Abstract
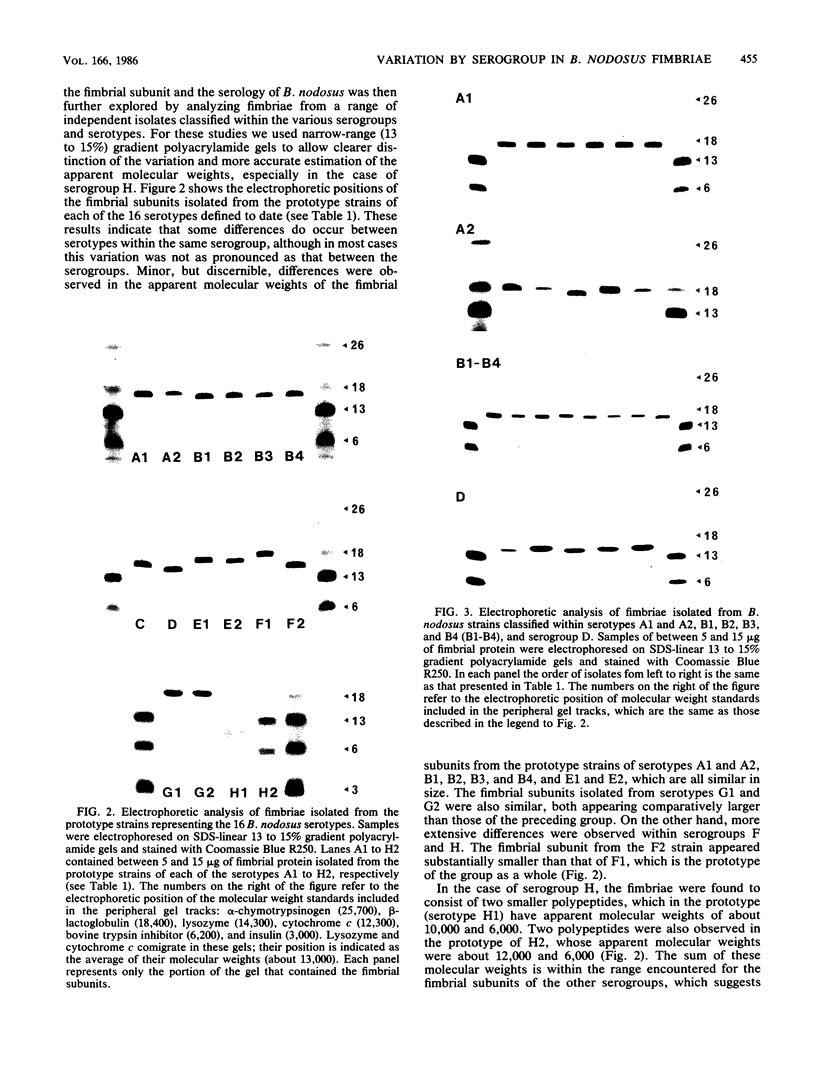
The fimbriae of Bacteroides nodosus play a major role in protective immunity against ovine footrot and are an important determinant in the serological classification system that divides field isolates into at least eight serogroups and 16 serotypes. Purified fimbriae contain two polypeptide antigens, the structural subunit of the fimbrial strand (molecular weight about 17,000) and a basal protein (molecular weight about 80,000), both of which exhibit structural variation. Fimbriae were prepared from all prototype strains, as well as from a number of other isolates representative of each of the B. nodosus serotypes, and analyzed by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Substantial variation was observed in the electrophoretic mobility of the fimbrial subunits from the prototypes of each of the eight serogroups. With the exception of serogroup H, which is an unusual case, the apparent molecular weights of the fimbrial subunits ranged from about 16,500 in serogroup D to 19,000 in serogroup F (serotype 1); in serogroup A, B, C and E, the apparent molecular weights were clustered in the range of 17,000 to 17,500, whereas serogroup G was about 18,500. Serogroup H fimbriae appeared to consist of two smaller polypeptides, which in the prototype (H1) had apparent molecular weights of about 6,000 and 10,000 and which seem to have arisen as a consequence of an internal proteolytic nick in the original subunit. Electrophoretic variation in the fimbrial subunit was also observed between different serotypes, although with the exceptions of serogroups F and H, this was not as pronounced as between the serogroups. Examination of a number of isolates classified within the same serotypes showed that some variation, although minor, also occurred at this level. The basal antigen exhibited significant variation at all levels of the serotypic hierarchy in a manner apparently unrelated to the classification system. Among the range of isolates examined, the apparent molecular weight of this antigen varied from about 77,000 to 88,000.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradley D. E. A function of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO polar pili: twitching motility. Can J Microbiol. 1980 Feb;26(2):146–154. doi: 10.1139/m80-022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan T. M. Antigenic heterogeneity of gonococcal pili. J Exp Med. 1975 Jun 1;141(6):1470–1475. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.6.1470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claxton P. D., Ribeiro L. A., Egerton J. R. Classification of Bacteroides nodosus by agglutination tests. Aust Vet J. 1983 Nov;60(11):331–334. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1983.tb02834.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Depiazzi L. J., Rood J. I. The thermostability of proteases from virulent and benign strains of Bacteroides nodosus. Vet Microbiol. 1984 Jul;9(3):227–236. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(84)90040-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duckworth M., Jackson D., Zak K., Heckels J. E. Structural variations in pili expressed during gonococcal infection. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 May;129(5):1593–1596. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-5-1593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egerton J. R., Roberts D. S., Parsonson I. M. The aetiology and pathogenesis of ovine foot-rot. I. A histological study of the bacterial invasion. J Comp Pathol. 1969 Apr;79(2):207–215. doi: 10.1016/0021-9975(69)90007-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egerton J. R. Significance of Fusiformis nodosus serotypes in resistance of vaccinated sheep to experimental foot-rot. Aust Vet J. 1974 Feb;50(2):59–62. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1974.tb05252.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egerton J. R. Surface and somatic antigens of Fusiformis nodosus. J Comp Pathol. 1973 Jan;83(1):151–159. doi: 10.1016/0021-9975(73)90038-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emery D. L., Clark B. L., Stewart D. J., O'Donnell I. J., Hewish D. R. Analysis of the outer membrane proteins of Bacteroides nodosus, the causal organism of ovine footrot. Vet Microbiol. 1984 Apr;9(2):155–168. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(84)90031-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emery D. L. Reactivity of sera from sheep immunised with individual outer membrane proteins of Bacteroides nodosus against heterologous bacterial strains. Vet Microbiol. 1984 Sep;9(5):453–466. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(84)90066-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Every D. Proteinase isoenzyme patterns of Bacteroides nodosus: distinction between ovine virulent isolates, ovine benign isolates and bovine isolates. J Gen Microbiol. 1982 Apr;128(4):809–812. doi: 10.1099/00221287-128-4-809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Every D. Purification of pili from Bacteroides nodosus and an examination of their chemical, physical and serological properties. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Dec;115(2):309–316. doi: 10.1099/00221287-115-2-309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Every D., Skerman T. M. Protection of sheep against experimental footrot by vaccination with pili purified from Bacteroides nodosus. N Z Vet J. 1982 Oct;30(10):156–158. doi: 10.1080/00480169.1982.34921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froholm L. O., Sletten K. Purification and N-terminal sequence of a fimbrial protein from Moraxella nonliquefaciens. FEBS Lett. 1977 Jan 15;73(1):29–32. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80008-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frost L. S., Paranchych W. Composition and molecular weight of pili purified from Pseudomonas aeruginosa K. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jul;131(1):259–269. doi: 10.1128/jb.131.1.259-269.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaastra W., de Graaf F. K. Host-specific fimbrial adhesins of noninvasive enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli strains. Microbiol Rev. 1982 Jun;46(2):129–161. doi: 10.1128/mr.46.2.129-161.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagblom P., Segal E., Billyard E., So M. Intragenic recombination leads to pilus antigenic variation in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Nature. 1985 May 9;315(6015):156–158. doi: 10.1038/315156a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henrichsen J. The occurrence of twitching motility among gram-negative bacteria. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1975 Jun;83(3):171–178. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1975.tb00089.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henrichsen J. Twitching motility. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1983;37:81–93. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.37.100183.000501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermodson M. A., Chen K. C., Buchanan T. M. Neisseria pili proteins: amino-terminal amino acid sequences and identification of an unusual amino acid. Biochemistry. 1978 Feb 7;17(3):442–445. doi: 10.1021/bi00596a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kortt A. A., Burns J. E., Stewart D. J. Detection of the extracellular proteases of Bacteroides nodosus in polyacrylamide gels: a rapid method of distinguishing virulent and benign ovine isolates. Res Vet Sci. 1983 Sep;35(2):171–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kortt A. A., O'Donnell I. J., Stewart D. J., Clark B. L. Activities and partial purification of extracellular proteases of Bacteroides nodosus from virulent and benign footrot. Aust J Biol Sci. 1982;35(5):481–489. doi: 10.1071/bi9820481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambden P. R. Biochemical comparison of pili from variants of Neisseria gonorrhoeae P9. J Gen Microbiol. 1982 Sep;128(9):2105–2111. doi: 10.1099/00221287-128-9-2105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. W., Alexander B., McGowan B. Purification, characterization, and serologic characteristics of Bacteroides nodosus pili and use of a purified pili vaccine in sheep. Am J Vet Res. 1983 Sep;44(9):1676–1681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrs C. F., Schoolnik G., Koomey J. M., Hardy J., Rothbard J., Falkow S. Cloning and sequencing of a Moraxella bovis pilin gene. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jul;163(1):132–139. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.1.132-139.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattick J. S., Anderson B. J., Mott M. R., Egerton J. R. Isolation and characterization of Bacteroides nodosus fimbriae: structural subunit and basal protein antigens. J Bacteriol. 1984 Nov;160(2):740–747. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.2.740-747.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattick J. S., Tsukamoto Y., Nickless J., Wakil S. J. The architecture of the animal fatty acid synthetase. I. Proteolytic dissection and peptide mapping. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 25;258(24):15291–15299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattick J. S., Zehner Z. E., Calabro M. A., Wakil S. J. The isolation and characterization of fatty-acid synthetase mRNA from rat mammary gland. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Mar;114(3):643–651. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05192.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKern N. M., O'Donnell I. J., Inglis A. S., Stewart D. J., Clark B. L. Amino acid sequence of pilin from Bacteroides nodosus (strain 198), the causative organism of ovine footrot. FEBS Lett. 1983 Nov 28;164(1):149–153. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80039-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKern N. M., O'Donnell I. J., Stewart D. J., Clark B. L. Primary structure of pilin protein from Bacteroides nodosus strain 216: comparison with the corresponding protein from strain 198. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Jan;131(1):1–6. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T. F., Billyard E., Haas R., Storzbach S., So M. Pilus genes of Neisseria gonorrheae: chromosomal organization and DNA sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):6110–6114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.6110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T. F., Mlawer N., So M. Pilus expression in Neisseria gonorrhoeae involves chromosomal rearrangement. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):45–52. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90010-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novotny P., Turner W. H. Immunological heterogeneity of pili of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Jul;89(1):87–92. doi: 10.1099/00221287-89-1-87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olafson R. W., McCarthy P. J., Bhatti A. R., Dooley J. S., Heckels J. E., Trust T. J. Structural and antigenic analysis of meningococcal piliation. Infect Immun. 1985 May;48(2):336–342. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.2.336-342.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottow J. C. Ecology, physiology, and genetics of fimbriae and pili. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1975;29:79–108. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.29.100175.000455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paranchych W., Sastry P. A., Frost L. S., Carpenter M., Armstrong G. D., Watts T. H. Biochemical studies on pili isolated from Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain PAO. Can J Microbiol. 1979 Oct;25(10):1175–1181. doi: 10.1139/m79-182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasloske B. L., Finlay B. B., Paranchych W. Cloning and sequencing of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAK pilin gene. FEBS Lett. 1985 Apr 22;183(2):408–412. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80821-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson J. N., Vincent P., Ward M. E. The preparation and properties of gonococcal pili. J Gen Microbiol. 1977 Sep;102(1):169–177. doi: 10.1099/00221287-102-1-169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothbard J. B., Fernandez R., Schoolnik G. K. Strain-specific and common epitopes of gonococcal pili. J Exp Med. 1984 Jul 1;160(1):208–221. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sastry P. A., Pearlstone J. R., Smillie L. B., Paranchych W. Amino acid sequence of pilin isolated from pseudomonas aeruginosa PAK. FEBS Lett. 1983 Jan 24;151(2):253–256. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80080-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoolnik G. K., Fernandez R., Tai J. Y., Rothbard J., Gotschlich E. C. Gonococcal pili. Primary structure and receptor binding domain. J Exp Med. 1984 May 1;159(5):1351–1370. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.5.1351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoolnik G. K., Tai J. Y., Gotschlich E. C. A pilus peptide vaccine for the prevention of gonorrhea. Prog Allergy. 1983;33:314–331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens D. S., Whitney A. M., Rothbard J., Schoolnik G. K. Pili of Neisseria meningitidis. Analysis of structure and investigation of structural and antigenic relationships to gonococcal pili. J Exp Med. 1985 Jun 1;161(6):1539–1553. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.6.1539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart D. J. An electron microscopic study of Fusiformis nodosus. Res Vet Sci. 1973 Jan;14(1):132–134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart D. J., Clark B. L., Peterson J. E., Griffiths D. A., Smith E. F. Importance of pilus-associated antigen in Bacteroides nodosus vaccines. Res Vet Sci. 1982 Mar;32(2):140–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart D. J. Studies on the antigenic structure of Bacteroides nodosus. Res Vet Sci. 1978 May;24(3):293–299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virji M., Heckels J. E. Antigenic cross-reactivity of Neisseria pili: investigations with type- and species-specific monoclonal antibodies. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Sep;129(9):2761–2768. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-9-2761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virji M., Heckels J. E. The role of common and type-specific pilus antigenic domains in adhesion and virulence of gonococci for human epithelial cells. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 May;130(5):1089–1095. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-5-1089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker P. D., Short J., Thomson R. O., Roberts D. S. The fine structure of Fusiformis nodosus with special reference to the location of antigens associated with immunogenicity. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 Aug;77(2):351–361. doi: 10.1099/00221287-77-2-351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]








