Abstract
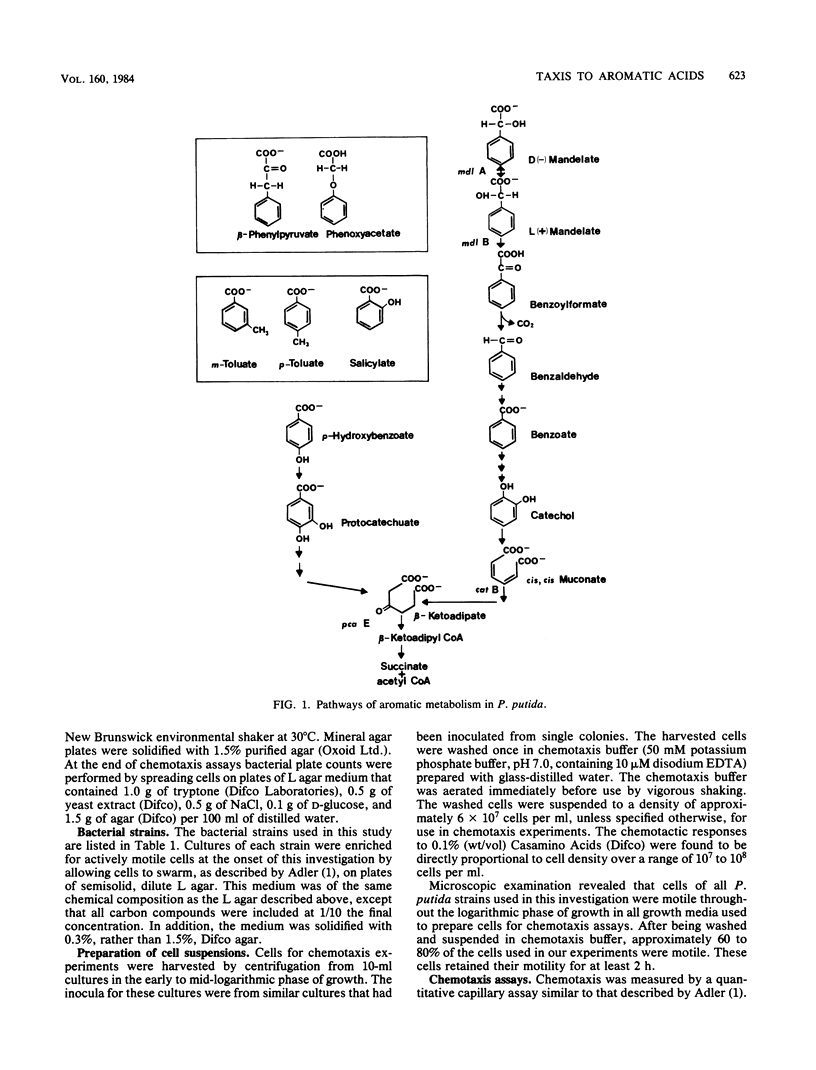
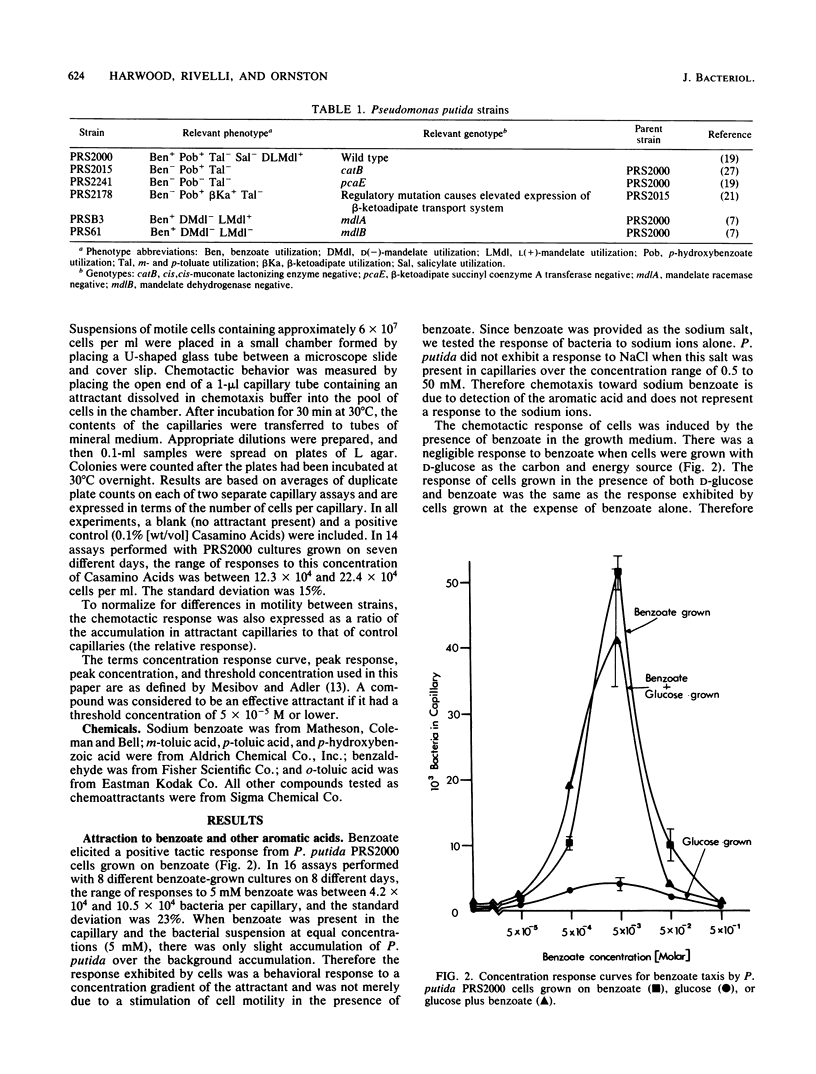
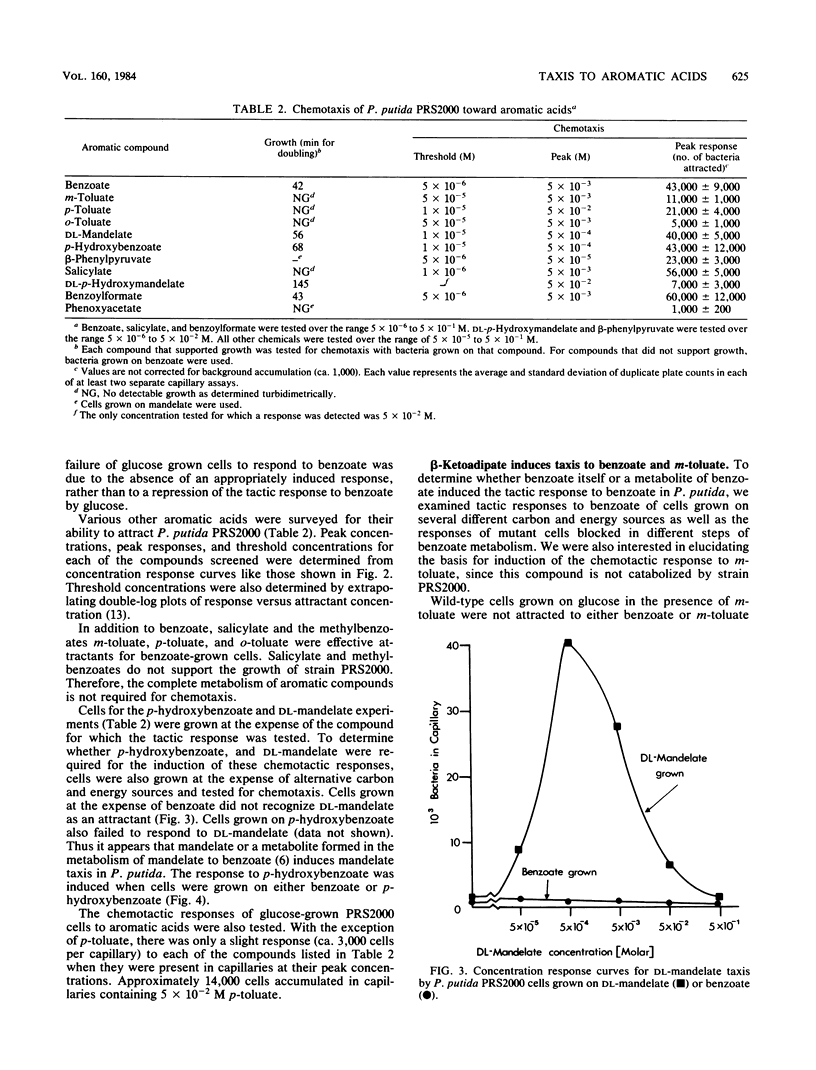
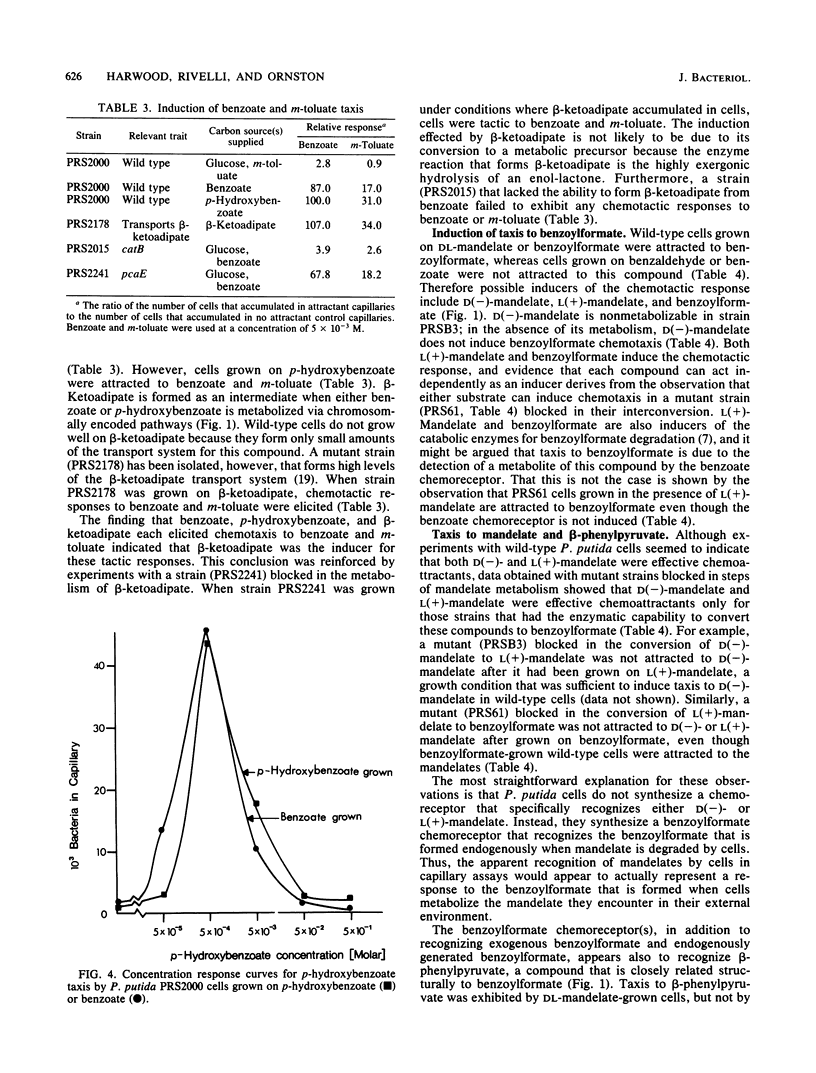
A quantitative capillary assay was used to show that aromatic acids, compounds that are chemorepellents for Escherichia coli and Salmonella sp., are chemoattractants for Pseudomonas putida PRS2000. The most effective attractants were benzoate; p-hydroxybenzoate; the methylbenzoates; m-, p-, and o-toluate; salicylate; DL-mandelate; beta-phenylpyruvate; and benzoylformate. The chemotactic responses to these compounds were inducible. Taxis to benzoate and m-toluate was induced by beta-ketoadipate, a metabolic intermediate formed when benzoate is dissimilated via enzymes specified by chromosomal genes. Benzoylformate taxis was induced by benzoylformate and L(+)-mandelate. Taxis to mandelate, benzoylformate, and beta-phenylpyruvate was exhibited by cells grown on mandelate, but not by cells grown on benzoate. Cells grown on benzoate were chemotactic to benzoate, the toluates, p-hydroxybenzoate, and salicylate. These results show that P. putida synthesizes at least two distinct chemoreceptors for aromatic acids. Although DL-mandelate was an effective attractant in capillary assays, additional experiments indicated that the cells were actually responding to benzoylformate, a metabolite formed from mandelate. With the exception of mandelate taxis, chemotaxis to aromatic acids was not dependent on the expression of pathways for aromatic degradation. Therefore, the tactic responses exhibited by cells cannot be attributed to an effect of the oxidation of aromatic acids on the energy metabolism of cells.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler J. A method for measuring chemotaxis and use of the method to determine optimum conditions for chemotaxis by Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 Jan;74(1):77–91. doi: 10.1099/00221287-74-1-77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adler J., Hazelbauer G. L., Dahl M. M. Chemotaxis toward sugars in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1973 Sep;115(3):824–847. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.3.824-847.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craven R. C., Montie T. C. Chemotaxis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: involvement of methylation. J Bacteriol. 1983 May;154(2):780–786. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.2.780-786.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas D. Genetic aspects of biodegradation by pseudomonads. Experientia. 1983 Nov 15;39(11):1199–1213. doi: 10.1007/BF01990357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazelbauer G. L., Harayama S. Sensory transduction in bacterial chemotaxis. Int Rev Cytol. 1983;81:33–70. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)62334-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hegeman G. D. Synthesis of the enzymes of the mandelate pathway by Pseudomonas putida. I. Synthesis of enzymes by the wild type. J Bacteriol. 1966 Mar;91(3):1140–1154. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.3.1140-1154.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hegeman G. D. Synthesis of the enzymes of the mandelate pathway by Pseudomonas putida. II. Isolation and properties of blocked mutants. J Bacteriol. 1966 Mar;91(3):1155–1160. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.3.1155-1160.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holloway B. W., Krishnapillai V., Morgan A. F. Chromosomal genetics of Pseudomonas. Microbiol Rev. 1979 Mar;43(1):73–102. doi: 10.1128/mr.43.1.73-102.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kihara M., Macnab R. M. Cytoplasmic pH mediates pH taxis and weak-acid repellent taxis of bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1209–1221. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1209-1221.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leidigh B. J., Wheelis M. L. The clustering on the Pseudomonas putida chromosome of genes specifying dissimilatory functions. J Mol Evol. 1973 Nov 27;2(4):235–242. doi: 10.1007/BF01654092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leisinger T. Microorganisms and xenobiotic compounds. Experientia. 1983 Nov 15;39(11):1183–1191. doi: 10.1007/BF01990355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macnab R. M. Sensory reception in bacteria. Symp Soc Exp Biol. 1982;35:77–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mesibov R., Adler J. Chemotaxis toward amino acids in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1972 Oct;112(1):315–326. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.1.315-326.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moench T. T., Konetzka W. A. Chemotaxis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jan;133(1):427–429. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.1.427-429.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moulton R. C., Montie T. C. Chemotaxis by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):274–280. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.274-280.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ornston L. N., Parke D. Properties of an inducible uptake system for beta-ketoadipate in Pseudomonas putida. J Bacteriol. 1976 Feb;125(2):475–488. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.2.475-488.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ornston L. N., Parke D. The evolution of induction mechanisms in bacteria: insights derived from the study of the beta-ketoadipate pathway. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1977;12:209–262. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152812-6.50011-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ornston L. N. Regulation of catabolic pathways in Pseudomonas. Bacteriol Rev. 1971 Jun;35(2):87–116. doi: 10.1128/br.35.2.87-116.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ornston L. N., Stanier R. Y. The conversion of catechol and protocatechuate to beta-ketoadipate by Pseudomonas putida. J Biol Chem. 1966 Aug 25;241(16):3776–3786. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ornston L. N. The conversion of catechol and protocatechuate to beta-ketoadipate by Pseudomonas putida. IV. Regulation. J Biol Chem. 1966 Aug 25;241(16):3800–3810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parke D., Ornston L. N. Constitutive synthesis of enzymes of the protocatechuate pathway and of the beta-ketoadipate uptake system in mutant strains of Pseudomonas putida. J Bacteriol. 1976 Apr;126(1):272–281. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.1.272-281.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Repaske D. R., Adler J. Change in intracellular pH of Escherichia coli mediates the chemotactic response to certain attractants and repellents. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1196–1208. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1196-1208.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroth M. N., Hancock J. G. Disease-suppressive soil and root-colonizing bacteria. Science. 1982 Jun 25;216(4553):1376–1381. doi: 10.1126/science.216.4553.1376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slonczewski J. L., Macnab R. M., Alger J. R., Castle A. M. Effects of pH and repellent tactic stimuli on protein methylation levels in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1982 Oct;152(1):384–399. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.1.384-399.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanier R. Y., Palleroni N. J., Doudoroff M. The aerobic pseudomonads: a taxonomic study. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 May;43(2):159–271. doi: 10.1099/00221287-43-2-159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tso W. W., Adler J. Negative chemotaxis in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1974 May;118(2):560–576. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.2.560-576.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheelis M. L., Ornston L. N. Genetic control of enzyme induction in the -ketoadipate pathway of Pseudomonas putida: deletion mapping of cat mutations. J Bacteriol. 1972 Feb;109(2):790–795. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.2.790-795.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



