Abstract
gamma-Glutamyltranspeptidase was purified ca. 15,200-fold from cell-free extracts of Proteus mirabilis to electrophoretic homogeneity and then crystallized. The enzyme has an estimated molecular weight of 80,000 and consists of two different subunits with molecular weights of ca. 47,000 and 28,000. The purified enzyme catalyzed hydrolysis and transpeptidation of various gamma-glutamyl compounds, including the oxidized and reduced forms of glutathione, gamma-glutamyl compounds of L-phenylalanine, L-tyrosine, L-histidine, L-alpha-aminobutyrate, L-leucine, and p-nitroaniline. Glycylglycine, L-phenylalanine, L-methionine, L-histidine, L-tryptophan, and L-isoleucine were good acceptors of the gamma-glutamyl moiety in the transpeptidation reaction. Km values for gamma-glutamyl compounds were on the order of 10(-4) to 10(-5) M, and those for acceptor peptides and amino acids were on the order of 10(-2) to 10(-3) M. The enzyme was inhibited by L-serine plus borate and 6-diazo-5-oxo-L-norleucine, which are inhibitors of gamma-glutamyltranspeptidases isolated from mammals. Various amino acids alone were found to inhibit the transpeptidation competitively with a gamma-glutamyl donor. Kinetic analysis suggested that the reaction sequence of substrate binding and product release proceeds according to a ping pong bi bi mechanism.
Full text
PDF

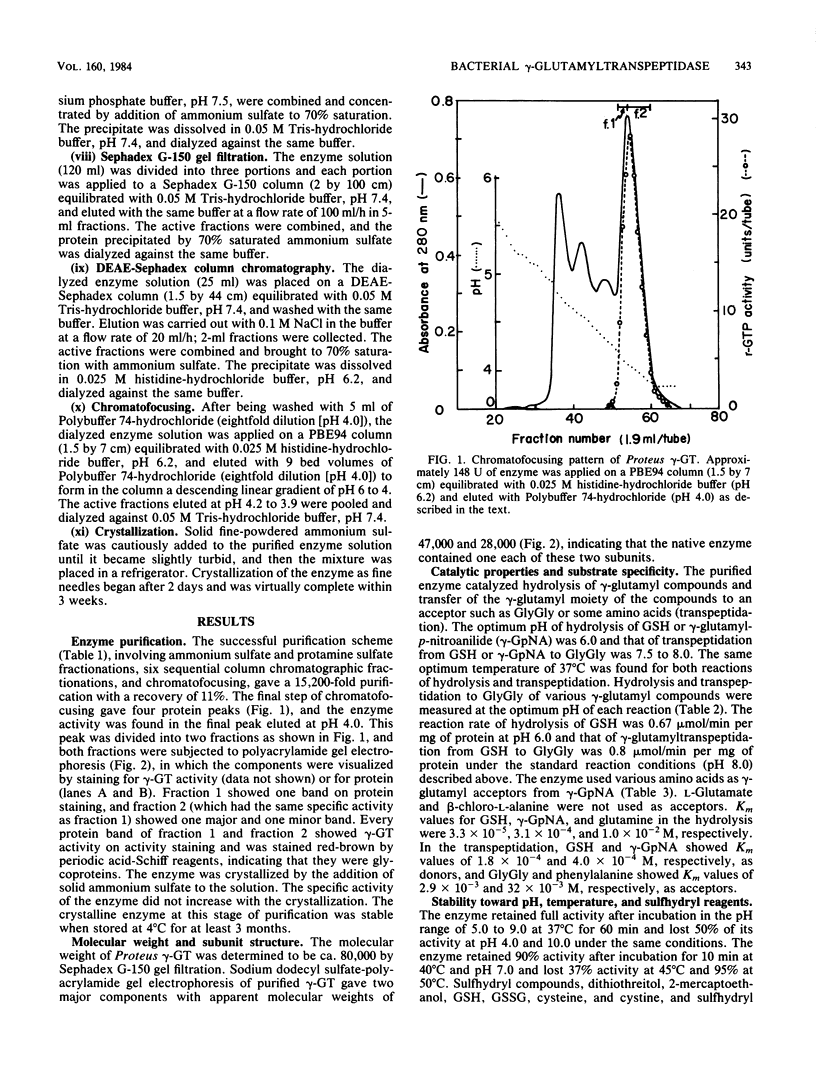
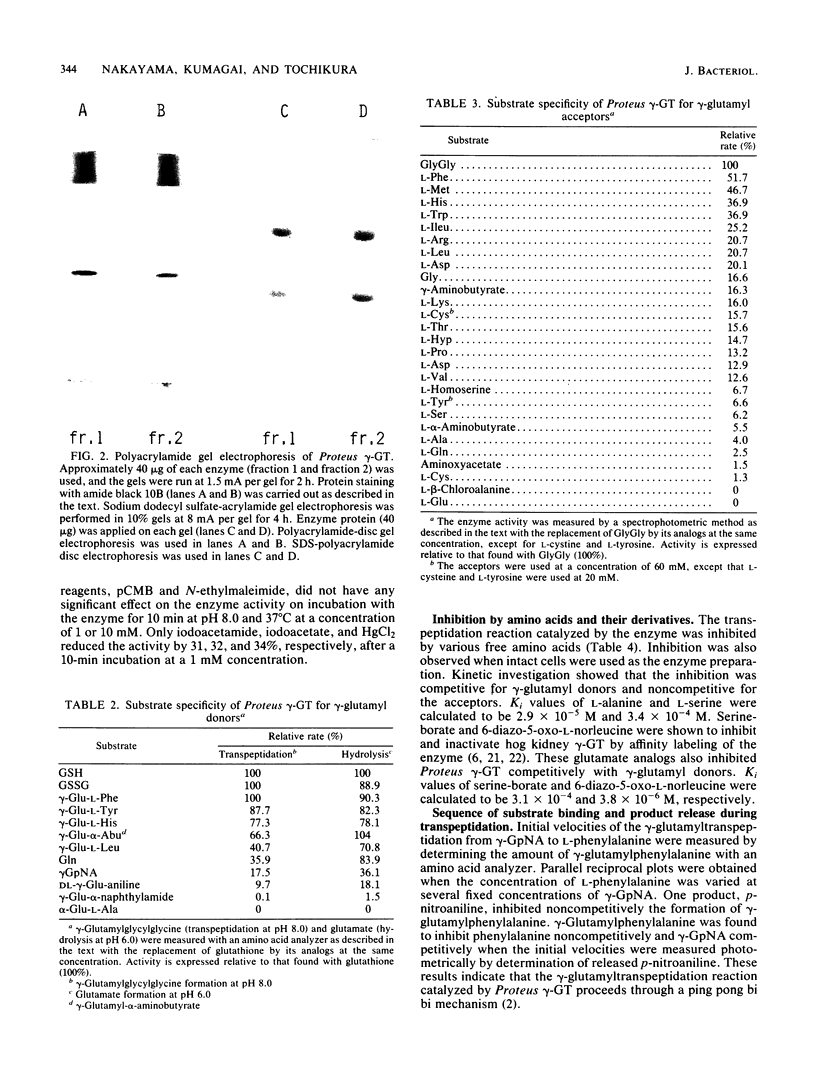
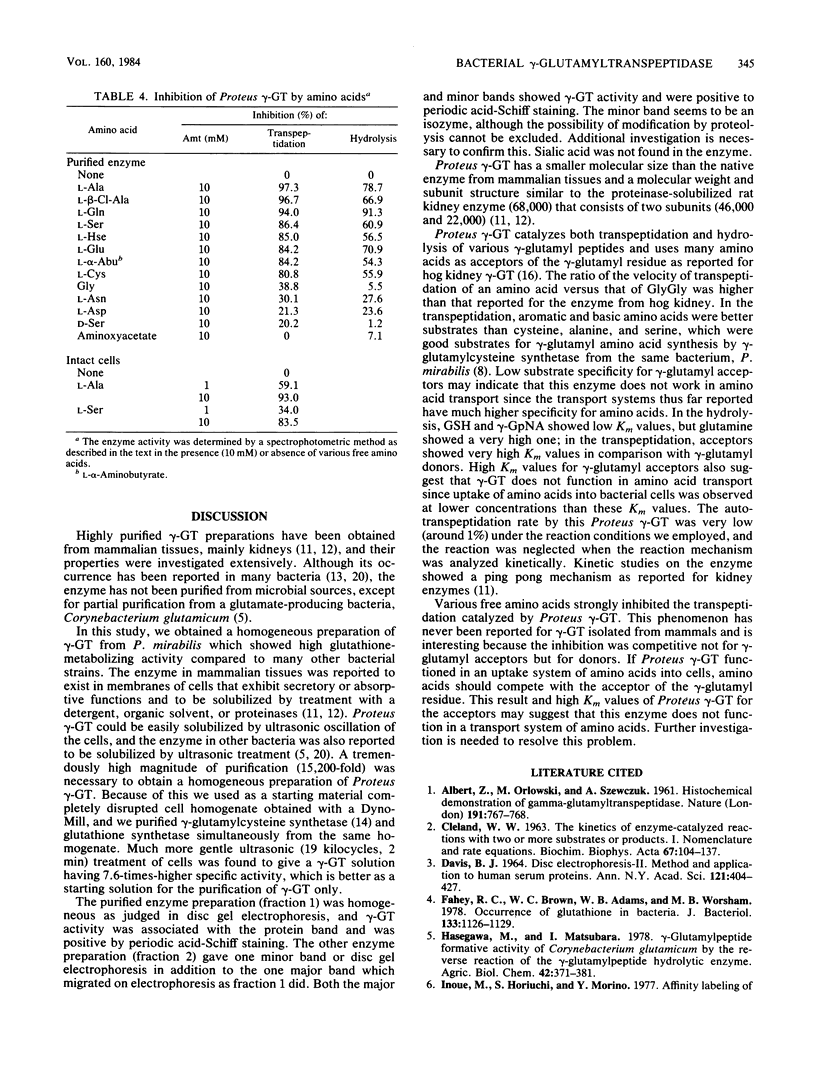

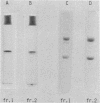
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALBERT Z., ORLOWSKI M., SZEWCZUK A. Histochemical demonstration of gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase. Nature. 1961 Aug 19;191:767–768. doi: 10.1038/191767a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLELAND W. W. The kinetics of enzyme-catalyzed reactions with two or more substrates or products. I. Nomenclature and rate equations. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Jan 8;67:104–137. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)91800-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahey R. C., Brown W. C., Adams W. B., Worsham M. B. Occurrence of glutathione in bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1978 Mar;133(3):1126–1129. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.3.1126-1129.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HJERTEN S., LEVIN O., TISELIUS A. Protein chromatography on calcium phosphate columns. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1956 Nov;65(1):132–155. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(56)90183-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosower N. S., Kosower E. M. The glutathione status of cells. Int Rev Cytol. 1978;54:109–160. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60166-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meister A., Anderson M. E. Glutathione. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:711–760. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.003431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meister A. On the enzymology of amino acid transport. Science. 1973 Apr 6;180(4081):33–39. doi: 10.1126/science.180.4081.33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meister A., Tate S. S. Glutathione and related gamma-glutamyl compounds: biosynthesis and utilization. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:559–604. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.003015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milbauer R., Grossowicz N. Gamma-glutamyl transfer reactions in bacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 Nov;41(2):185–194. doi: 10.1099/00221287-41-2-185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mooz E. D., Wigglesworth L. Evidence for the gamma-glutamyl cycle in yeast. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Feb 23;68(4):1066–1072. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90304-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama R., Kumagai H., Tochikura T. Leakage of glutathione from bacterial cells caused by inhibition of gamma-glutamyltranspeptidase. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Apr;47(4):653–657. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.4.653-657.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ORLOWSKI M., MEISTER A. ISOLATION OF GAMMA-GLUTAMYL TRANSPEPTIDASE FROM HOG KIDNEY. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jan;240:338–347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osuji G. O. The pathways of the gamma-glutamyl cycle-mediated uptake of amino acids in yeast. FEBS Lett. 1979 Dec 1;108(1):240–242. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)81219-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins R. J., Davies D. D. The role of glutathione in amino-acid absorption. Lack of correlation between glutathione turnover and amino-acid absorption by the yeast Candida utilis. Biochem J. 1981 Jan 15;194(1):63–70. doi: 10.1042/bj1940063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TALALAY P. S. Glutathione breakdown and transpeptidation reactions in Proteus vulgaris. Nature. 1954 Sep 11;174(4428):516–517. doi: 10.1038/174516b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tate S. S., Meister A. Affinity labeling of gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase and location of the gamma-glutamyl binding site on the light subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):931–935. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tate S. S., Meister A. Serine-borate complex as a transition-state inhibitor of gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4806–4809. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]