. B., Epstein W. Cation transport in Escherichia coli. VIII. Potassium transport mutants. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Mar;67(3):325–341. doi: 10.1085/jgp.67.3.325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhoads D. B., Woo A., Epstein W. Discrimination between Rb+ and K+ by Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Aug 15;469(1):45–51. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90324-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


