Abstract
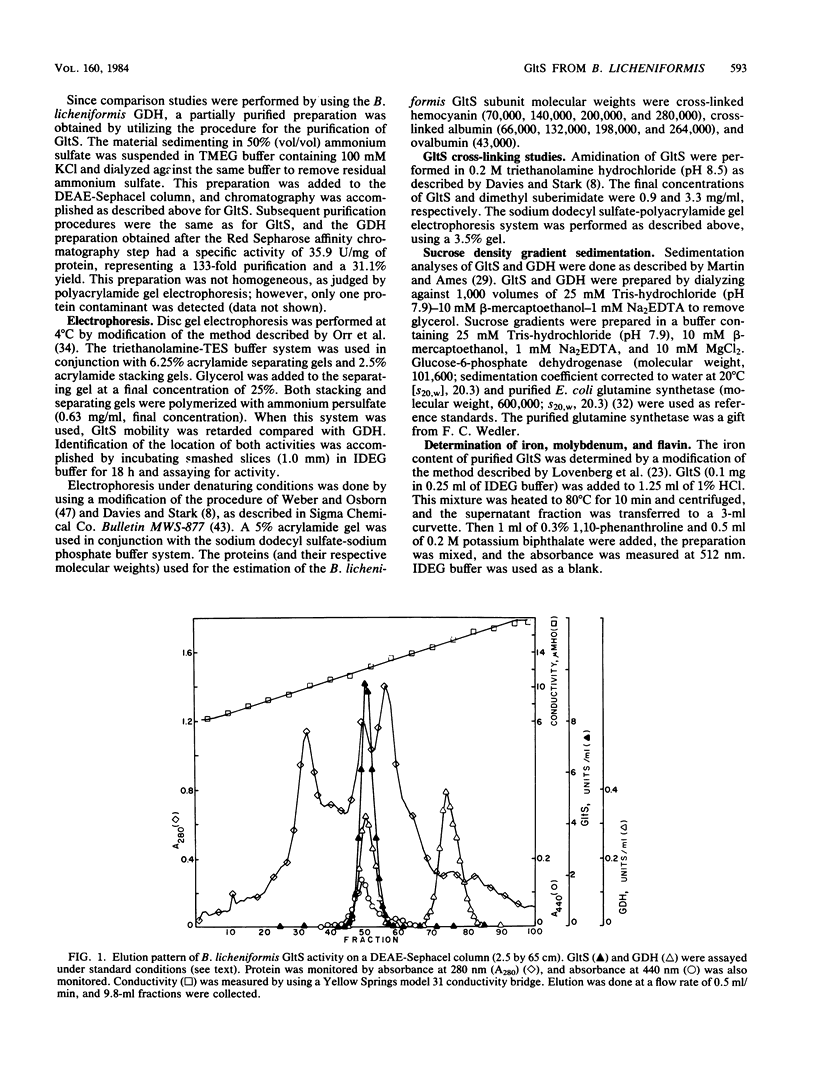
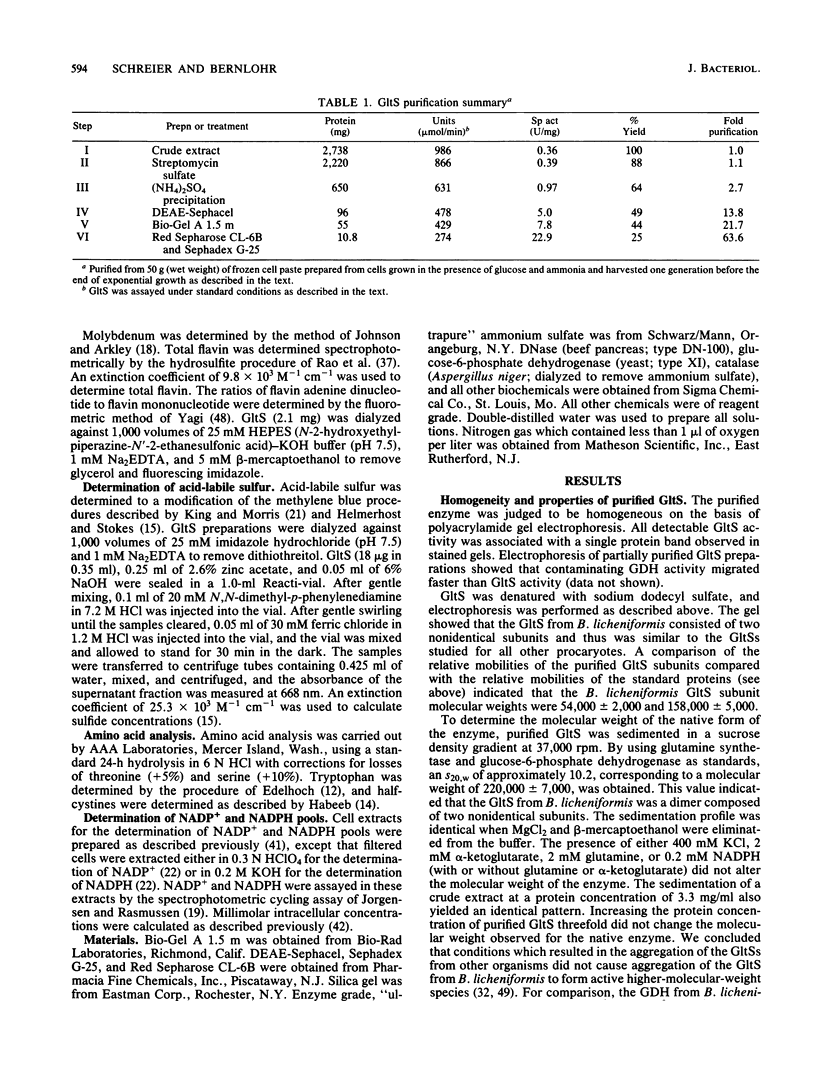
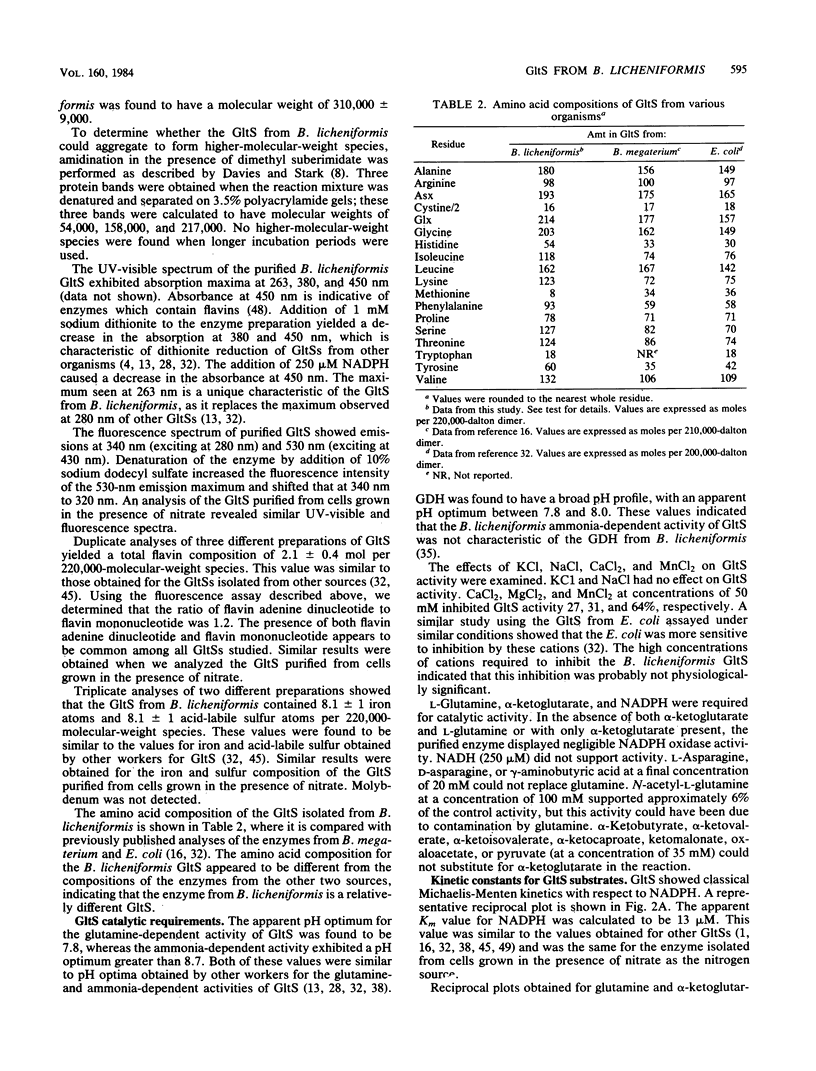
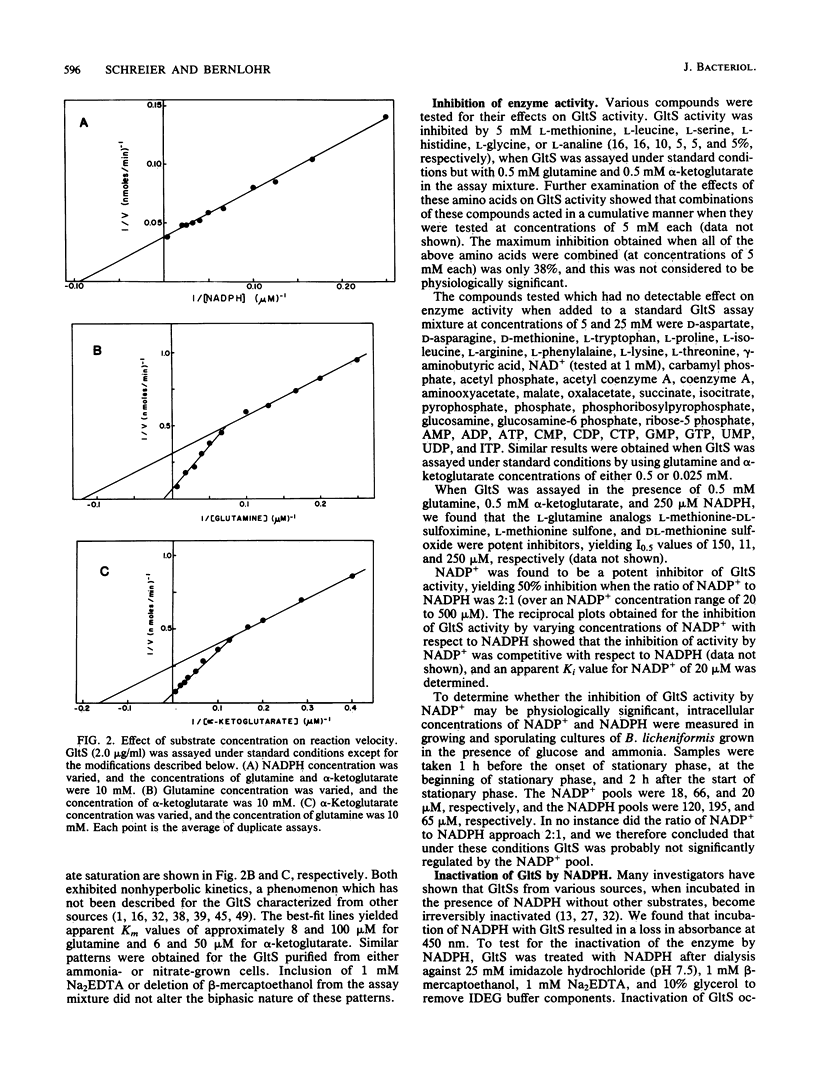
Glutamate synthase [L-glutamate:NADP+ oxidoreductase (transaminating); EC 1.4.1.13](GltS) was purified to homogeneity from Bacillus licheniformis A5. The native enzyme had a molecular weight of approximately 220,000 and was composed of two nonidentical subunits (molecular weights, approximately 158,000 and approximately 54,000). The enzyme was found to contain 8.1 +/- 1 iron atoms and 8.1 +/- 1 acid-labile sulfur atoms per 220,000-dalton dimer. Two flavin moieties were found per 220,000-dalton dimer, with a ratio of flavin adenine dinucleotide to flavin mononucleotide of 1.2. The UV-visible spectrum of the enzyme exhibited maxima at 263,380 and 450 nm. The GltS from B. licheniformis had a requirement for NADPH, alpha-ketoglutarate, and glutamine. Classical hyperbolic kinetics were seen for NADPH affinity, which resulted in an apparent Km value of 13 microM. Nonhyperbolic kinetics were obtained for alpha-ketoglutarate and glutamine affinities, and the reciprocal plots obtained for these substrates were biphasic. The apparent Km values obtained for glutamine were 8 and 100 microM, and the apparent Km values obtained for alpha-ketoglutarate were 6 and 50 microM. GltS activity was found to be relatively insensitive to inhibition by amino acids, keto acids, or various nucleotides. L-Methionine-DL-sulfoximine, L-methionine sulfone, and DL-methionine sulfoxide were found to be potent inhibitors of GltS activity, yielding I0.5 values of 150, 11, and 250 microM, respectively. GltSs were purified from cells grown in the presence of ammonia and nitrate as sole nitrogen sources and were compared. Both yielded identical final specific activities and identical physical (UV-visible spectra, flavin, and iron-sulfur composition) and kinetic characteristics.
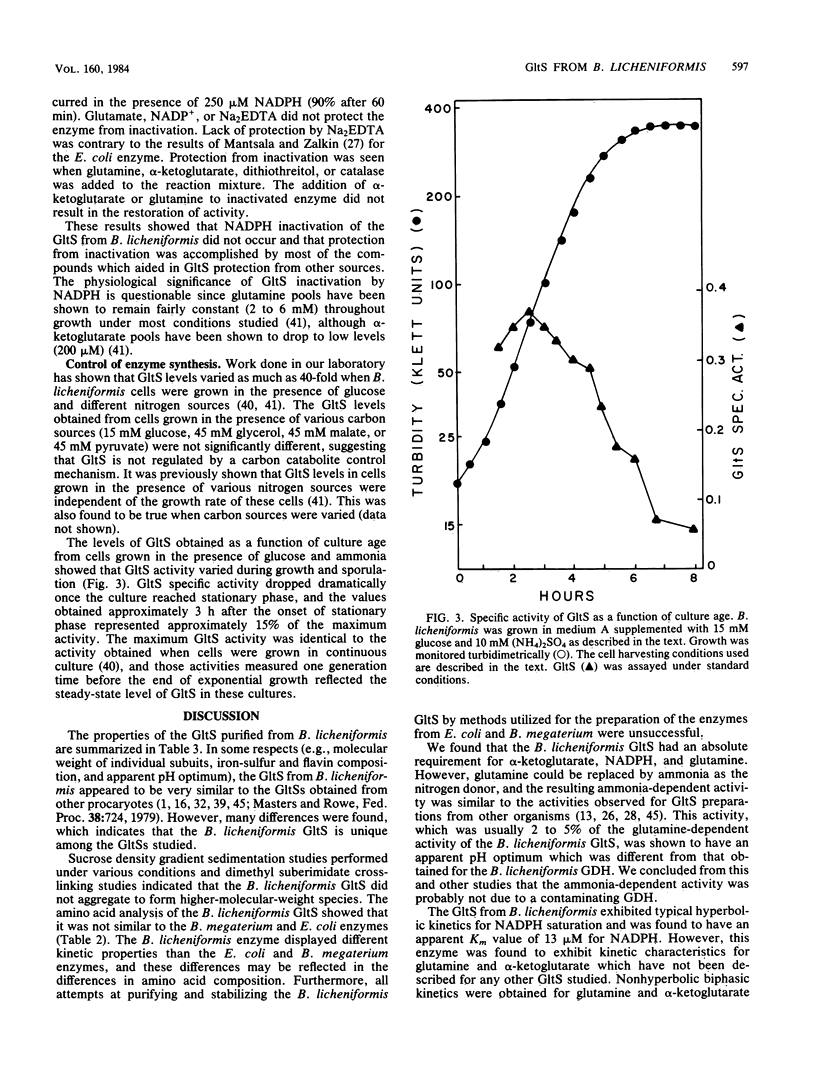
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adachi K., Suzuki I. Purification and properties of glutamate synthase from Thiobacillus thioparus. J Bacteriol. 1977 Mar;129(3):1173–1182. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.3.1173-1182.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernlohr R. W., Clark V. Characterization and regulation of protease synthesis and activity in Bacillus licheniformis. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jan;105(1):276–283. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.1.276-283.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bower S., Zalkin H. Chemical modification and ligand binding studies with Escherichia coli glutamate synthase. Biochemistry. 1983 Mar 29;22(7):1613–1620. doi: 10.1021/bi00276a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenchley J. E. Effect of methionine sulfoximine and methionine sulfone on glutamate synthesis in Klebsiella aerogenes. J Bacteriol. 1973 May;114(2):666–673. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.2.666-673.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark V. L., Peterson D. E., Bernlohr R. W. Changes in free amino acid production and intracellular amino acid pools of Bacillus licheniformis as a function of culture age and growth media. J Bacteriol. 1972 Nov;112(2):715–725. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.2.715-725.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook W. R., Hoffman J. H., Bernlohr R. W. Occurrence of an inducible glutaminase in Bacillus licheniformis. J Bacteriol. 1981 Oct;148(1):365–367. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.1.365-367.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies G. E., Stark G. R. Use of dimethyl suberimidate, a cross-linking reagent, in studying the subunit structure of oligomeric proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jul;66(3):651–656. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.3.651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deuel T. F., Prusiner S. Regulation of glutamine synthetase from Bacillus subtilis by divalent cations, feedback inhibitors, and L-glutamine. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 10;249(1):257–264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donohue T. J., Bernlohr R. W. Properties of the Bacillus licheniformis A5 glutamine synthetase purified from cells grown in the presence of ammonia or nitrate. J Bacteriol. 1981 Aug;147(2):589–601. doi: 10.1128/jb.147.2.589-601.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donohue T. J., Bernlohr R. W. Regulation of the activity of the Bacillus licheniformis A5 glutamine synthetase. J Bacteriol. 1981 Oct;148(1):174–182. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.1.174-182.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelhoch H. Spectroscopic determination of tryptophan and tyrosine in proteins. Biochemistry. 1967 Jul;6(7):1948–1954. doi: 10.1021/bi00859a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geary L. E., Meister A. On the mechanism of glutamine-dependent reductive amination of alpha-ketoglutarate catalyzed by glutamate synthase. J Biol Chem. 1977 May 25;252(10):3501–3508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helmerhorst E., Stokes G. B. Generation of an acid-stable and protein-bound persulfide-like residue in alkali- or sulfhydryl-treated insulin by a mechanism consonant with the beta-elimination hypothesis of disulfide bond lysis. Biochemistry. 1983 Jan 4;22(1):69–75. doi: 10.1021/bi00270a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemmilä I. A., Mäntsälä P. I. Purification and properties of glutamate synthase and glutamate dehydrogenase from Bacillus megaterium. Biochem J. 1978 Jul 1;173(1):45–52. doi: 10.1042/bj1730045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt J. B., Smyrniotis P. Z., Ginsburg A., Stadtman E. R. Metal ion requirement by glutamine synthetase of Escherichia coli in catalysis of gamma-glutamyl transfer. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Jan;166(1):102–124. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90370-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jørgensen B. M., Rasmussen H. N. Recycling analysis of nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide phosphates (NADP and NADPH). Anal Biochem. 1979 Nov 1;99(2):297–303. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(79)80010-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalb V. F., Jr, Bernlohr R. W. A new spectrophotometric assay for protein in cell extracts. Anal Biochem. 1977 Oct;82(2):362–371. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90173-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOVENBERG W., BUCHANAN B. B., RABINOWITZ J. C. STUDIES ON THE CHEMICAL NATURE OF CLOSTRIDIAL FERREDOXIN. J Biol Chem. 1963 Dec;238:3899–3913. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN R. G., AMES B. N. A method for determining the sedimentation behavior of enzymes: application to protein mixtures. J Biol Chem. 1961 May;236:1372–1379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magasanik B. Genetic control of nitrogen assimilation in bacteria. Annu Rev Genet. 1982;16:135–168. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.16.120182.001031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantsala P., Zalkin H. Active subunits of Escherichia coli glutamate synthase. J Bacteriol. 1976 Apr;126(1):539–541. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.1.539-541.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marzluf G. A. Regulation of nitrogen metabolism and gene expression in fungi. Microbiol Rev. 1981 Sep;45(3):437–461. doi: 10.1128/mr.45.3.437-461.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masters D. S., Jr, Meister A. Inhibition of homocysteine sulfonamide of glutamate synthase purified from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):8711–8715. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. E., Stadtman E. R. Glutamate synthase from Escherichia coli. An iron-sulfide flavoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 25;247(22):7407–7419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mäntsälä P., Zalkin H. Glutamate synthase. Properties of the glutamine-dependent activity. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jun 10;251(11):3294–3299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mäntsälä P., Zalkin H. Properties of apoglutamate synthase and comparison with glutamate dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jun 10;251(11):3300–3305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr M. D., Blakley R. L., Panagou D. Discontinuous buffer systems for analytical and preparative electrophoresis of enzymes on polyacrylamide gel. Anal Biochem. 1972 Jan;45(1):68–85. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90008-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phibbs P. V., Jr, Bernlohr R. W. Purification, properties, and regulation of glutamic dehydrogenase of Bacillus licheniformis. J Bacteriol. 1971 May;106(2):375–385. doi: 10.1128/jb.106.2.375-385.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rendina A. R., Orme-Johnson W. H. Glutamate synthase: on the kinetic mechanism of the enzyme from Escherichia coli W. Biochemistry. 1978 Dec 12;17(25):5388–5393. doi: 10.1021/bi00618a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roon R. J., Even H. L., Larimore F. Glutamate synthase: properties of the reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide-dependent enzyme from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1974 Apr;118(1):89–95. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.1.89-95.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreier H. J., Smith T. M., Bernlohr R. W. Regulation of nitrogen catabolic enzymes in Bacillus spp. J Bacteriol. 1982 Aug;151(2):971–975. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.2.971-975.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel W. H., Donohue T., Bernlohr R. W. Determination of pools of tricarboxylic acid cycle and related acids in bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Nov;34(5):512–517. doi: 10.1128/aem.34.5.512-517.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trotta P. P., Platzer K. E., Haschemeyer R. H., Meister A. Glutamine-binding subunit of glutamate synthase and partial reactions catalyzed by this glutamine amidotransferase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Nov;71(11):4607–4611. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.11.4607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyler B. Regulation of the assimilation of nitrogen compounds. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:1127–1162. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.005403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YAGI K. Chemical determination of flavins. Methods Biochem Anal. 1962;10:319–356. doi: 10.1002/9780470110270.ch10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



