Abstract
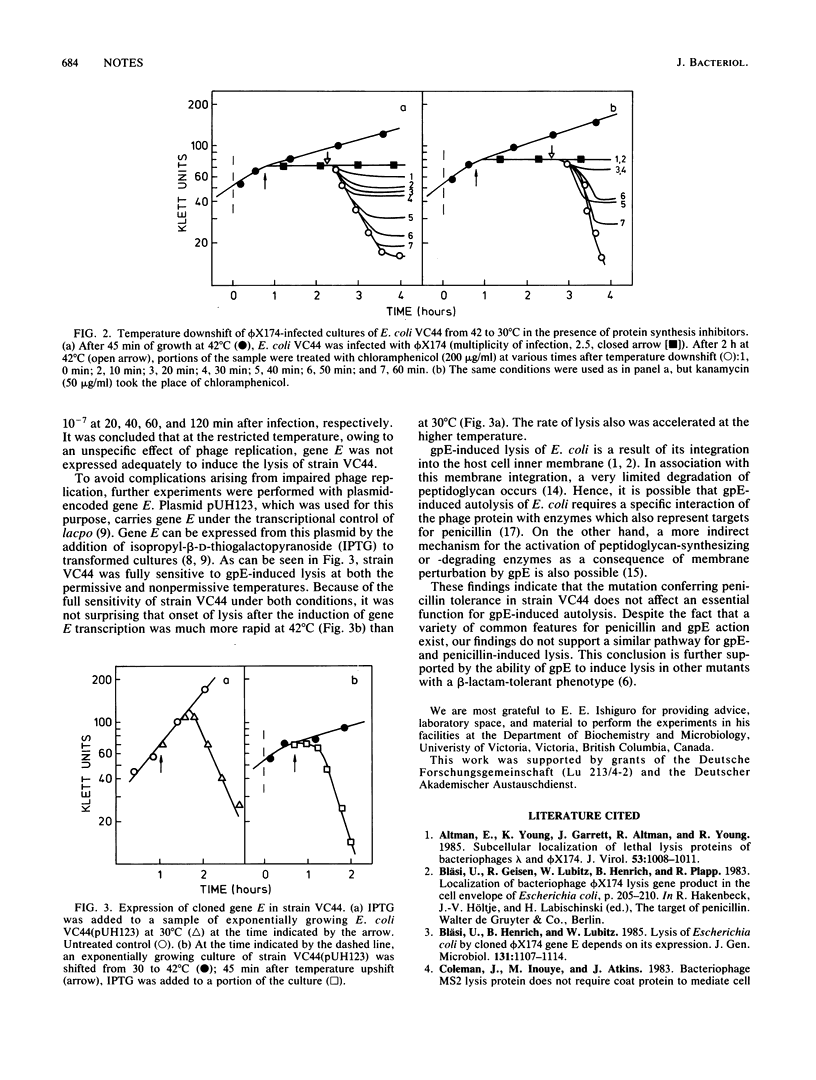
The behavior of the temperature-sensitive, penicillin-tolerant Escherichia coli mutant VC44 to endogenously induced autolysis by the bacteriophage phi X174 gene E product (gpE) was investigated. Expression of the cloned phi X174 lysis gene showed that cultures of strain VC44 grown at the restricted temperature were fully sensitive to endogenously induced autolysis. The results revealed that the modes of E. coli lysis induction by gpE and by penicillin differ and that the trigger mechanisms for autolysis depend greatly on the specific inducer used.
Full text
PDF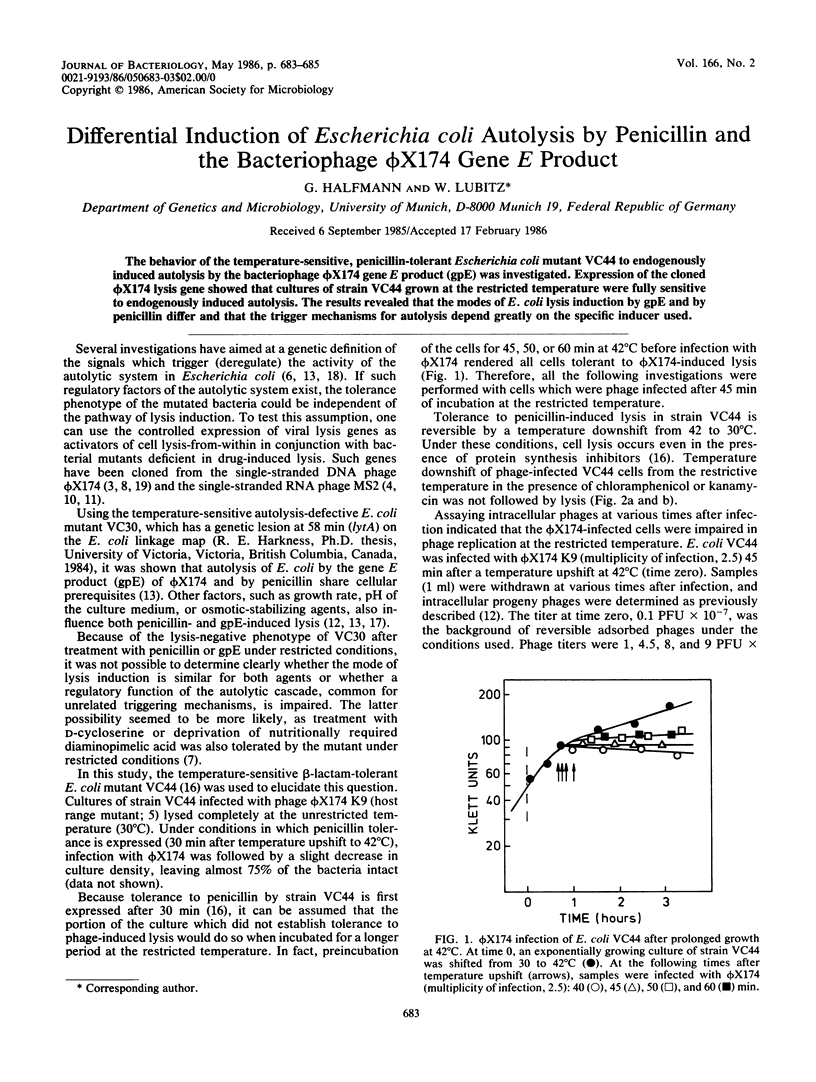

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altman E., Young K., Garrett J., Altman R., Young R. Subcellular localization of lethal lysis proteins of bacteriophages lambda and phiX174. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):1008–1011. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.1008-1011.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bläsi U., Henrich B., Lubitz W. Lysis of Escherichia coli by cloned phi X174 gene E depends on its expression. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 May;131(5):1107–1114. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-5-1107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman J., Inouye M., Atkins J. Bacteriophage MS2 lysis protein does not require coat protein to mediate cell lysis. J Bacteriol. 1983 Feb;153(2):1098–1100. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.2.1098-1100.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowell C. E., Jansz H. S., Zandberg J. Infection of escherichia coli K-12 by bacteriophage phi X-174. Virology. 1981 Oct 15;114(1):252–255. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90271-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harkness R. E., Ishiguro E. E. Temperature-sensitive autolysis-defective mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jul;155(1):15–21. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.1.15-21.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henrich B., Lubitz W., Plapp R. Lysis of Escherichia coli by induction of cloned phi X174 genes. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;185(3):493–497. doi: 10.1007/BF00334146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kastelein R. A., Remaut E., Fiers W., van Duin J. Lysis gene expression of RNA phage MS2 depends on a frameshift during translation of the overlapping coat protein gene. Nature. 1982 Jan 7;295(5844):35–41. doi: 10.1038/295035a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubitz W., Halfmann G., Plapp R. Lysis of Escherichia coli after infection with phiX174 depends on the regulation of the cellular autolytic system. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 May;130(5):1079–1087. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-5-1079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubitz W., Harkness R. E., Ishiguro E. E. Requirement for a functional host cell autolytic enzyme system for lysis of Escherichia coli by bacteriophage phi X174. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jul;159(1):385–387. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.1.385-387.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimmin L. C., Vanderwel D., Harkness R. E., Currie B. R., Galloway C. A., Ishiguro E. E. Temperature-sensitive beta-lactam-tolerant mutants of Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Jun;130(6):1315–1323. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-6-1315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasz A. The mechanism of the irreversible antimicrobial effects of penicillins: how the beta-lactam antibiotics kill and lyse bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1979;33:113–137. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.33.100179.000553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young K. D., Young R. Lytic action of cloned phi X174 gene E. J Virol. 1982 Dec;44(3):993–1002. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.3.993-1002.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


