Abstract
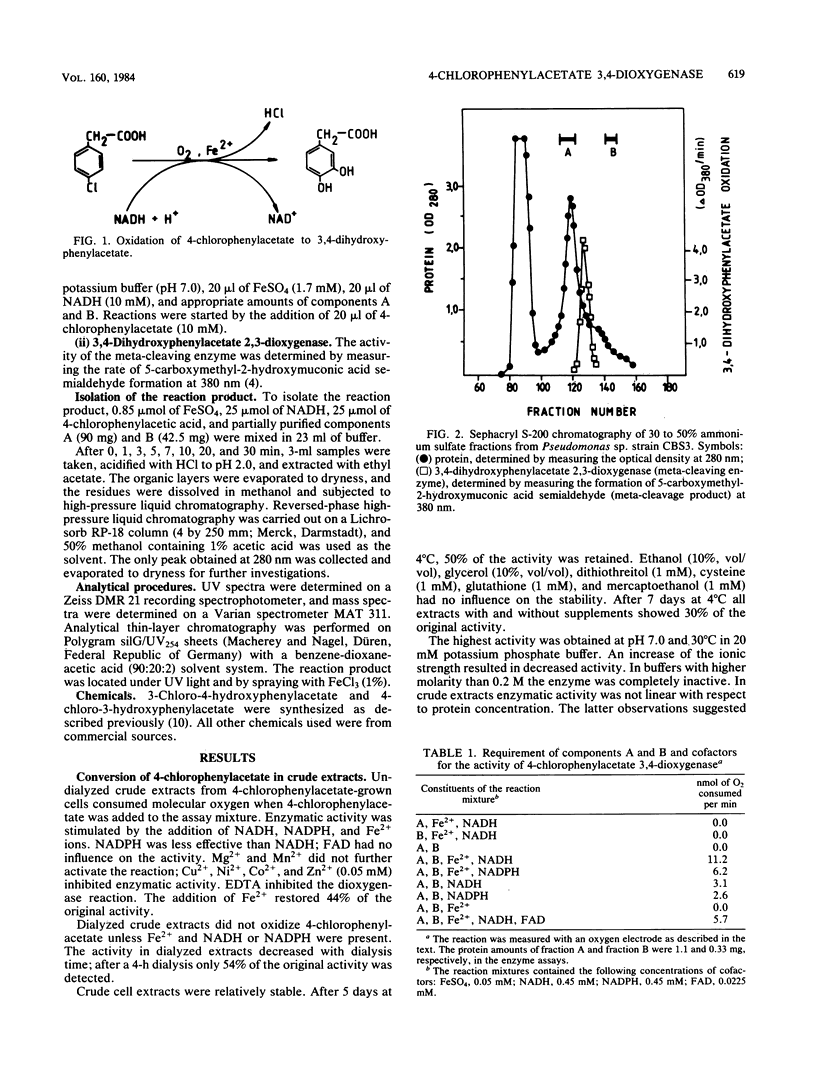
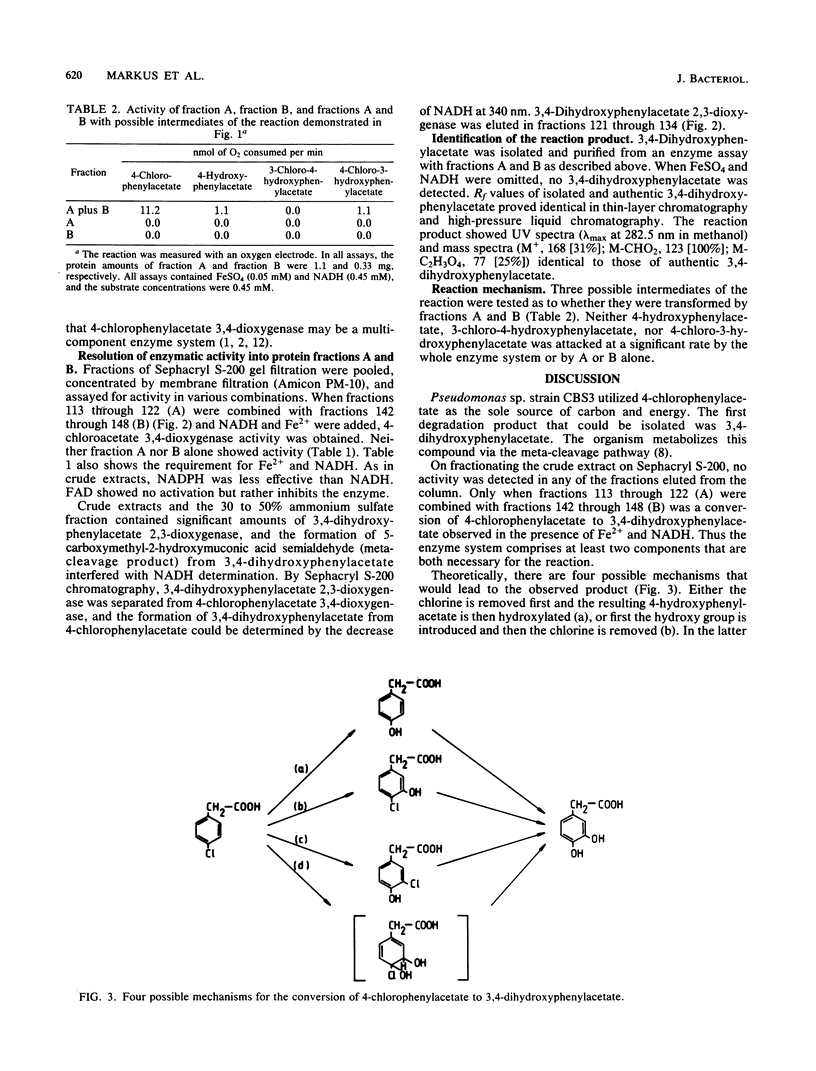
In cell-free extracts from Pseudomonas sp. strain CBS3 the conversion of 4-chlorophenylacetate to 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetate was demonstrated. By Sephacryl S-200 chromatography two protein fractions, A and B, were obtained which both were essential for enzyme activity. Fe2+ and NADH were cofactors of the reaction. NADPH also activated the enzyme, but less effectively than NADH. FAD had no influence on enzyme activity. 4-Hydroxyphenylacetate, 4-chloro-3-hydroxyphenylacetate, and 3-chloro-4-hydroxyphenylacetate were poor substrates for the enzyme, suggesting that these substances are not intermediates of the reaction. We therefore suggest that the reaction proceeds via a dioxygenated intermediate.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Axcell B. C., Geary P. J. Purification and some properties of a soluble benzene-oxidizing system from a strain of Pseudomonas. Biochem J. 1975 Jan;146(1):173–183. doi: 10.1042/bj1460173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ensley B. D., Gibson D. T., Laborde A. L. Oxidation of naphthalene by a multicomponent enzyme system from Pseudomonas sp. strain NCIB 9816. J Bacteriol. 1982 Mar;149(3):948–954. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.3.948-954.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klages U., Krauss S., Lingens F. 2-Haloacid dehalogenase from a 4-chlorobenzoate-degrading Pseudomonas spec. CBS 3. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1983 May;364(5):529–535. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1983.364.1.529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klages U., Markus A., Lingens F. Degradation of 4-chlorophenylacetic acid by a Pseudomonas species. J Bacteriol. 1981 Apr;146(1):64–68. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.1.64-68.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markus A., Klages U., Lingens F. Mikrobieller Abbau von 4-Chlorphenylessigsäure. Chemische Synthese von 3-Chlor-4-hydroxy-, 4-Chlor-3-hydroxy- und 4-Chlor-2-hydroxyphenylessigsäure. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1982 Apr;363(4):431–437. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mires M. H., Alexander C. H. The prophylactic treatment tuberculosis. Del Med J. 1972 Jul;44(7):187–190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruisinger S., Klages U., Lingens F. Abbau der 4-chlorbenzoesäure durch eine Arthrobacter-Species. Arch Microbiol. 1976 Nov 2;110(23):253–256. doi: 10.1007/BF00690235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh W. K., Gibson D. T., Liu T. N. Toluene dioxygenase: a multicomponent enzyme system. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Sep 9;78(1):401–410. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91268-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



