Abstract
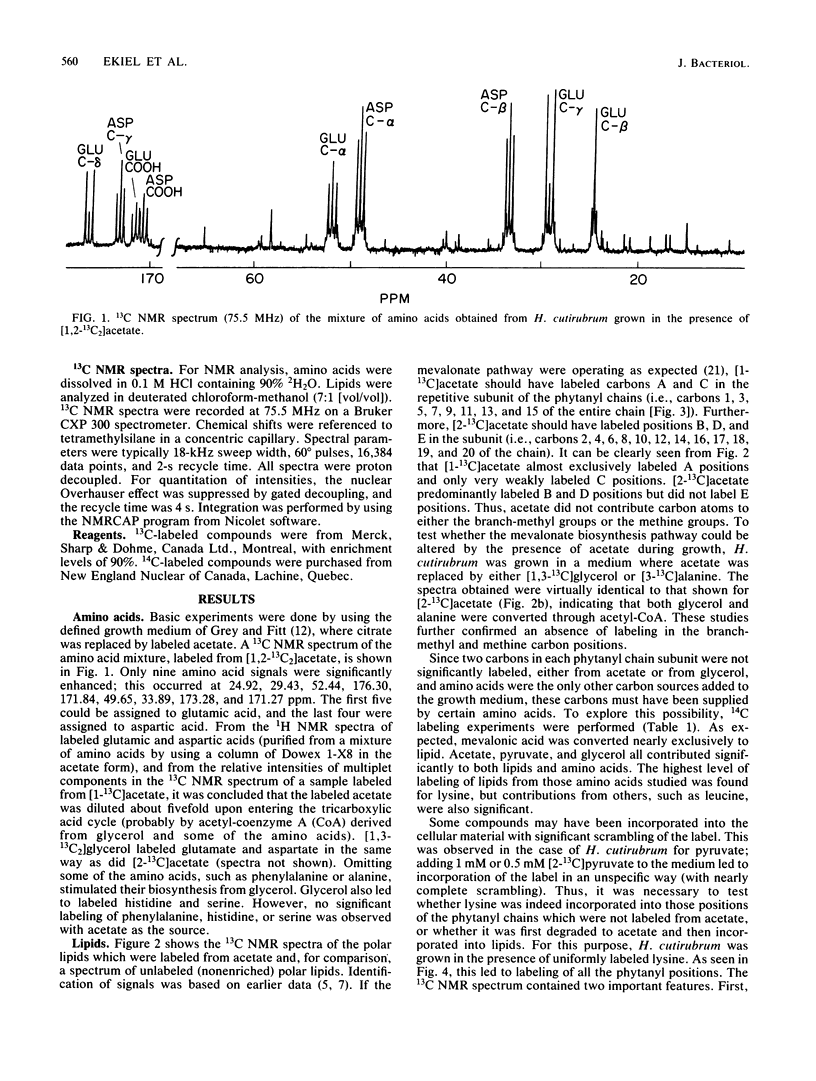
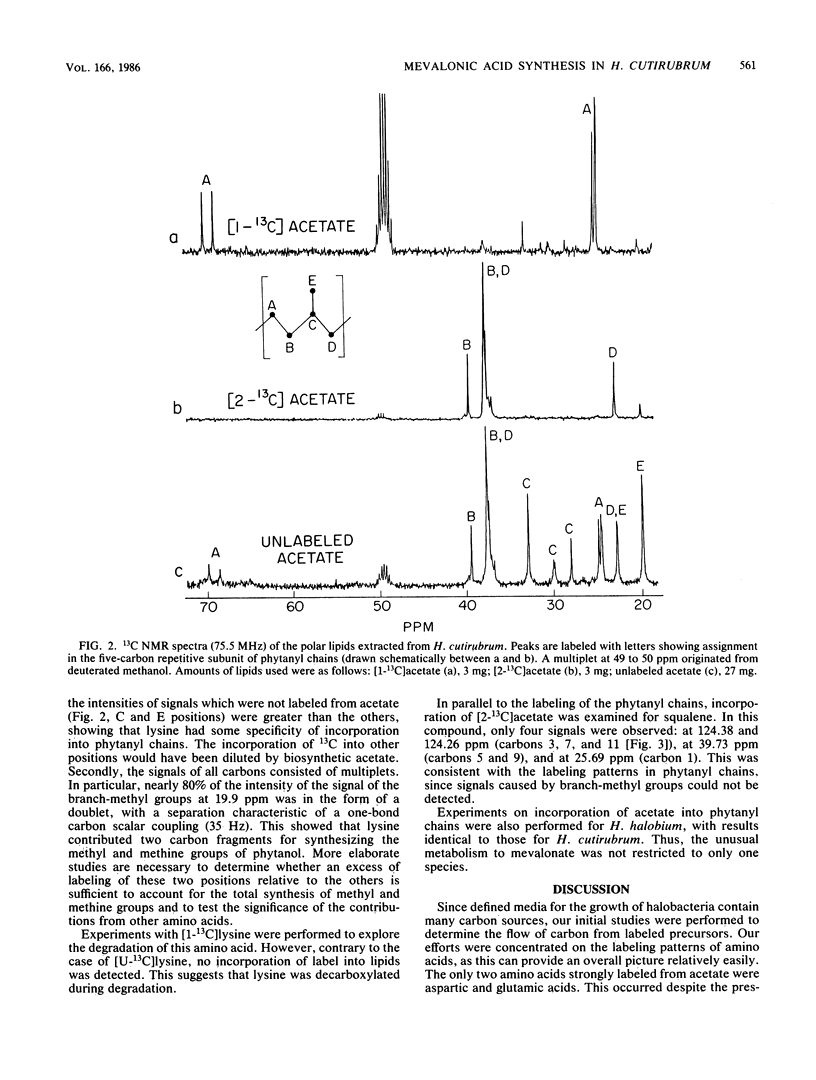
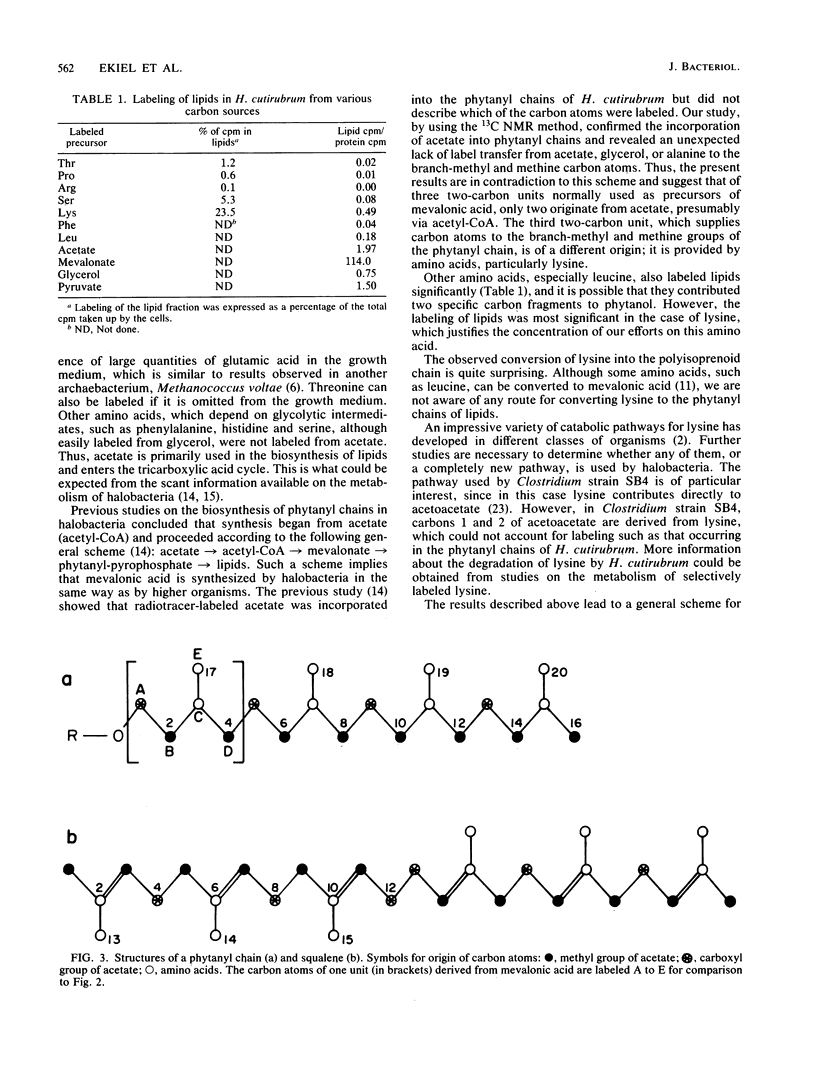
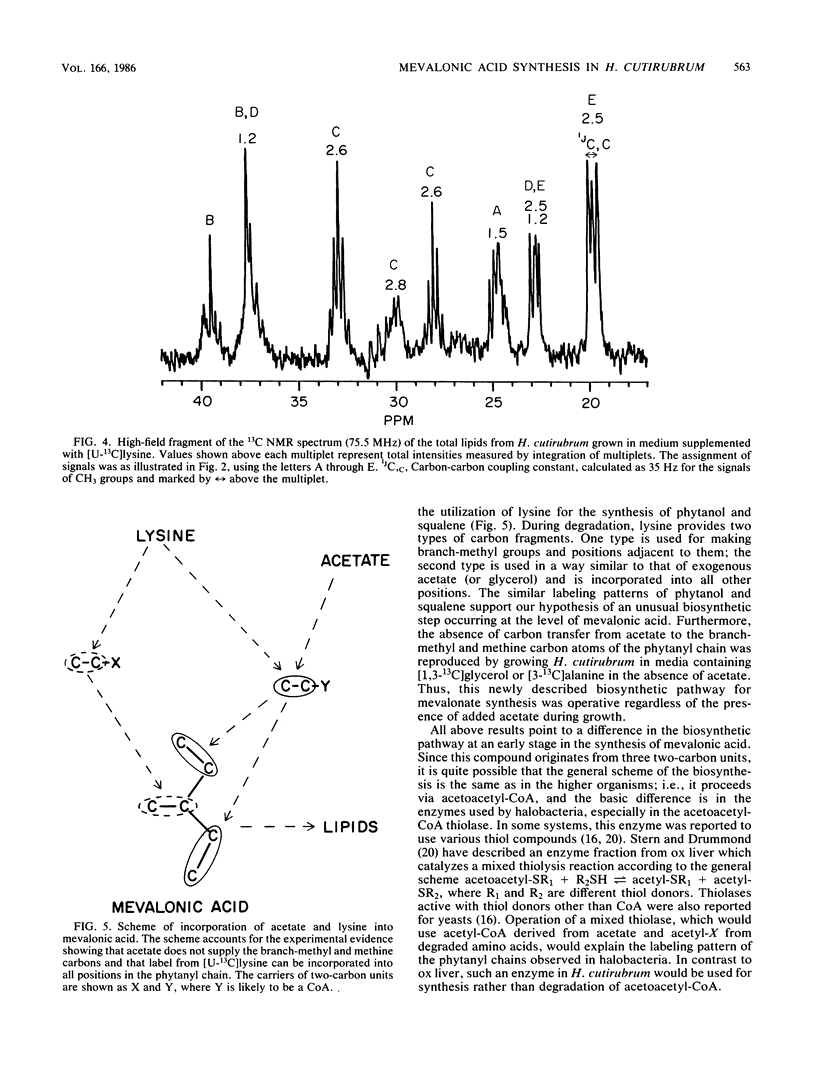
13C nuclear magnetic resonance revealed an unusual pathway for the biosynthesis of lipids in Halobacterium cutirubrum and H. halobium. Mevalonic acid was not synthesized from three acetyl-coenzyme A molecules, as has been suggested previously, and the branch-methyl and methine carbons in phytanyl chains were derived from neither acetate nor glycerol. Instead, they were supplied by the degradation of amino acids, in particular of lysine. Presumably, two different types of two-carbon fragments were used simultaneously by halobacteria for the biosynthesis of mevalonate. The labeling pattern of squalene supported the above conclusions. Based on these data, a general scheme is proposed to account for the contribution of lysine-to-lipid biosynthesis.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aitken D. M., Brown A. D. Citrate and glyoxylate cycles in the halophil, Halobacterium salinarium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Apr 1;177(2):351–354. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(69)90148-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRODIE J. D., WASSON G., PORTER J. W. The participation of malonyl coenzyme A in the biosynthesis of mevalonic acid. J Biol Chem. 1963 Apr;238:1294–1301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Degani H., Danon A., Caplan S. R. Proton and carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance studies of the polar lipids of Halobacterium halobium. Biochemistry. 1980 Apr 15;19(8):1626–1631. doi: 10.1021/bi00549a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekiel I., Jarrell K. F., Sprott G. D. Amino acid biosynthesis and sodium-dependent transport in Methanococcus voltae, as revealed by 13C NMR. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Jun 3;149(2):437–444. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08944.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekiel I., Smith I. C., Sprott G. D. Biosynthetic pathways in Methanospirillum hungatei as determined by 13C nuclear magnetic resonance. J Bacteriol. 1983 Oct;156(1):316–326. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.1.316-326.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekiel I., Sprott G. D., Patel G. B. Acetate and CO2 assimilation by Methanothrix concilii. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jun;162(3):905–908. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.3.905-908.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grey V. L., Fitt P. S. An improved synthetic growth medium for Halobacterium cutirubrum. Can J Microbiol. 1976 Mar;22(3):440–442. doi: 10.1139/m76-068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kates M., Wassef M. K., Kushner D. J. Radioisotopic studies on the biosynthesis of the glyceryl diether lipids of Halobacterium cutirubrum. Can J Biochem. 1968 Aug;46(8):971–977. doi: 10.1139/o68-145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornblatt J. A., Rudney H. Two forms of acetoacetyl coenzyme A thiolase in yeast. I. Separation and properties. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jul 25;246(14):4417–4423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ONISHI H., MCCANCE E., GIBBONS N. E. A SYNTHETIC MEDIUM FOR EXTREMELY HALOPHILIC BACTERIA. Can J Microbiol. 1965 Apr;11:365–373. doi: 10.1139/m65-044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STERN J. R., DRUMMOND G. I. Enzymes of ketone body metabolism. III. Enzymic thiolysis of acetoacetyl coenzyme A and acetoacetyl-pantetheine by mono- and dithiol compounds. J Biol Chem. 1961 Nov;236:2892–2897. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprott G. D., Usher J. R. The electrochemical proton gradient and phenylalanine transport in Escherichia coli irradiated with near-ultraviolet light. Can J Microbiol. 1977 Dec;23(12):1683–1688. doi: 10.1139/m77-242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoeckenius W., Lozier R. H., Bogomolni R. A. Bacteriorhodopsin and the purple membrane of halobacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Mar 14;505(3-4):215–278. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(79)90006-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WAGNER A. F., FOLKERS K. The organic and biological chemistry of mevalonic acid. Endeavour. 1961 Oct;20:177–187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yorifuji T., Jeng I. M., Barker H. A. Purification and properties of 3-keto-5-aminohexanoate cleavage enzyme from a lysine-fermenting Clostridium. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jan 10;252(1):20–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


