Abstract
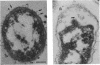
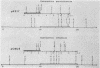
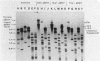
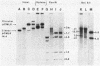
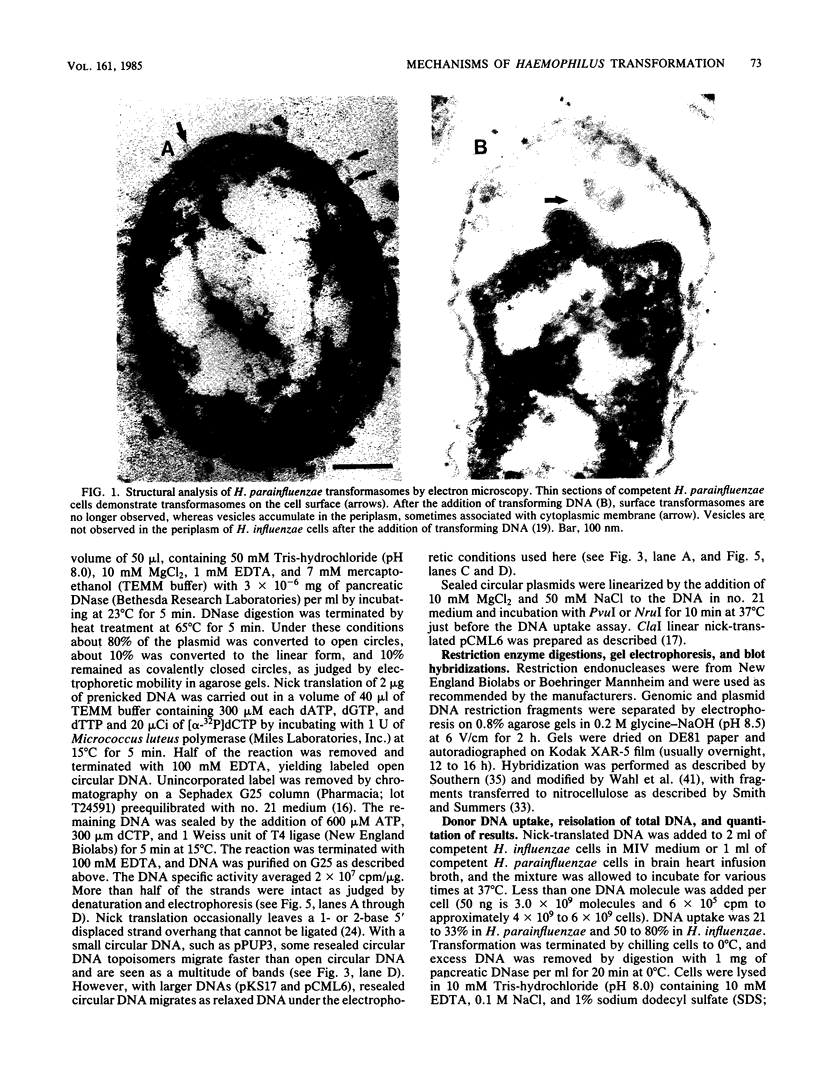
Transformation pathways in two closely related bacterial species, Haemophilus parainfluenzae and Haemophilus influenzae, were studied. Both organisms rapidly take up transforming DNA within minutes into specialized membranous structures on the cell surface (transformasomes). DNA within transformasomes is in a protected state, inaccessible to external DNase or internal restriction and modification enzymes. However, the subsequent processing of donor DNA differs in these two organisms. In H. influenzae, linear DNA immediately undergoes degradation from one end at a constant rate, leaving a lower-molecular-weight intermediate in the transformasome. The end undergoing degradation is searching for homologous regions of the chromosome. Once pairing is initiated, the remaining lower-molecular-weight DNA exits from the transformasome, and a single strand undergoes efficient integration. In contrast, in H. parainfluenzae little degradation of donor DNA is observed, with the majority remaining intact within the transformasomes after 1 h. Thus, whereas only 10% of donor DNA molecules leave the protected state after 1 h, portions of each molecule appear to become quantitatively integrated.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barany F., Kahn M. E., Smith H. O. Directional transport and integration of donor DNA in Haemophilus influenzae transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(23):7274–7278. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.23.7274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beattie K. L., Setlow J. K. Transformation between Haemophilus influenzae and Haemophilus parainfluenzae. J Bacteriol. 1970 Oct;104(1):390–400. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.1.390-400.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bron S., Luxen E., Trautner T. A. Restriction and modification in B. subtilis: the role of homology between donor and recipient DNA in transformation and transfection. Mol Gen Genet. 1980;179(1):111–117. doi: 10.1007/BF00268452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danner D. B., Smith H. O., Narang S. A. Construction of DNA recognition sites active in Haemophilus transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(7):2393–2397. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.7.2393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOX M. S., ALLEN M. K. ON THE MECHANISM OF DEOXYRIBONUCLEATE INTEGRATION IN PNEUMOCOCCAL TRANSFORMATION. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Aug;52:412–419. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.2.412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodgal S. H. DNA uptake in Haemophilus transformation. Annu Rev Genet. 1982;16:169–192. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.16.120182.001125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodgal S. H., Postel E. H. On the mechanism of integration following transformation with single-stranded DNA of Hemophilus influenzae. J Mol Biol. 1967 Sep 14;28(2):261–273. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(67)80008-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gromkova R., Goodgal S. Transformation by plasmid and chromosomal DNAs in Haemophilus parainfluenzae. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Jun 27;88(4):1428–1434. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91139-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herriott R. M., Meyer E. M., Vogt M. Defined nongrowth media for stage II development of competence in Haemophilus influenzae. J Bacteriol. 1970 Feb;101(2):517–524. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.2.517-524.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn M. E., Barany F., Smith H. O. Transformasomes: specialized membranous structures that protect DNA during Haemophilus transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):6927–6931. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn M. E., Maul G., Goodgal S. H. Possible mechanism for donor DNA binding and transport in Haemophilus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6370–6374. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn M. E., Smith H. O. Transformation in Haemophilus: a problem in membrane biology. J Membr Biol. 1984;81(2):89–103. doi: 10.1007/BF01868974. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn M., Concino M., Gromkova R., Goodgal S. DNA binding activity of vesicles produced by competence deficient mutants of Haemophilus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Apr 13;87(3):764–772. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)92024-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LACKS S. Molecular fate of DNA in genetic transformation of Pneumococcus. J Mol Biol. 1962 Jul;5:119–131. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80067-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacks S., Greenberg B., Neuberger M. Identification of a deoxyribonuclease implicated in genetic transformation of Diplococcus pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jul;123(1):222–232. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.1.222-232.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacks S., Greenberg B., Neuberger M. Role of a deoxyribonuclease in the genetic transformation of Diplococcus pneumoniae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jun;71(6):2305–2309. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.6.2305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundquist R. C., Olivera B. M. Transient generation of displaced single-stranded DNA during nick translation. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):53–60. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90404-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muckerman C. C., Springhorn S. S., Greenberg B., Lacks S. A. Transformation of restriction endonuclease phenotype in Streptococcus pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1982 Oct;152(1):183–190. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.1.183-190.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathans D., Smith H. O. Restriction endonucleases in the analysis and restructuring of dna molecules. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:273–293. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.001421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notani N. K., Setlow J. K. Mechanism of bacterial transformation and transfection. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1974;14(0):39–100. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60205-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notani N., Goodgal S. H. On the nature of recombinants formed during transformation in Hemophilus influenzae. J Gen Physiol. 1966 Jul;49(6):197–209. doi: 10.1085/jgp.49.6.197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radloff R., Bauer W., Vinograd J. A dye-buoyant-density method for the detection and isolation of closed circular duplex DNA: the closed circular DNA in HeLa cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 May;57(5):1514–1521. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.5.1514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scocca J. J., Poland R. L., Zoon K. C. Specificity in deoxyribonucleic acid uptake by transformable Haemophilus influenzae. J Bacteriol. 1974 May;118(2):369–373. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.2.369-373.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sisco K. L., Smith H. O. Sequence-specific DNA uptake in Haemophilus transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):972–976. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. E., Summers M. D. The bidirectional transfer of DNA and RNA to nitrocellulose or diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper. Anal Biochem. 1980 Nov 15;109(1):123–129. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90019-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. O., Danner D. B., Deich R. A. Genetic transformation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:41–68. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.000353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stassi D. L., Lopez P., Espinosa M., Lacks S. A. Cloning of chromosomal genes in Streptococcus pneumoniae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):7028–7032. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.7028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuy J. H. Fate of transforming DNA in the Haemophilus influenzae transformation system. J Mol Biol. 1965 Sep;13(2):554–570. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80117-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuy J. H. Restriction enzymes do not play a significant role in Haemophilus homospecific or heterospecific transformation. J Bacteriol. 1976 Oct;128(1):212–220. doi: 10.1128/jb.128.1.212-220.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOLL M. J., GOODGAL S. H. Recombination during transformation in Hemophilus influenzae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1961 Apr 15;47:505–512. doi: 10.1073/pnas.47.4.505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox K. W., Smith H. O. Isolation and characterization of mutants of Haemophilus influenzae deficient in an adenosine 5'-triphosphate-dependent deoxyribonuclease activity. J Bacteriol. 1975 May;122(2):443–453. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.2.443-453.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoon K. C., Habersat M., Scocca J. J. Synthesis of envelope polypeptides by Haemophilus influenzae during development of competence for genetic transformation. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jul;127(1):545–554. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.1.545-554.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]