Abstract
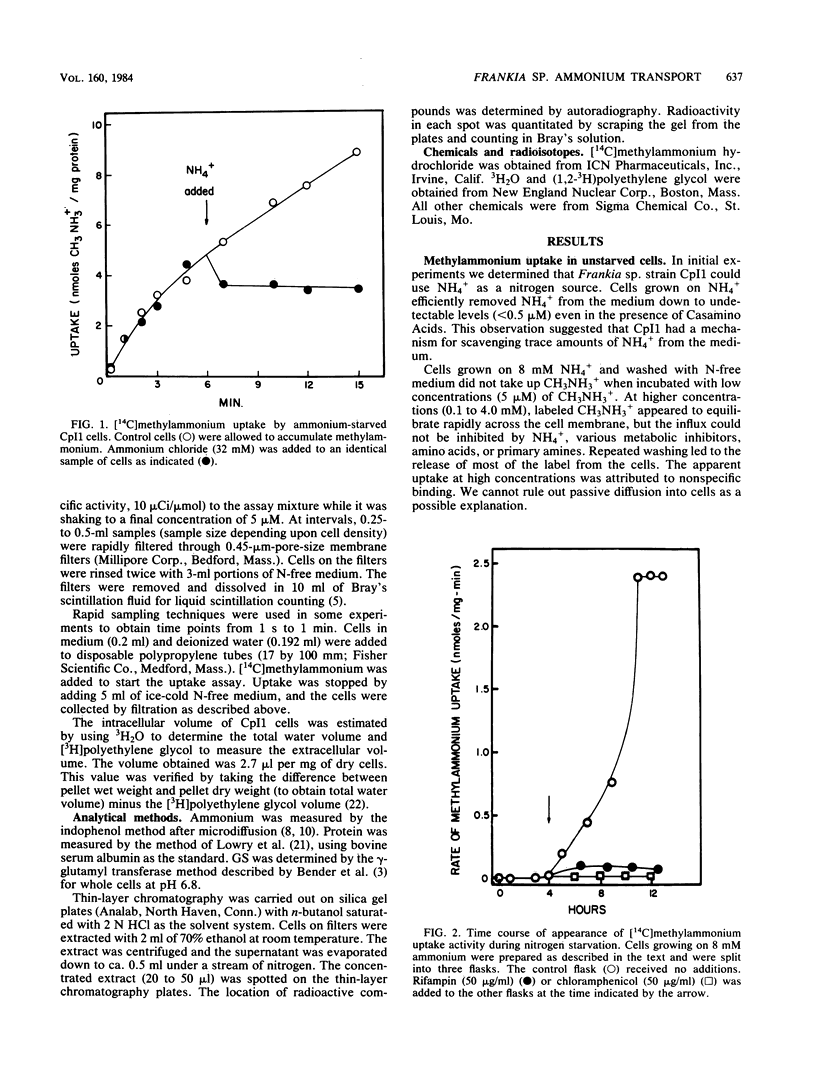
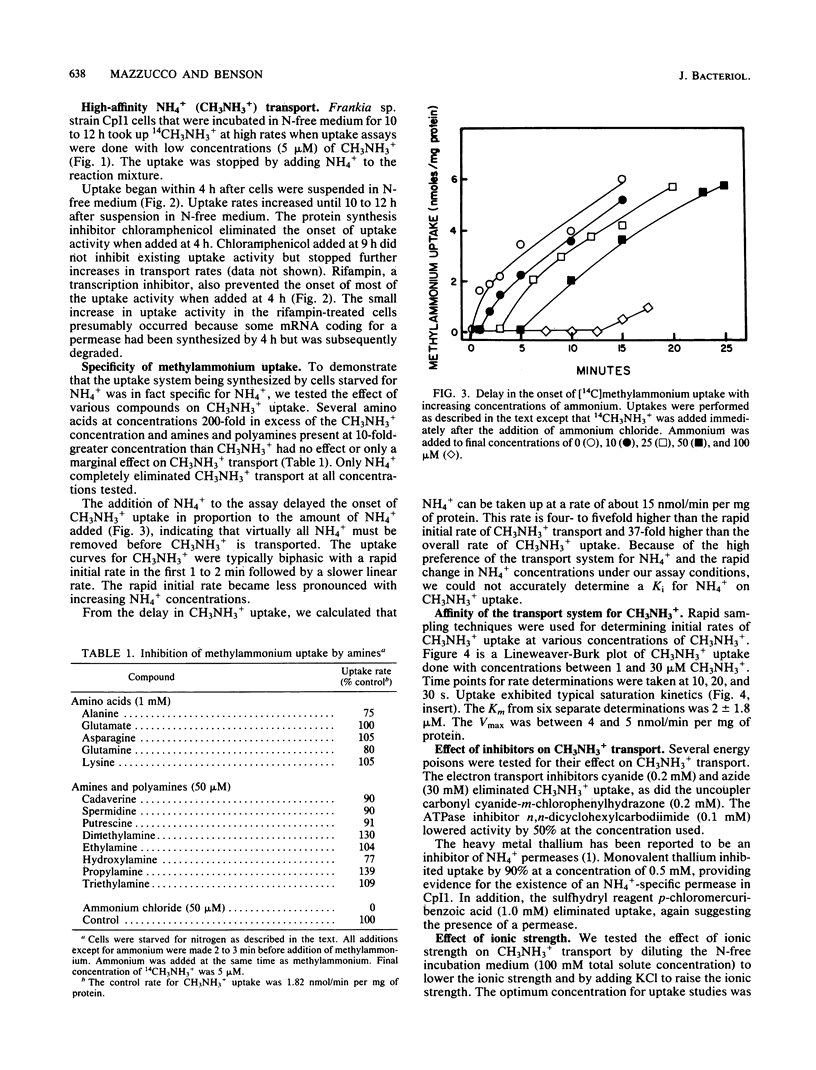
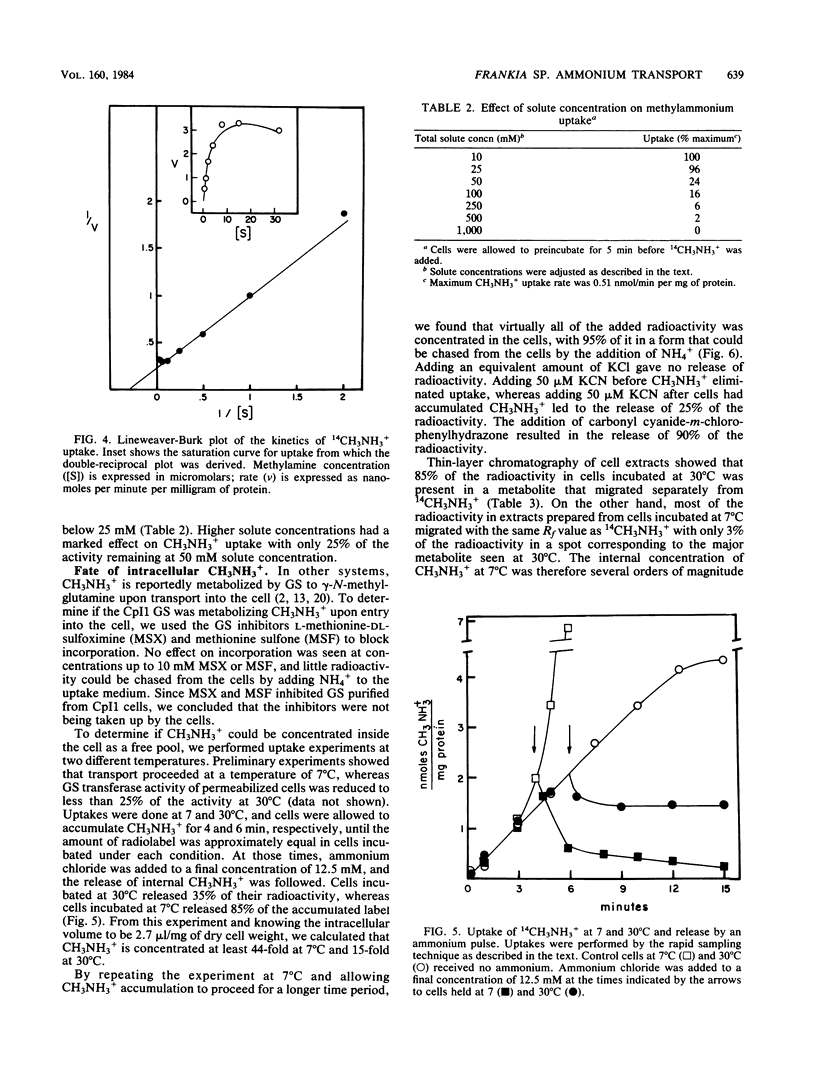
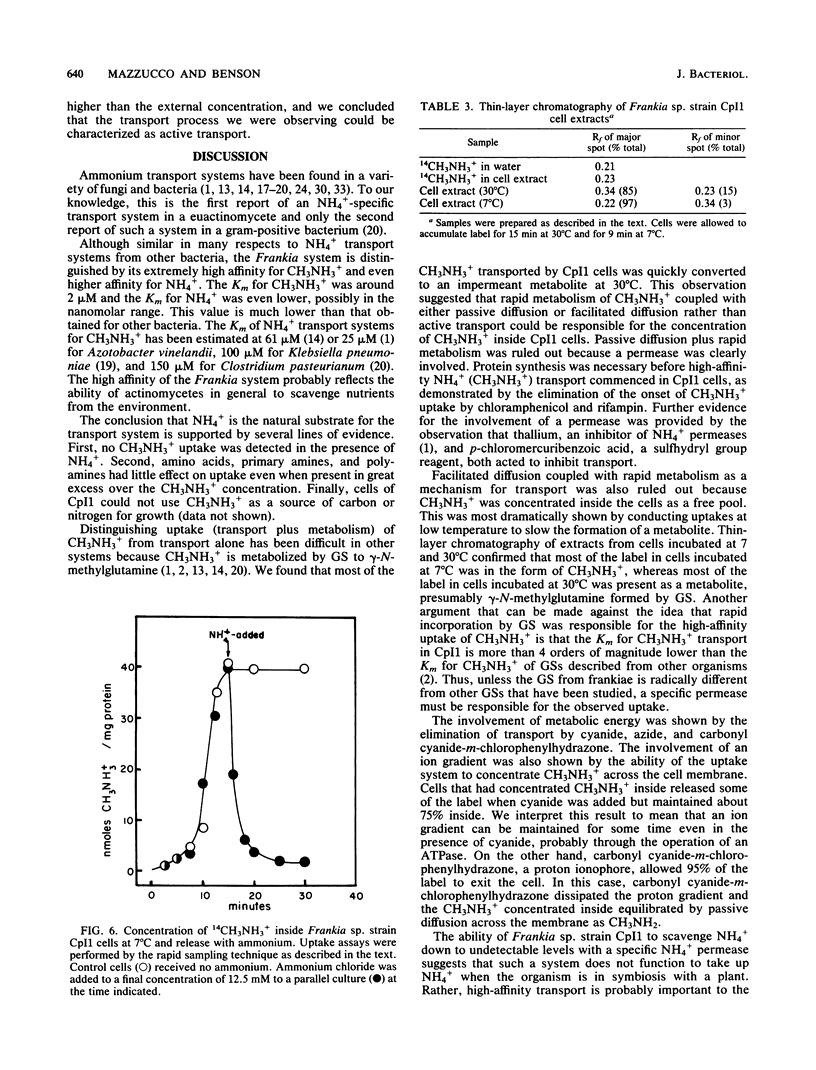
We describe an NH4+-specific transport system in the N2-fixing symbiotic actinomycete Frankia sp. strain CpI1. [14C]methylammonium was used as an NH4+ analog. No specific transport process was detected when cells were grown on high concentrations of NH4+. A transport system with a high affinity for CH3NH3+ was synthesized after 3 to 4 h of nitrogen starvation. Methylammonium transport was not significantly inhibited by a variety of amino acids, primary amines, and polyamines. Ammonium completely eliminated CH3NH3+ transport. The Km for CH3NH3+ transport was around 2 +/- 1.8 microM with a Vmax of 4 to 5 nmol/min per mg of protein. The electron transport inhibitors cyanide and azide eliminated uptake, as did the uncoupler carbonyl cyanide-m-chlorophenylhydrazone. The sulfydryl reagent p-chloromercuribenzoic acid and the heavy metal thallium also inhibited uptake, suggesting the presence of an NH4+-specific permease. Concentration of CH3NH3+ across the membrane was demonstrated by conducting uptakes at low temperature to slow the metabolism of CH3NH3+ by glutamine synthetase. At 7 degrees C most of the label was concentrated inside the cells in a form that could be chased from the cells by adding excess NH4+ to the medium. At 30 degrees C most of the label was present as an impermeant metabolite. Thin-layer chromatography of cell extracts confirmed that the radioactivity inside the cells was mainly in the form of CH3NH3+ at 7 degrees C but was present as an unidentified metabolite at 30 degrees C. These studies demonstrate that Frankia sp. strain CpI1 has a high-affinity NH4+ transport system that is synthesized in response to NH4+ starvation.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnes E. M., Jr, Zimniak P., Jayakumar A. Role of glutamine synthetase in the uptake and metabolism of methylammonium by Azotobacter vinelandii. J Bacteriol. 1983 Nov;156(2):752–757. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.2.752-757.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes E. M., Jr, Zimniak P. Transport of ammonium and methylammonium ions by Azotobacter vinelandii. J Bacteriol. 1981 May;146(2):512–516. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.2.512-516.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender R. A., Janssen K. A., Resnick A. D., Blumenberg M., Foor F., Magasanik B. Biochemical parameters of glutamine synthetase from Klebsiella aerogenes. J Bacteriol. 1977 Feb;129(2):1001–1009. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.2.1001-1009.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown C. M., Dilworth M. J. Ammonia assimilation by rhizobium cultures and bacteroids. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Jan;86(1):39–48. doi: 10.1099/00221287-86-1-39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callaham D., Deltredici P., Torrey J. G. Isolation and Cultivation in vitro of the Actinomycete Causing Root Nodulation in Comptonia. Science. 1978 Feb 24;199(4331):899–902. doi: 10.1126/science.199.4331.899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaykin S. Assay of nicotinamide deamidase. Determination of ammonia by the indophenol reaction. Anal Biochem. 1969 Oct 1;31(1):375–382. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90278-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubois E., Grenson M. Methylamine/ammonia uptake systems in saocharomyces cerevisiae: multiplicity and regulation. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Aug;175(1):67–76. doi: 10.1007/BF00267857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gober J. W., Kashket E. R. Methylammonium uptake by Rhizobium sp. strain 32H1. J Bacteriol. 1983 Mar;153(3):1196–1201. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.3.1196-1201.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. K., Moore R. A. Ammonium and methylammonium transport by the nitrogen-fixing bacterium Azotobacter vinelandii. J Bacteriol. 1981 Nov;148(2):435–442. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.2.435-442.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackette S. L., Skye G. E., Burton C., Segel I. H. Characterization of an ammonium transport system in filamentous fungi with methylammonium-14C as the substrate. J Biol Chem. 1970 Sep 10;245(17):4241–4250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleiner D. Ammonium (methylammonium) transport by Klebsiella pneumoniae. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Jun 28;688(3):702–708. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90282-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleiner D. Ammonium uptake and metabolism by mitrogen fixing bacteria. II. Klebsiella pneumoniae. Arch Microbiol. 1976 Dec 1;111(1-2):85–91. doi: 10.1007/BF00446553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleiner D. Ammonium uptake by nitrogen fixing bacteria I. Azotobacter vinelandii. Arch Microbiol. 1975 Jun 22;104(2):163–169. doi: 10.1007/BF00447319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleiner D., Fitzke E. Some properties of a new electrogenic transport system: the ammonium (methylammonium) carrier from Clostridium pasteurianum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Feb 20;641(1):138–147. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90577-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Gara F., Shanmugam K. T. Regulation of nitrogen fixation by Rhizobia. Export of fixed N2 as NH+4. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jul 21;437(2):313–321. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(76)90001-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roon R. J., Even H. L., Dunlop P., Larimore F. L. Methylamine and ammonia transport in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1975 May;122(2):502–509. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.2.502-509.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert K. R., Coker G. T. Ammonia Assimilation in Alnus glutinosa and Glycine max: SHORT-TERM STUDIES USING [N]AMMONIUM. Plant Physiol. 1981 Apr;67(4):662–665. doi: 10.1104/pp.67.4.662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serrano R. Plasma membrane ATPase of fungi and plants as a novel type of proton pump. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1984;23:87–126. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152823-2.50007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson R., Silver S. Methylammonium uptake by Escherichia coli: evidence for a bacterial NH4+ transport system. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Apr 25;75(4):1133–1139. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91501-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


