Abstract
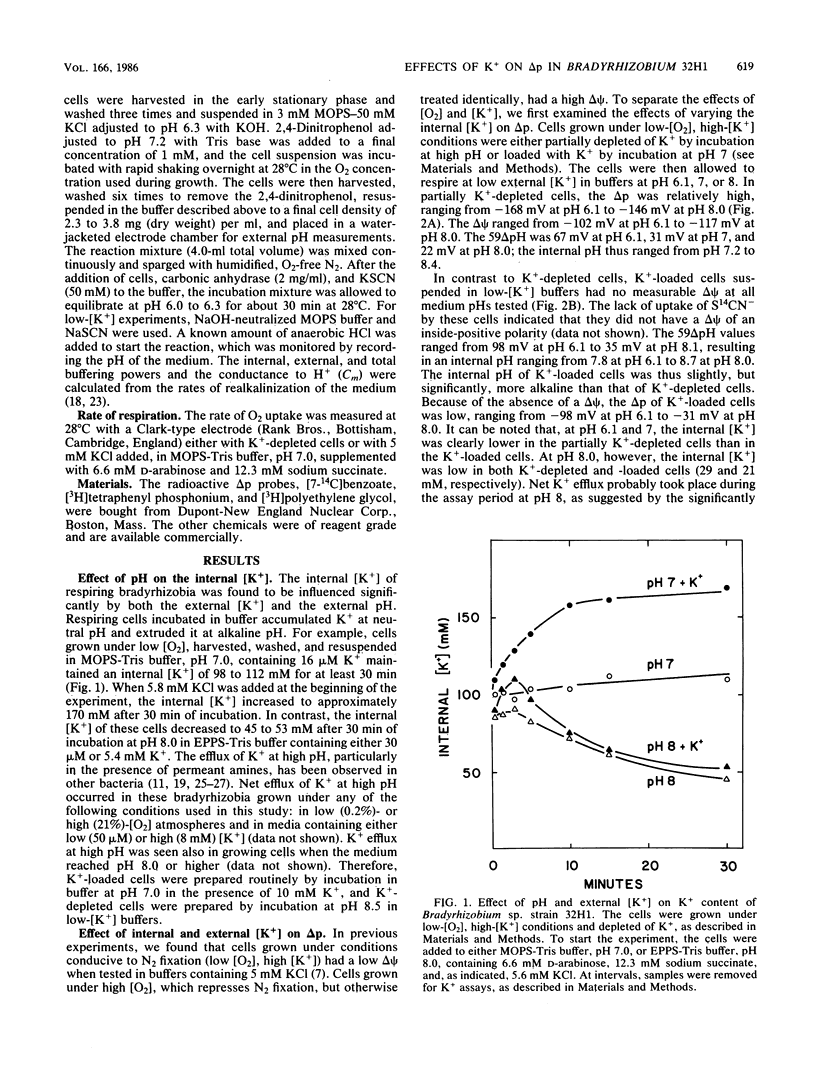
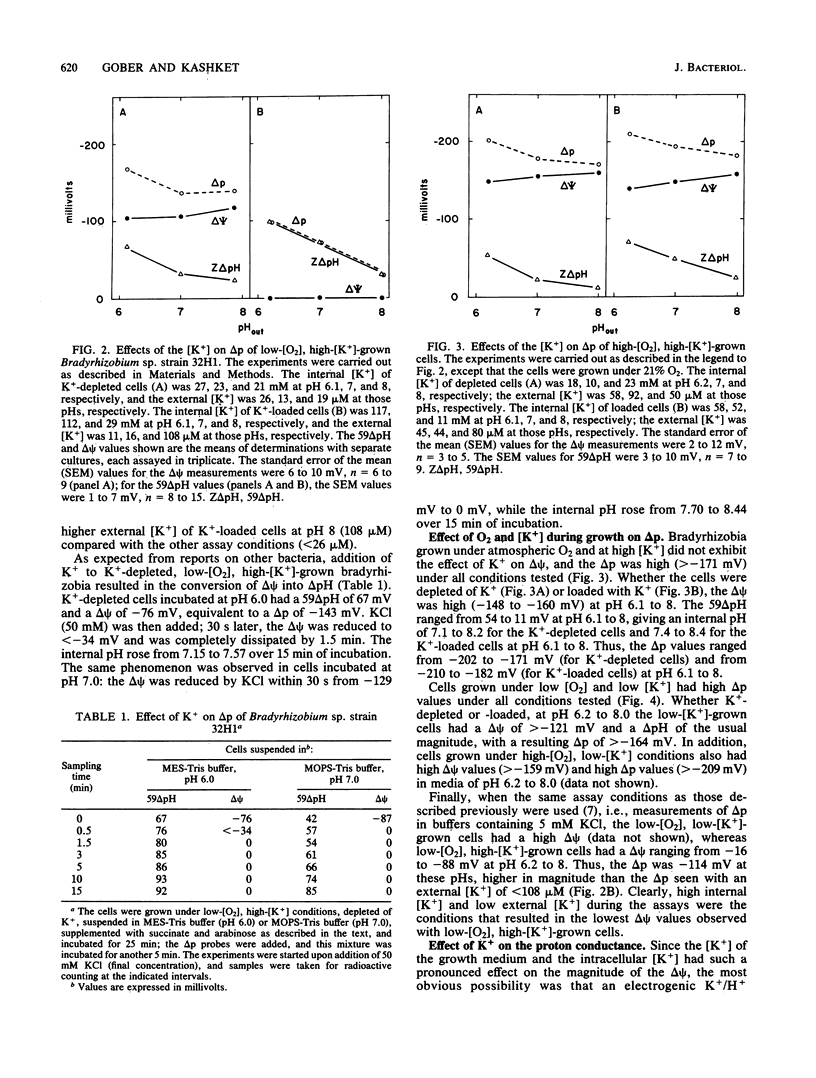
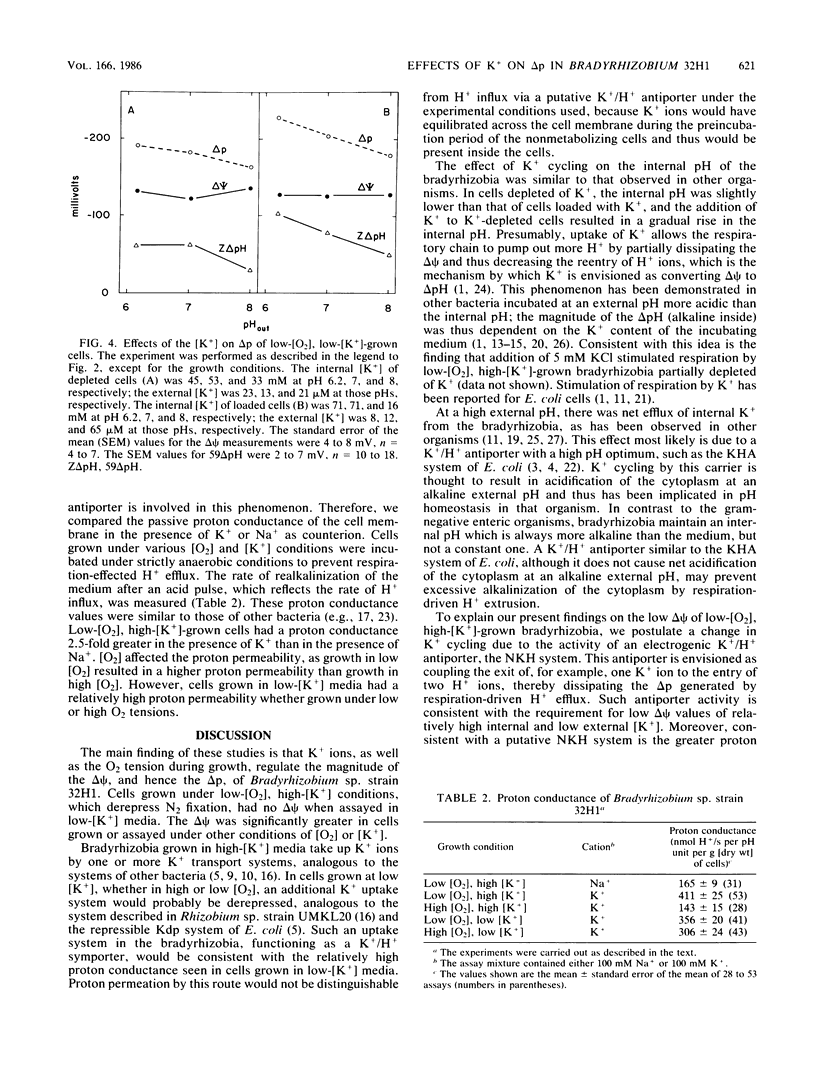
In previous studies, respiring Bradyrhizobium sp. strain 32H1 cells grown under 0.2% O2, conditions that derepress N2 fixation, were found to have a low proton motive force of less than -121 mV, because of a low membrane potential (delta psi). In contrast, cells grown under 21% O2, which do not fix N2, had high proton motive force values of -175 mV or more, which are typical of respiring bacteria, because of high delta psi values. In the present study, we found that a delta psi of 0 mV in respiring cells requires growth in relatively high-[K+] media (8 mM), low O2 tension, and high internal [K+]. When low-[O2], high-[K+]-grown cells were partially depleted of K+, the delta psi was high. When cells were grown under 21% O2 or in media low in K+ (50 microM K+), the delta psi was again high. The transmembrane pH gradient was affected only slightly by varying the growth or assay conditions. In addition, low-[O2], high-[K+]-grown cells had a greater proton permeability than did high-[O2]-grown cells. To explain these findings, we postulate that cells grown under conditions that derepress N2 fixation contain an electrogenic K+/H+ antiporter that is responsible for the dissipation of the delta psi. The consequence of this alteration in K+ cycling is rerouting of proton circuits so that the putative antiporter becomes the major pathway for H+ influx, rather than the H+-ATP synthase.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bakker E. P., Mangerich W. E. Interconversion of components of the bacterial proton motive force by electrogenic potassium transport. J Bacteriol. 1981 Sep;147(3):820–826. doi: 10.1128/jb.147.3.820-826.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booth I. R., Kroll R. G. Regulation of cytoplasmic pH (pH1) in bacteria and its relationship to metabolism. Biochem Soc Trans. 1983 Jan;11(1):70–72. doi: 10.1042/bst0110070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brey R. N., Beck J. C., Rosen B. P. Cation/proton antiport systems in Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Aug 29;83(4):1588–1594. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91403-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brey R. N., Rosen B. P., Sorensen E. N. Cation/proton antiport systems in Escherichia coli. Properties of the potassium/proton antiporter. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 10;255(1):39–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gober J. W., Kashket E. R. H+/ATP stoichiometry of cowpea Rhizobium sp. strain 32H1 cells grown under nitrogen-fixing and nitrogen-nonfixing conditions. J Bacteriol. 1984 Oct;160(1):216–221. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.1.216-221.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gober J. W., Kashket E. R. Methylammonium uptake by Rhizobium sp. strain 32H1. J Bacteriol. 1983 Mar;153(3):1196–1201. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.3.1196-1201.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harold F. M., Papineau D. Cation transport and electrogenesis by Streptococcus faecalis. I. The membrane potential. J Membr Biol. 1972;8(1):27–44. doi: 10.1007/BF01868093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heefner D. L. Transport of H+, K+, Na+ and Ca++ in Streptococcus. Mol Cell Biochem. 1982 Apr 30;44(2):81–106. doi: 10.1007/BF00226893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakinuma Y., Harold F. M. ATP-driven exchange of Na+ and K+ ions by Streptococcus faecalis. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2086–2091. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashket E. R., Barker S. L. Effects of potassium ions on the electrical and pH gradients across the membrane of Streptococcus lactis cells. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jun;130(3):1017–1023. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.3.1017-1023.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashket E. R. Effects of K+ and Na+ on the proton motive force of respiring Escherichia coli at alkaline pH. J Bacteriol. 1985 Aug;163(2):423–429. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.2.423-429.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashket E. R. The proton motive force in bacteria: a critical assessment of methods. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1985;39:219–242. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.39.100185.001251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroll R. G., Booth I. R. The relationship between intracellular pH, the pH gradient and potassium transport in Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1983 Dec 15;216(3):709–716. doi: 10.1042/bj2160709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroll R. G., Booth I. R. The role of potassium transport in the generation of a pH gradient in Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1981 Sep 15;198(3):691–698. doi: 10.1042/bj1980691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maloney P. C. Membrane H+ conductance of Streptococcus lactis. J Bacteriol. 1979 Oct;140(1):197–205. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.1.197-205.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P., Moyle J. Acid-base titration across the membrane system of rat-liver mitochondria. Catalysis by uncouplers. Biochem J. 1967 Aug;104(2):588–600. doi: 10.1042/bj1040588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Tokuda H., Unemoto T. K+/H+ antiporter functions as a regulator of cytoplasmic pH in a marine bacterium, Vibrio alginolyticus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Oct 3;776(2):330–336. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(84)90222-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padan E., Zilberstein D., Rottenberg H. The proton electrochemical gradient in Escherichia coli cells. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Apr 1;63(2):533–541. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10257.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plack R. H., Jr, Rosen B. P. Cation/proton antiport systems in Escherichia coli. Absence of potassium/proton antiporter activity in a pH-sensitive mutant. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 10;255(9):3824–3825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholes P., Mitchell P. Acid-base titration across the plasma membrane of Micrococcus denitrificans: factors affecting the effective proton conductance and the respiratory rate. J Bioenerg. 1970 Jun;1(1):61–72. doi: 10.1007/BF01516089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skulachev V. P. Membrane-linked energy buffering as the biological function of Na+/K+ gradient. FEBS Lett. 1978 Mar 15;87(2):171–179. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80326-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprott G. D., Shaw K. M., Jarrell K. F. Ammonia/potassium exchange in methanogenic bacteria. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 25;259(20):12602–12608. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokuda H., Nakamura T., Unemoto T. Potassium ion is required for the generation of pH-dependent membrane potential and delta pH by the marine bacterium Vibrio alginolyticus. Biochemistry. 1981 Jul 7;20(14):4198–4203. doi: 10.1021/bi00517a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamasaki K., Moriyama Y., Futai M., Tsuchiya T. Uptake and extrusion of k+ regulated by extracellular pH in Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1980 Oct 20;120(1):125–127. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)81061-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


