Abstract
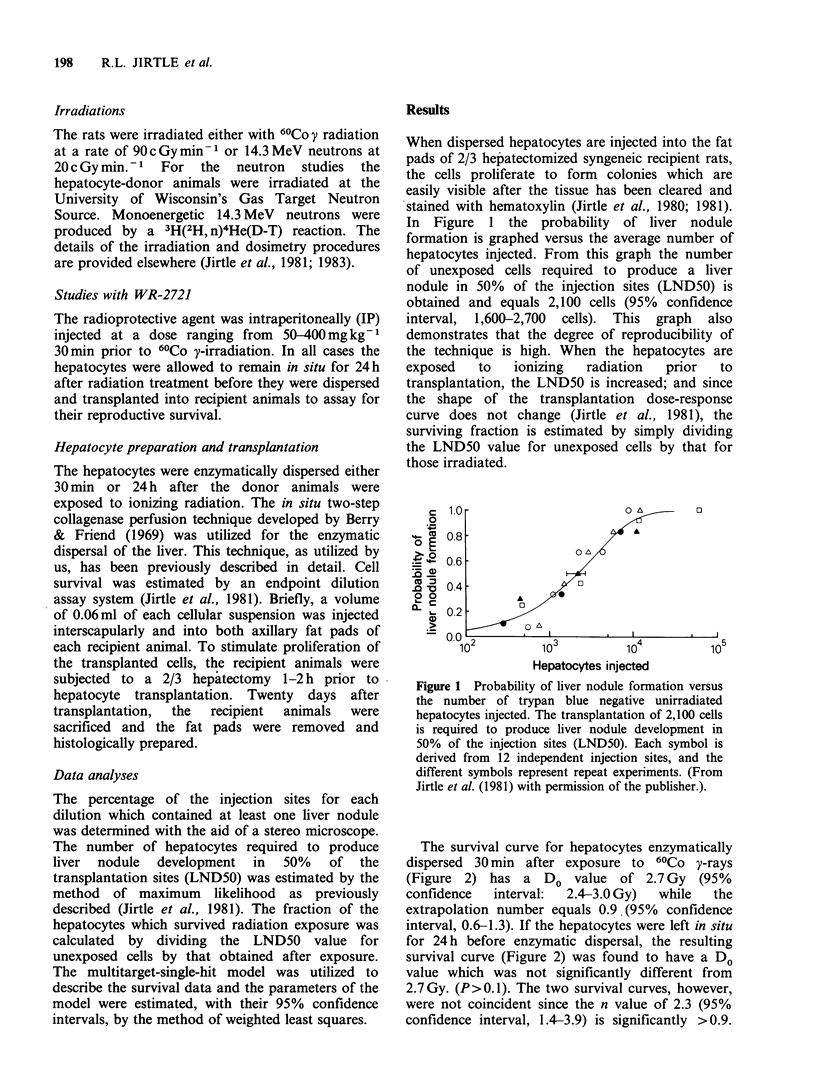
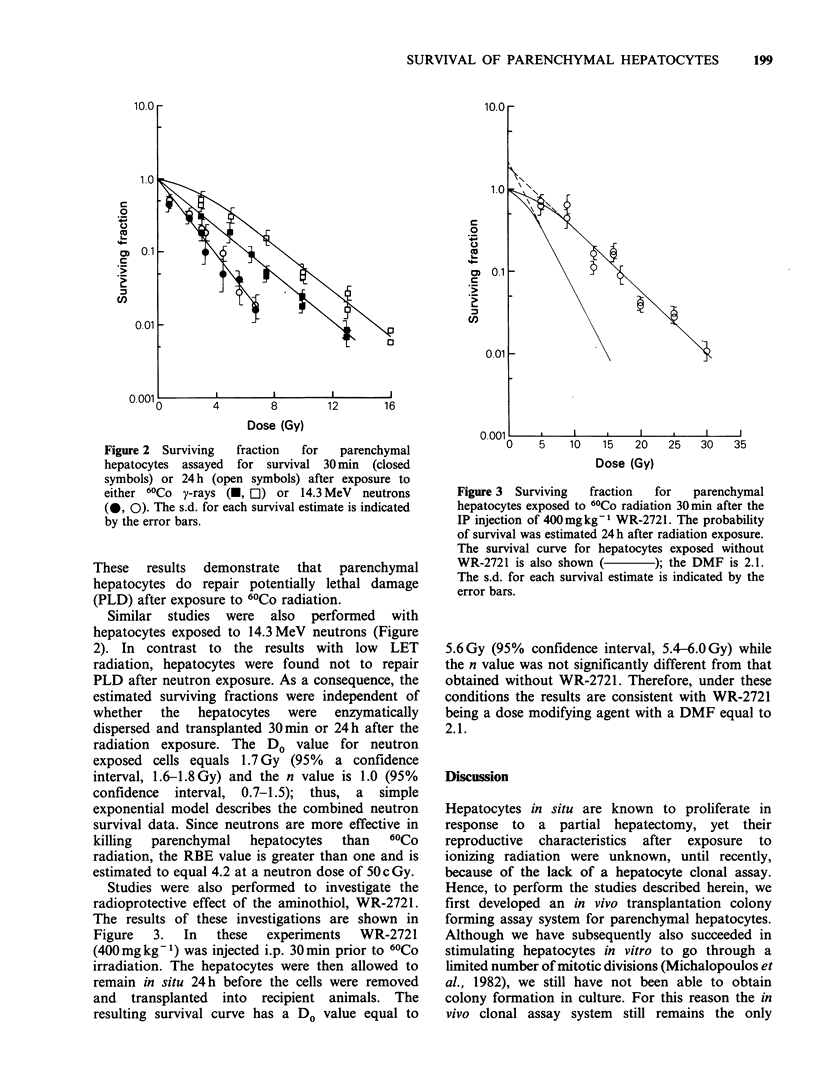
We have developed an in vivo clonogenic assay system for parenchymal hepatocytes which has enabled us to investigate the reproductive survival and repair capacity of liver cells exposed to genotoxic agents. In this report we present our results with hepatocytes irradiated 60Co and neutrons. The survival curve for parenchymal hepatocytes enzymatically dispersed 30 min after exposure to 60Co has a D0 value of 2.7 Gy and an extrapolation number insignificantly different from unity. However, when the hepatocytes were allowed to remain in situ for 24 h before being assayed for survival, the extrapolation number significantly increased to 2.3, whereas the D0 value remained unchanged. Therefore, normal parenchymal hepatocytes in G0 are able to repair potentially lethal damage (PLD) after exposure to 60Co and this repair phenomenon is expressed solely as an increase in the n value. In contrast, with hepatocytes exposed to 14.3 MeV neutrons, the survival curve is exponential with a D0 value of 1.7 Gy regardless of whether the cells remained in situ for 30 min or 24 h before the assessment of their reproductive survival. A comparison of the 60Co and neutron survival curves, where 24 h is allowed for PLD repair to occur, demonstrates that the RBE of neutrons for hepatocytes increases with decreasing dose and equals 4.2 at 50 cGy. The radioprotective agent WR-2721 was shown to act as a dose modifying agent with a DMF of 2.1, implying that it may be of potential clinical value as a radiation hepato-protective drug.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berry M. N., Friend D. S. High-yield preparation of isolated rat liver parenchymal cells: a biochemical and fine structural study. J Cell Biol. 1969 Dec;43(3):506–520. doi: 10.1083/jcb.43.3.506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field S. B., Michalowski A. Endpoints for damage to normal tissues. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1979 Aug;5(8):1185–1196. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(79)90638-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geraci J. P., Jackson K. L., Thrower P. D., Mariano M. S. Relative biological effectiveness of cyclotron fast neutrons for late hepatic injury in rats. Radiat Res. 1980 Jun;82(3):570–578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould M. N., Clifton K. H. Evidence for a unique in situ component of the repair of radiation damage. Radiat Res. 1979 Jan;77(1):149–155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jirtle R. L., Biles C., Michalopoulos G. Morphologic and histochemical analysis of hepatocytes transplanted into syngeneic hosts. Am J Pathol. 1980 Oct;101(1):115–126. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jirtle R. L., McLain J. R., Strom S. C., Michalopoulos G. Repair of radiation damage in noncycling parenchymal hepatocytes. Br J Radiol. 1982 Nov;55(659):847–851. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-55-659-847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jirtle R. L., Michalopoulos G., McLain J. R., Crowley J. Transplantation system for determining the clonogenic survival of parenchymal hepatocytes exposed to ionizing radiation. Cancer Res. 1981 Sep;41(9 Pt 1):3512–3518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalopoulos G., Cianciulli H. D., Novotny A. R., Kligerman A. D., Strom S. C., Jirtle R. L. Liver regeneration studies with rat hepatocytes in primary culture. Cancer Res. 1982 Nov;42(11):4673–4682. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulcahy R. T., Gould M. N., Clifton K. H. The survival of thyroid cells: in vivo irradiation and in situ repair. Radiat Res. 1980 Dec;84(3):523–528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheldon T. E., Michalowski A. S., Kirk J. The effect of irradiation on function in self-renewing normal tissues with differing proliferative organisation. Br J Radiol. 1982 Oct;55(658):759–766. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-55-658-759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuhas J. M., Spellman J. M., Culo F. The role of WR-2721 in radiotherapy and/or chemotherapy. Cancer Clin Trials. 1980 Fall;3(3):211–216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



