Abstract
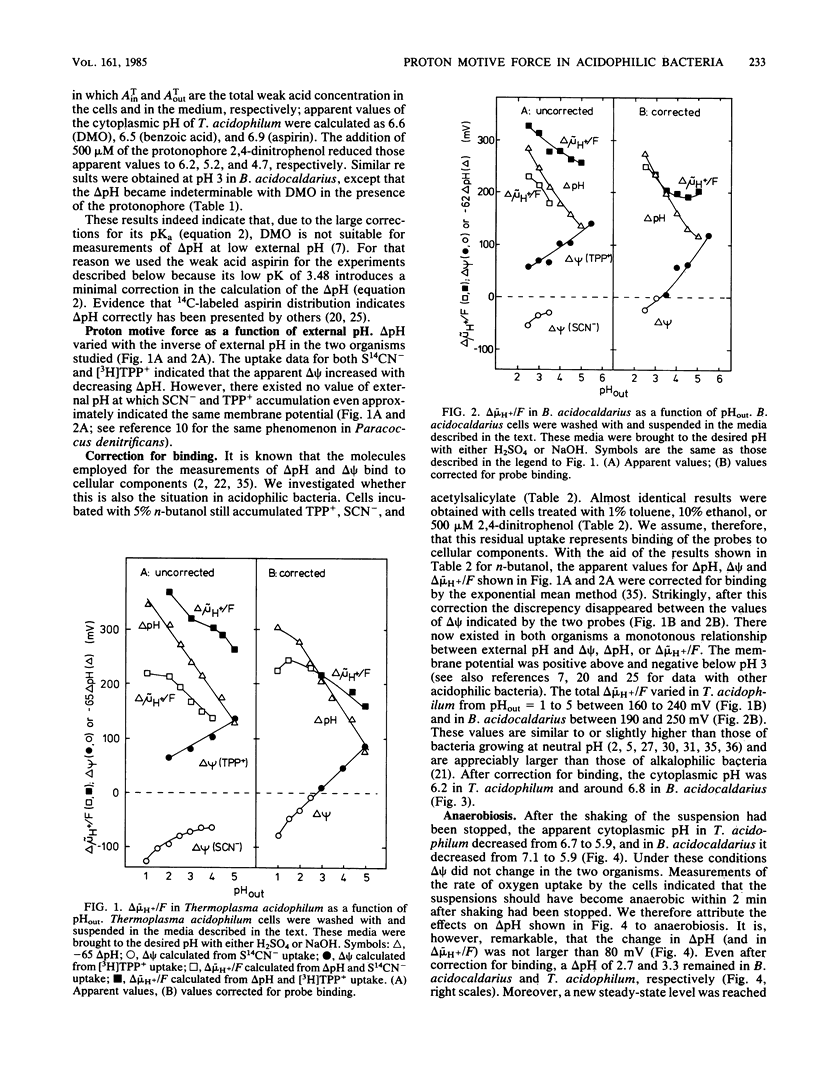
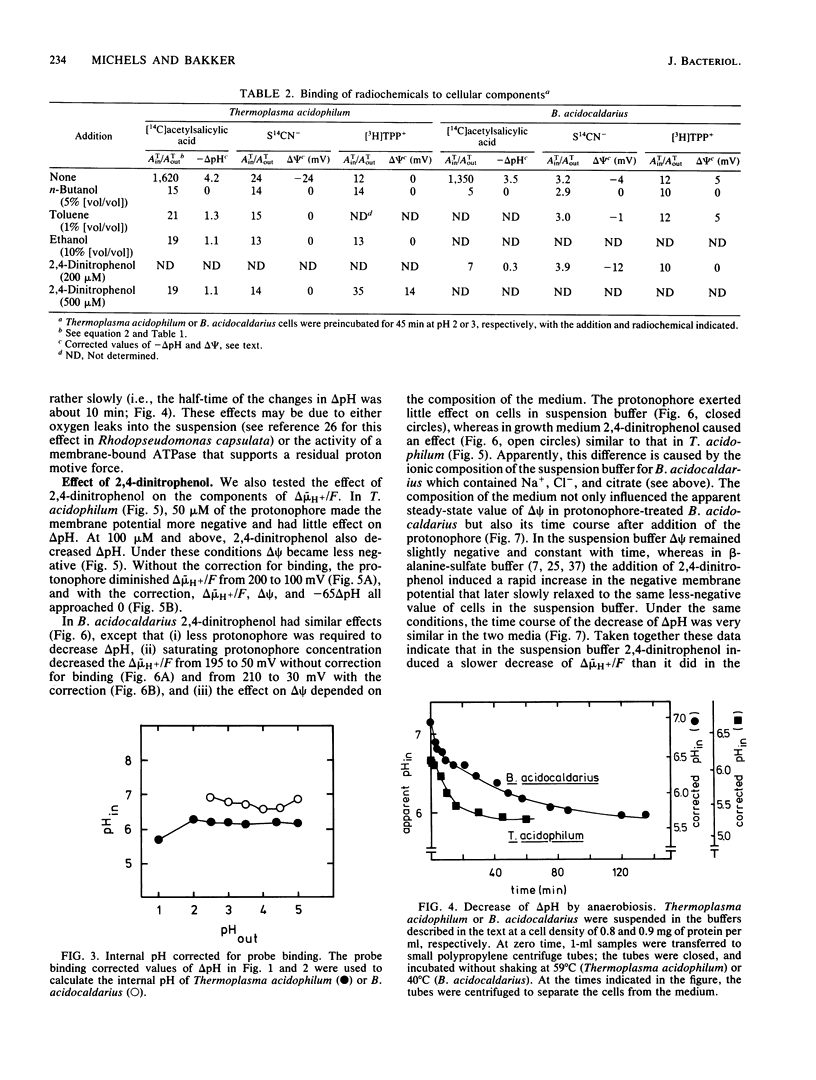
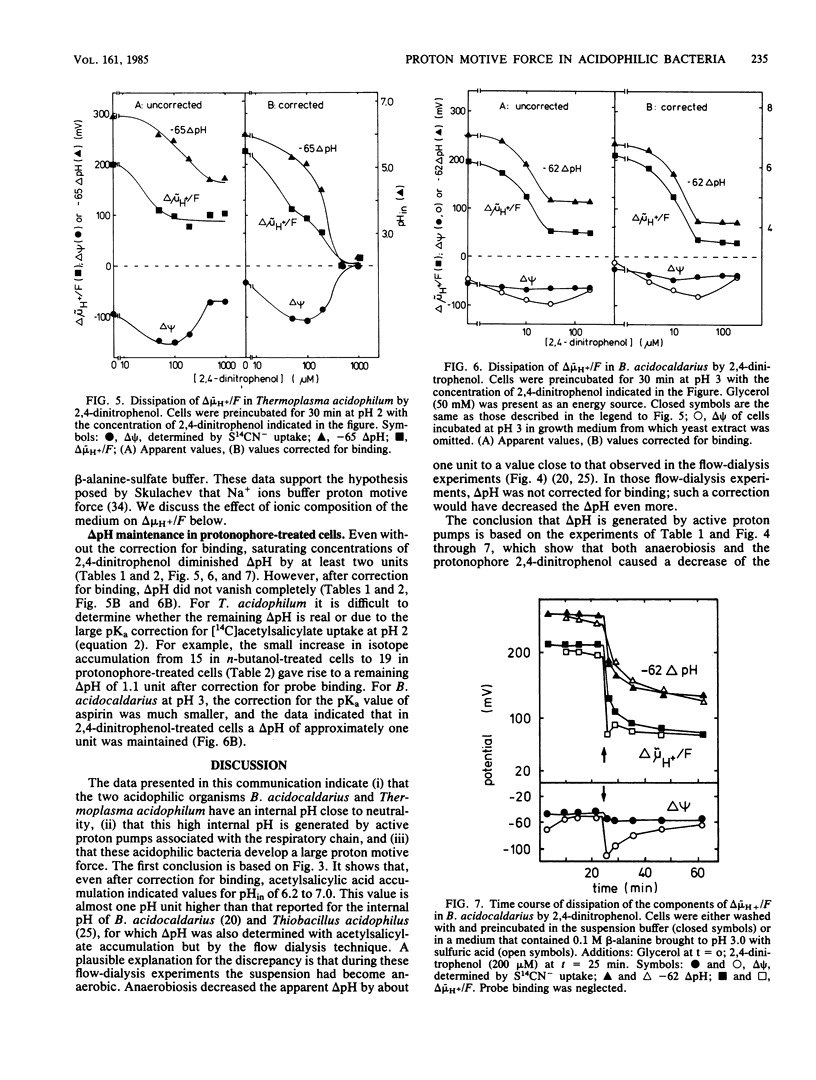
The mechanism by which acidophilic bacteria generate and maintain their cytoplasmic pH close to neutrality was investigated. For this purpose we determined the components of proton motive force in the eubacterium Bacillus acidocaldarius and the archaebacterium Thermoplasma acidophilum. After correction for probe binding, the proton motive force of untreated cells was 190 to 240 mV between external pH 2 and 4. Anoxia diminished total proton motive force and the transmembrane pH difference by 60 to 80 mV. The protonophore 2,4-dinitrophenol abolished the total proton motive force almost completely and diminished the transmembrane pH difference by at least two units. However, even after correction for probe binding, protonophore-treated cells maintained a pH difference of approximately one unit.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Addanki A., Cahill F. D., Sotos J. F. Determination of intramitochondrial pH and intramitochondrial-extramitochondrial pH gradient of isolated heart mitochondria by the use of 5,5-dimethyl-2,4-oxazolidinedione. I. Changes during respiration and adenosine triphosphate-dependent transport of Ca++, Mg++, and Zn++. J Biol Chem. 1968 May 10;243(9):2337–2348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakker E. P., Mangerich W. E. Interconversion of components of the bacterial proton motive force by electrogenic potassium transport. J Bacteriol. 1981 Sep;147(3):820–826. doi: 10.1128/jb.147.3.820-826.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakker E. P. Membrane potential in a potassium transport-negative mutant of Escherichia coli K-12. The distribution of rubidium in the presence of valinomycin indicates a higher potential than that of the tetraphenylphosphonium cation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Sep 15;681(3):474–483. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(82)90190-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakker E. P., Rottenberg H., Caplan S. R. An estimation of the light-induced electrochemical potential difference of protons across the membrane of Halobacterium halobium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Sep 13;440(3):557–572. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(76)90042-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booth I. R., Mitchell W. J., Hamilton W. A. Quantitative analysis of proton-linked transport systems. The lactose permease of Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1979 Sep 15;182(3):687–696. doi: 10.1042/bj1820687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobley J. G., Cox J. C. Energy conservation in acidophilic bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Dec;47(4):579–595. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.4.579-595.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox J. C., Nicholls D. G., Ingledew W. J. Transmembrane electrical potential and transmembrane pH gradient in the acidophile Thiobacillus ferro-oxidans. Biochem J. 1979 Jan 15;178(1):195–200. doi: 10.1042/bj1780195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darland G., Brock T. D., Samsonoff W., Conti S. F. A thermophilic, acidophilic mycoplasma isolated from a coal refuse pile. Science. 1970 Dec 25;170(3965):1416–1418. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3965.1416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutsch C. J., Kula T. Transmembrane electrical and pH gradients of Paracoccus denitrificans and their relationship to oxidative phosphorylation. FEBS Lett. 1978 Mar 1;87(1):145–151. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80154-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harold F. M. Conservation and transformation of energy by bacterial membranes. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Jun;36(2):172–230. doi: 10.1128/br.36.2.172-230.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsung J. C., Haug A. Intracellular pH of Thermoplasma acidophila. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 May 21;389(3):477–482. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90158-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsung J. C., Haug A. Membrane potential of Thermoplasma acidophila. FEBS Lett. 1977 Jan 15;73(1):47–50. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80011-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingledew W. J. Thiobacillus ferrooxidans. The bioenergetics of an acidophilic chemolithotroph. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Nov 30;683(2):89–117. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(82)90007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashket E. R., Barker S. L. Effects of potassium ions on the electrical and pH gradients across the membrane of Streptococcus lactis cells. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jun;130(3):1017–1023. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.3.1017-1023.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashket E. R., Blanchard A. G., Metzger W. C. Proton motive force during growth of Streptococcus lactis cells. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jul;143(1):128–134. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.1.128-134.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroll R. G., Booth I. R. The role of potassium transport in the generation of a pH gradient in Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1981 Sep 15;198(3):691–698. doi: 10.1042/bj1980691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krulwich T. A., Davidson L. F., Filip S. J., Jr, Zuckerman R. S., Guffanti A. A. The protonmotive force and beta-galactoside transport in Bacillus acidocaldarius. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jul 10;253(13):4599–4603. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krulwich T. A., Guffanti A. A. Physiology of acidophilic and alkalophilic bacteria. Adv Microb Physiol. 1983;24:173–214. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60386-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langworthy T. A. Long-chain diglycerol tetraethers from Thermoplasma acidophilum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Apr 26;487(1):37–50. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(77)90042-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matin A., Wilson B., Zychlinsky E., Matin M. Proton motive force and the physiological basis of delta pH maintenance in thiobacillus acidophilus. J Bacteriol. 1982 May;150(2):582–591. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.2.582-591.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McEwan A. G., Ferguson S. J., Jackson J. B. Electron flow to dimethylsulphoxide or trimethylamine-N-oxide generates a membrane potential in Rhodopseudomonas capsulata. Arch Microbiol. 1983 Dec;136(4):300–305. doi: 10.1007/BF00425221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. Chemiosmotic coupling in oxidative and photosynthetic phosphorylation. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 1966 Aug;41(3):445–502. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-185x.1966.tb01501.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oshima T., Arakawa H., Baba M. Biochemical studies on an acidophilic, thermophilic bacterium, Bacillus acidocaldarius: isolation of bacteria, intracellular pH, and stabilities of biopolymers. J Biochem. 1977 Apr;81(4):1107–1113. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padan E., Zilberstein D., Rottenberg H. The proton electrochemical gradient in Escherichia coli cells. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Apr 1;63(2):533–541. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10257.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padan E., Zilberstein D., Schuldiner S. pH homeostasis in bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Dec;650(2-3):151–166. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(81)90004-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottenberg H. The measurement of membrane potential and deltapH in cells, organelles, and vesicles. Methods Enzymol. 1979;55:547–569. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)55066-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Searcy D. G. Thermoplasma acidophilum: intracellular pH and potassium concentration. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Nov 18;451(1):278–286. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(76)90278-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skulachev V. P. Membrane-linked energy buffering as the biological function of Na+/K+ gradient. FEBS Lett. 1978 Mar 15;87(2):171–179. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80326-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaritsky A., Kihara M., Macnab R. M. Measurement of membrane potential in Bacillus subtilis: a comparison of lipophilic cations, rubidium ion, and a cyanine dye as probes. J Membr Biol. 1981;63(3):215–231. doi: 10.1007/BF01870983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zilberstein D., Schuldiner S., Padan E. Proton electrochemical gradient in Escherichia coli cells and its relation to active transport of lactose. Biochemistry. 1979 Feb 20;18(4):669–673. doi: 10.1021/bi00571a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zychlinsky E., Matin A. Cytoplasmic pH homeostasis in an acidophilic bacterium, Thiobacillus acidophilus. J Bacteriol. 1983 Dec;156(3):1352–1355. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.3.1352-1355.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zychlinsky E., Matin A. Effect of starvation on cytoplasmic pH, proton motive force, and viability of an acidophilic bacterium, Thiobacillus acidophilus. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):371–374. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.371-374.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



