Abstract
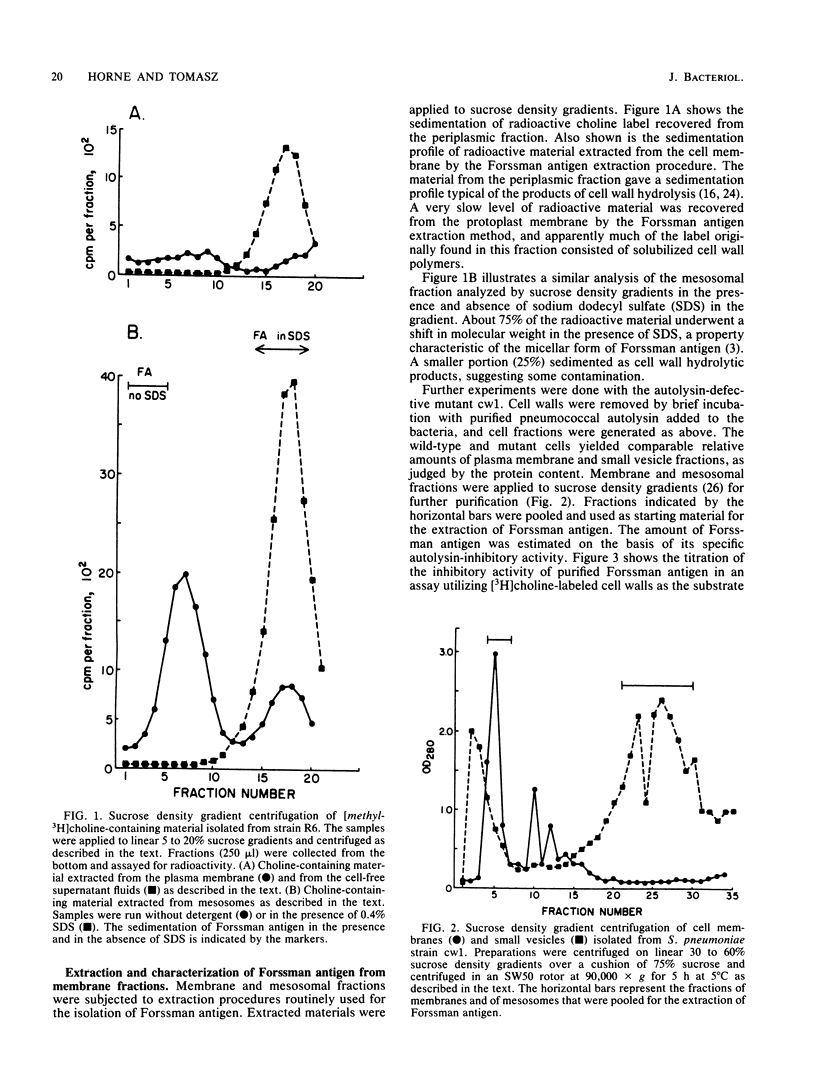
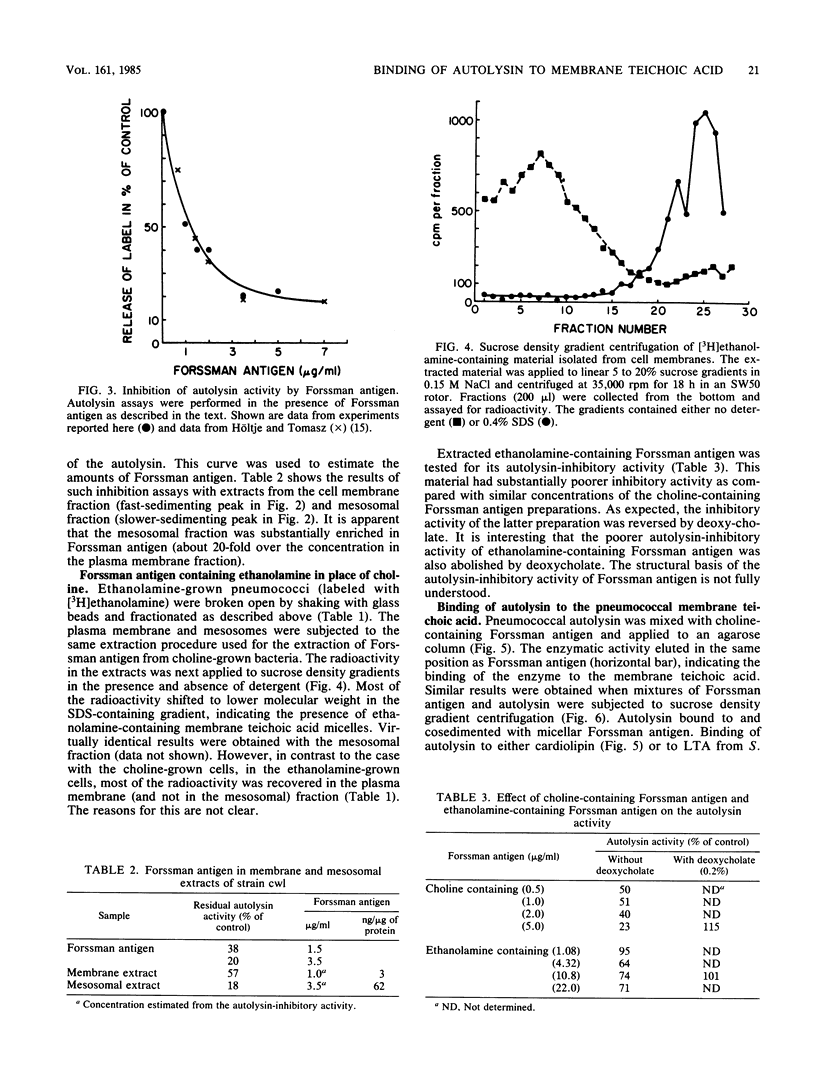
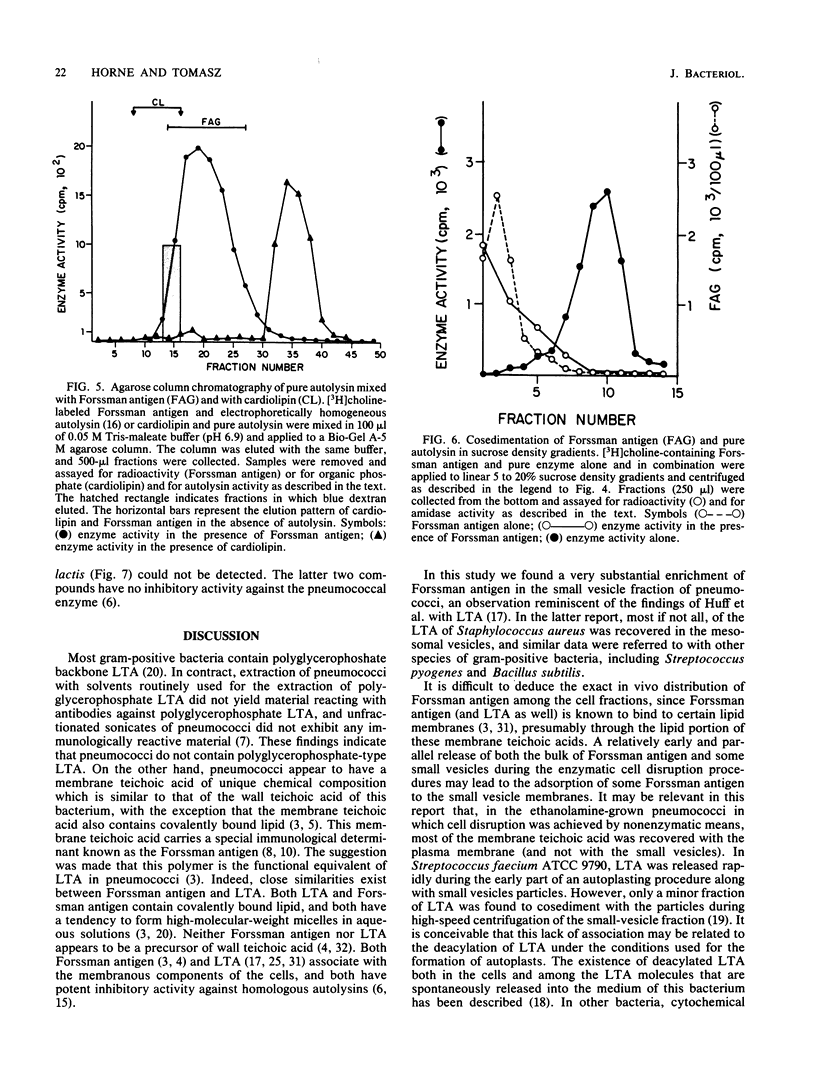
The choline-containing pneumococcal membrane teichoic acid (Forssman antigen) can be isolated with the membrane fractions of the bacteria. The small vesicle (mesosomal) fraction generated during the formation of protoplasts seems to be highly enriched in this material. Forssman antigen was identified in cell fractions on the basis of (i) radioactive choline label, (ii) autolysin-inhibitory activity, and (iii) the sedimentation profile in sucrose density gradients with and without detergent. A membrane teichoic acid could also be isolated from pneumococci grown in medium in which choline was replaced by ethanolamine as the nutritionally required amino alcohol. This material contained radioactive ethanolamine label and behaved similarly to the choline-containing membrane teichoic acid during centrifugation in detergent-containing and detergent-free density gradients. On the other hand, the material had only low autolysin-inhibitory activity. Binding of pure pneumococcal autolysin to micelles of purified Forssman antigen could be demonstrated by mixing these components in vitro and analyzing them by sucrose density gradients and by agarose chromatography. No binding could be observed between the pneumococcal enzyme and the micellar forms of either cardiolipin or polyglycerophosphate-type lipoteichoic acid isolated from Streptococcus lactis.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMES B. N., DUBIN D. T. The role of polyamines in the neutralization of bacteriophage deoxyribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1960 Mar;235:769–775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briles E. B., Tomasz A. Membrane lipoteichoic acid is not a precursor to wall teichoic acid in pneumococci. J Bacteriol. 1975 Apr;122(1):335–337. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.1.335-337.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briles E. B., Tomasz A. Pneumococcal Forssman antigen. A choline-containing lipoteichoic acid. J Biol Chem. 1973 Sep 25;248(18):6394–6397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brundish D. E., Baddiley J. Pneumococcal C-substance, a ribitol teichoic acid containing choline phosphate. Biochem J. 1968 Dec;110(3):573–582. doi: 10.1042/bj1100573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland R. F., Holtje J. V., Wicken A. J., Tomasz A., Daneo-Moore L., Shockman G. D. Inhibition of bacterial wall lysins by lipoteichoic acids and related compounds. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Dec 1;67(3):1128–1135. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90791-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland R. F., Wicken A. J., Daneo-Moore L., Shockman G. D. Inhibition of wall autolysis in Streptococcus faecalis by lipoteichoic acid and lipids. J Bacteriol. 1976 Apr;126(1):192–197. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.1.192-197.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara M. The Forssman antigen of pneumococcus. Jpn J Exp Med. 1967 Dec;37(6):581–592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giudicelli S., Tomasz A. Attachment of pneumococcal autolysin to wall teichoic acids, an essential step in enzymatic wall degradation. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jun;158(3):1188–1190. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.3.1188-1190.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenawalt J. W., Whiteside T. L. Mesosomes: membranous bacterial organelles. Bacteriol Rev. 1975 Dec;39(4):405–463. doi: 10.1128/br.39.4.405-463.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins M. L., Daneo-Moore L. Factors influencing the frequency of mesosomes observed in fixed and unfixed cells of Streptococcus faecalis. J Cell Biol. 1974 May;61(2):288–300. doi: 10.1083/jcb.61.2.288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holtje J. V., Tomasz A. Biological effects of lipoteichoic acids. J Bacteriol. 1975 Nov;124(2):1023–1027. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.2.1023-1027.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huff E., Cole R. M., Theodore T. S. Lipoteichoic acid localization in mesosomal vesicles of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1974 Oct;120(1):273–281. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.1.273-281.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höltje J. V., Tomasz A. Lipoteichoic acid: a specific inhibitor of autolysin activity in Pneumococcus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 May;72(5):1690–1694. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.5.1690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höltje J. V., Tomasz A. Purification of the pneumococcal N-acetylmuramyl-L-alanine amidase to biochemical homogeneity. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jul 25;251(14):4199–4207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höltje J. V., Tomasz A. Specific recognition of choline residues in the cell wall teichoic acid by the N-acetylmuramyl-L-alanine amidase of Pneumococcus. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 10;250(15):6072–6076. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph R., Shockman G. D. Cellular localization of lipoteichoic acid in Streptococcus faecalis. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jun;122(3):1375–1386. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.3.1375-1386.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph R., Shockman G. D. Synthesis and excretion of glycerol teichoic acid during growth of two streptococcal species. Infect Immun. 1975 Aug;12(2):333–338. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.2.333-338.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knox K. W., Wicken A. J. Immunological properties of teichoic acids. Bacteriol Rev. 1973 Jun;37(2):215–257. doi: 10.1128/br.37.2.215-257.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIU T. Y., GOTSCHLICH E. C. The chemical composition of pneumococcal C-polysaccharide. J Biol Chem. 1963 Jun;238:1928–1934. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacks S. Mutants of Diplococcus pneumoniae that lack deoxyribonucleases and other activities possibly pertinent to genetic transformation. J Bacteriol. 1970 Feb;101(2):373–383. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.2.373-383.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosser J. L., Tomasz A. Choline-containing teichoic acid as a structural component of pneumococcal cell wall and its role in sensitivity to lysis by an autolytic enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1970 Jan 25;245(2):287–298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHOCKMAN G. D., SLADE H. D. THE CELLULAR LOCATION OF THE STREPTOCOCCAL GROUP D ANTIGEN. J Gen Microbiol. 1964 Dec;37:297–305. doi: 10.1099/00221287-37-3-297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOMASZ A., JAMIESON J. D., OTTOLENGHI E. THE FINE STRUCTURE OF DIPLOCOCCUS PNEUMONIAE. J Cell Biol. 1964 Aug;22:453–467. doi: 10.1083/jcb.22.2.453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theodore T. S., Popkin T. J., Cole R. M. The separation and isolation of plasma membranes and mesosomal vesicles from Staphylococcus aureus. Prep Biochem. 1971;1(3):233–248. doi: 10.1080/00327487108081942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasz A. Biological consequences of the replacement of choline by ethanolamine in the cell wall of Pneumococcus: chanin formation, loss of transformability, and loss of autolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jan;59(1):86–93. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.1.86. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasz A., Westphal M. Abnormal autolytic enzyme in a pneumococus with altered teichoic acid composition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Nov;68(11):2627–2630. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.11.2627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Driel D., Wicken A. J., Dickson M. R., Knox K. W. Cellular location of the lipoteichoic acids of Lactobacillus fermenti NCTC 6991 and Lactobacillus casei NCTC 6375. J Ultrastruct Res. 1973 Jun;43(5):483–497. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(73)90025-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward J. B. Teichoic and teichuronic acids: biosynthesis, assembly, and location. Microbiol Rev. 1981 Jun;45(2):211–243. doi: 10.1128/mr.45.2.211-243.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wicken A. J., Knox K. W. Studies on the group F antigen of lactobacilli: isolation of a teichoic acid-lipid complex from Lactobacillus fermenti NCTC 6991. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Mar;60(3):293–301. doi: 10.1099/00221287-60-3-293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


