Abstract
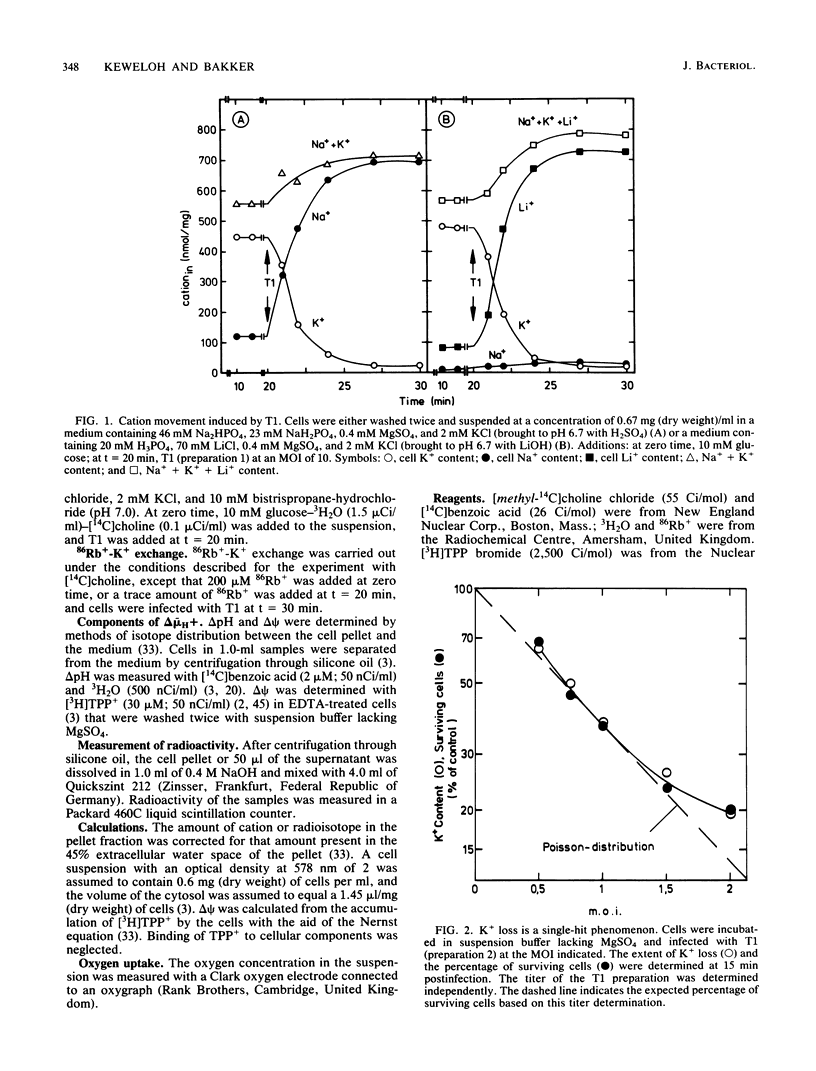
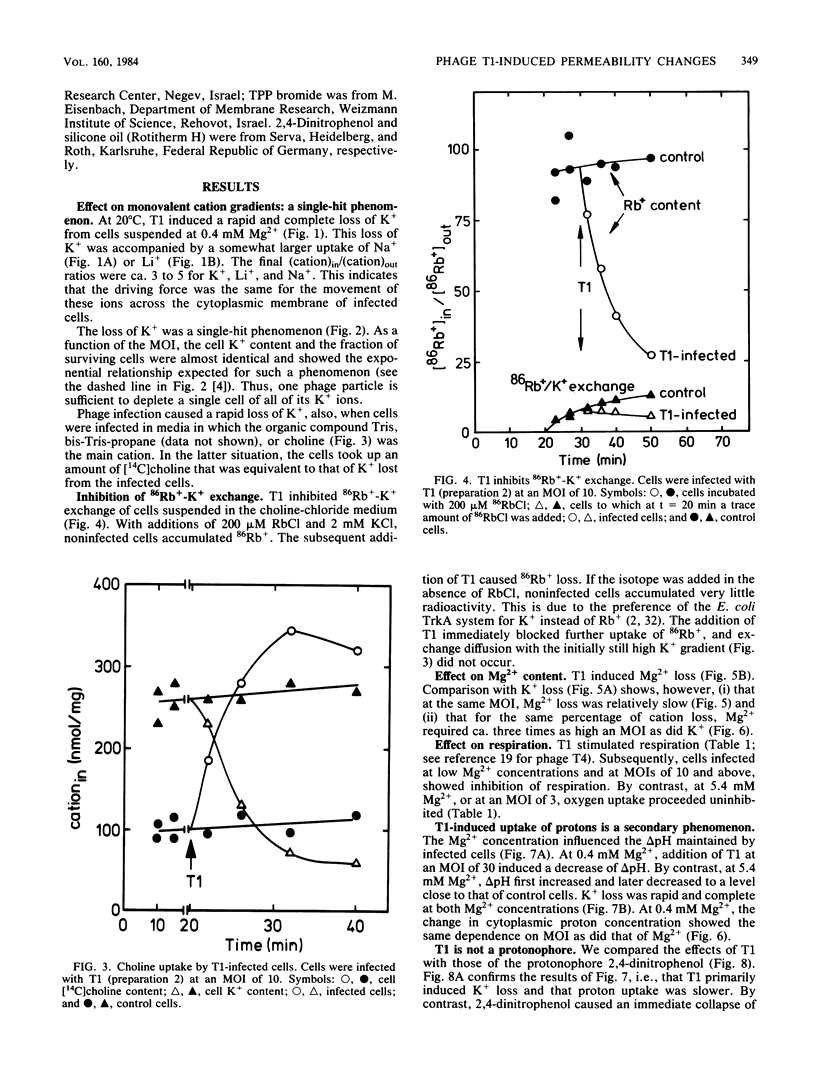
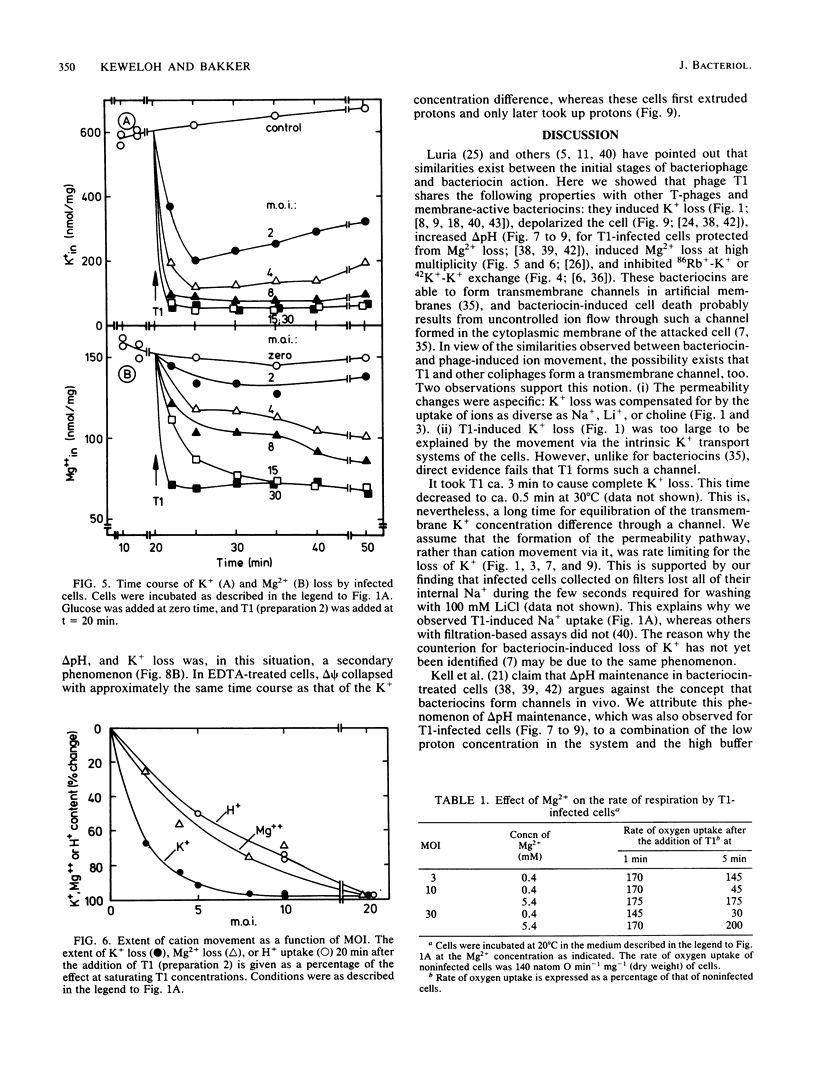
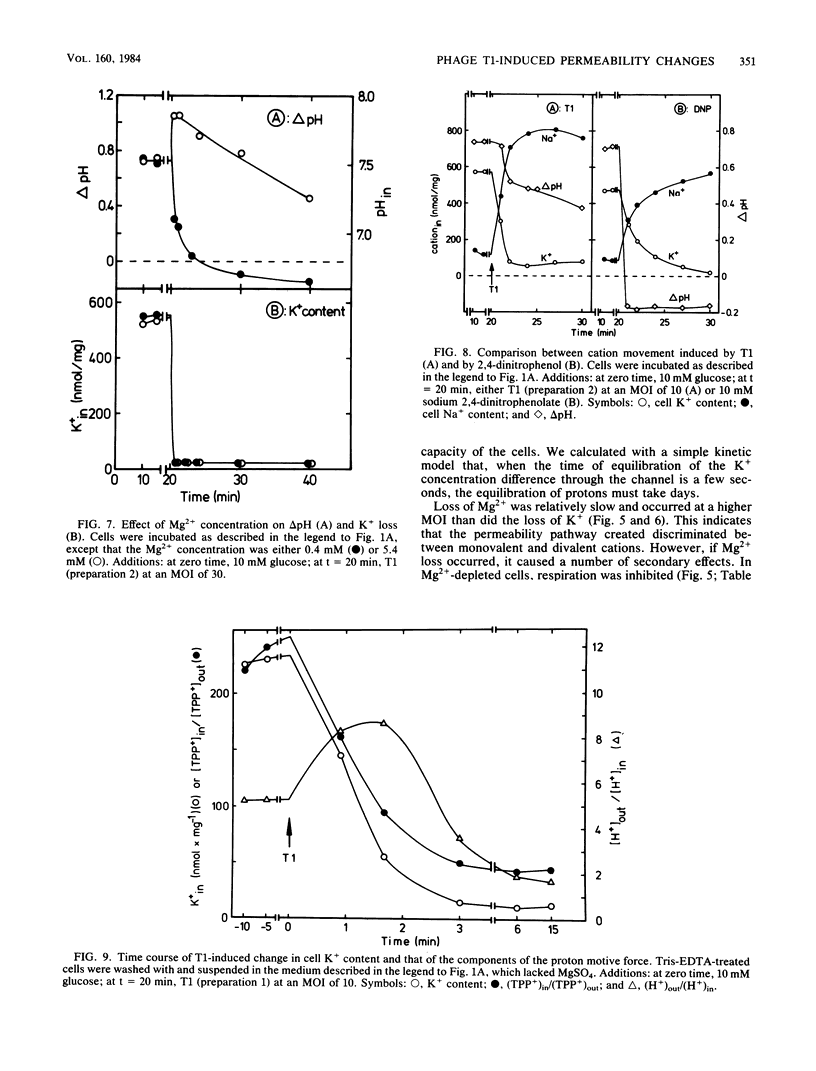
The nature of the bacteriophage T1-induced changes in the permeability of the cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli K-12 was investigated. At 20 degrees C and with glucose as a substrate, the addition of one bacteriophage per cell induced a complete and irreversible loss of K+ ions (single-hit phenomenon). K+ loss was compensated by an uptake of Na+, Li+, or choline by the cell, depending on which of these ions was the major cation in the medium. T1 depolarized the cells and inhibited 86Rb+-K+ exchange across the cytoplasmic membrane. The loss of K+ occurred independently of the Mg2+ concentration in the medium. By contrast, at low but not at high Mg2+ concentrations, T1 caused efflux of Mg2+ which in turn caused inhibition of respiration and a decrease of delta pH.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bakker E. P., Mangerich W. E. Interconversion of components of the bacterial proton motive force by electrogenic potassium transport. J Bacteriol. 1981 Sep;147(3):820–826. doi: 10.1128/jb.147.3.820-826.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakker E. P. Membrane potential in a potassium transport-negative mutant of Escherichia coli K-12. The distribution of rubidium in the presence of valinomycin indicates a higher potential than that of the tetraphenylphosphonium cation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Sep 15;681(3):474–483. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(82)90190-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. E. Ultrastructure of bacteriophage and bacteriocins. Bacteriol Rev. 1967 Dec;31(4):230–314. doi: 10.1128/br.31.4.230-314.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke D. J., Morley C. D., Kell D. B., Morris J. G. On the mode of action of the bacteriocin butyricin 7423. Effects on membrane potential and potassium-ion accumulation in Clostridium pasteurianum. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Sep;127(1):105–116. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06843.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cramer W. A., Dankert J. R., Uratani Y. The membrane channel-forming bacteriocidal protein, colicin El. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Mar 21;737(1):173–193. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(83)90016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dandeu J. P., Billault A., Barbu E. Action des colicines sur la vitesse de sortie du potassium intracellulaire. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1969 Nov 17;269(20):2044–2047. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felle H., Porter J. S., Slayman C. L., Kaback H. R. Quantitative measurements of membrane potential in Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1980 Jul 22;19(15):3585–3590. doi: 10.1021/bi00556a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields K. L. Comparison of the action of colicins E1 and K on Escherichia coli with the effects of abortive infection by virulent bacteriophages. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jan;97(1):78–82. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.1.78-82.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filali Maltouf A., Labedan B. Host cell metabolic energy is not required for injection of bacteriophage T5 DNA. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):124–133. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.124-133.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furukawa H., Kuroiwa T., Mizushima S. DNA injection during bacteriophage T4 infection of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1983 May;154(2):938–945. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.2.938-945.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenn J., Duckworth D. H. Ion fluxes during T5 bacteriophage infection of Escherichia coli. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1980 May;201(2):576–585. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(80)90547-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinius L. Nucleic acid transport driven by ion gradient across cell membrane. FEBS Lett. 1980 Apr 21;113(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80482-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. W., Braun V. Nature of the energy requirement for the irreversible adsorption of bacteriophages T1 and phi80 to Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1976 Feb;125(2):409–415. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.2.409-415.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harold F. M. Conservation and transformation of energy by bacterial membranes. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Jun;36(2):172–230. doi: 10.1128/br.36.2.172-230.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata H., Fukui S., Ishikawa S. Initial events caused by colicin K infection--cation movement and depletion of ATP pool. J Biochem. 1969 May;65(5):843–847. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a129088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalasauskaite E. V., Kadisaite D. L., Daugelavicius R. J., Grinius L. L., Jasaitis A. A. Studies on energy supply for genetic processes. Requirement for membrane potential in Escherichia coli infection by phage T4. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jan 17;130(1):123–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashket E. R., Barker S. L. Effects of potassium ions on the electrical and pH gradients across the membrane of Streptococcus lactis cells. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jun;130(3):1017–1023. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.3.1017-1023.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keweloh H. W., Bakker E. P. Increased permeability and subsequent resealing of the host cell membrane early after infection of Escherichia coli with bacteriophage T1. J Bacteriol. 1984 Oct;160(1):354–359. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.1.354-359.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LURIA S. E. ON THE MECHANISMS OF ACTION OF COLICINS. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1964 Nov;107:SUPPL–SUPPL:73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labedan B., Letellier L. Membrane potential changes during the first steps of coliphage infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):215–219. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusk J. E., Nelson D. L. Effects of colicins E1 and K on permeability to magnesium and cobaltous ions. J Bacteriol. 1972 Oct;112(1):148–160. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.1.148-160.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. Chemiosmotic coupling in oxidative and photosynthetic phosphorylation. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 1966 Aug;41(3):445–502. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-185x.1966.tb01501.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PUCK T. T., LEE H. H. Mechanism of cell wall penetration by viruses. I. An increase in host cell permeability induced by bacteriophage infection. J Exp Med. 1954 May 1;99(5):481–494. doi: 10.1084/jem.99.5.481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PUCK T. T., LEE H. H. Mechanism of cell wall penetration by viruses. II. Demonstration of cyclic permeability change accompanying virus infection of Escherichia coli B cells. J Exp Med. 1955 Feb 1;101(2):151–175. doi: 10.1084/jem.101.2.151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponta H., Altendorf K. H., Schweiger M., Hirsch-Kaufmann M., Pfennig-Yeh M. L., Herrlich P. E. coli membranes become permeable to ions following T7-virus-infection. Mol Gen Genet. 1976 Dec 8;149(2):145–150. doi: 10.1007/BF00332882. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhoads D. B., Waters F. B., Epstein W. Cation transport in Escherichia coli. VIII. Potassium transport mutants. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Mar;67(3):325–341. doi: 10.1085/jgp.67.3.325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhoads D. B., Woo A., Epstein W. Discrimination between Rb+ and K+ by Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Aug 15;469(1):45–51. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90324-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottenberg H. The measurement of membrane potential and deltapH in cells, organelles, and vesicles. Methods Enzymol. 1979;55:547–569. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)55066-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabelnikov A. G., Domaradsky I. V. Effect of metabolic inhibitors on entry of exogenous deoxyribonucleic acid into Ca2+-treated Escherichia coli cells. J Bacteriol. 1981 May;146(2):435–443. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.2.435-443.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schein S. J., Kagan B. L., Finkelstein A. Colicin K acts by forming voltage-dependent channels in phospholipid bilayer membranes. Nature. 1978 Nov 9;276(5684):159–163. doi: 10.1038/276159a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapira A., Giberman E., Kohn A. Recoverable potassium fluxes variations following adsorption of T4 phage and their ghosts on Escherichia coli B. J Gen Virol. 1974 May;23(2):159–171. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-23-2-159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver S., Levine E., Spielman P. M. Cation fluxes and permeability changes accompanying bacteriophage infection of Escherichia coli. J Virol. 1968 Aug;2(8):763–771. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.8.763-771.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokuda H., Konisky J. In vitro depolarization of Escherichia coli membrane vesicles by colicin Ia. J Biol Chem. 1978 Nov 10;253(21):7731–7737. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokuda H., Konisky J. Mode of action of colicin Ia: effect of colicin on the Escherichia coli proton electrochemical gradient. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2579–2583. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner E. F., Ponta H., Schweiger M. Development of Escherichia coli virus T1. The role of the proton-motive force. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 25;255(2):534–539. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner E. F., Schweiger M. Development of escherichia coli virus T1. ATP-mediated discrimination of gene expression. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 25;255(2):540–542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss M. J., Luria S. E. Reduction of membrane potential, an immediate effect of colicin K. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2483–2487. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wendt L. Mechanism of colicin action: early events. J Bacteriol. 1970 Dec;104(3):1236–1241. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.3.1236-1241.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. B., Okabe A. A second function of the S gene of bacteriophage lambda. J Bacteriol. 1982 Dec;152(3):1091–1095. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.3.1091-1095.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zilberstein D., Schuldiner S., Padan E. Proton electrochemical gradient in Escherichia coli cells and its relation to active transport of lactose. Biochemistry. 1979 Feb 20;18(4):669–673. doi: 10.1021/bi00571a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



