Abstract
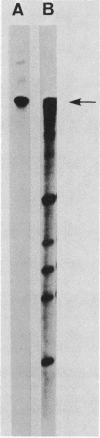
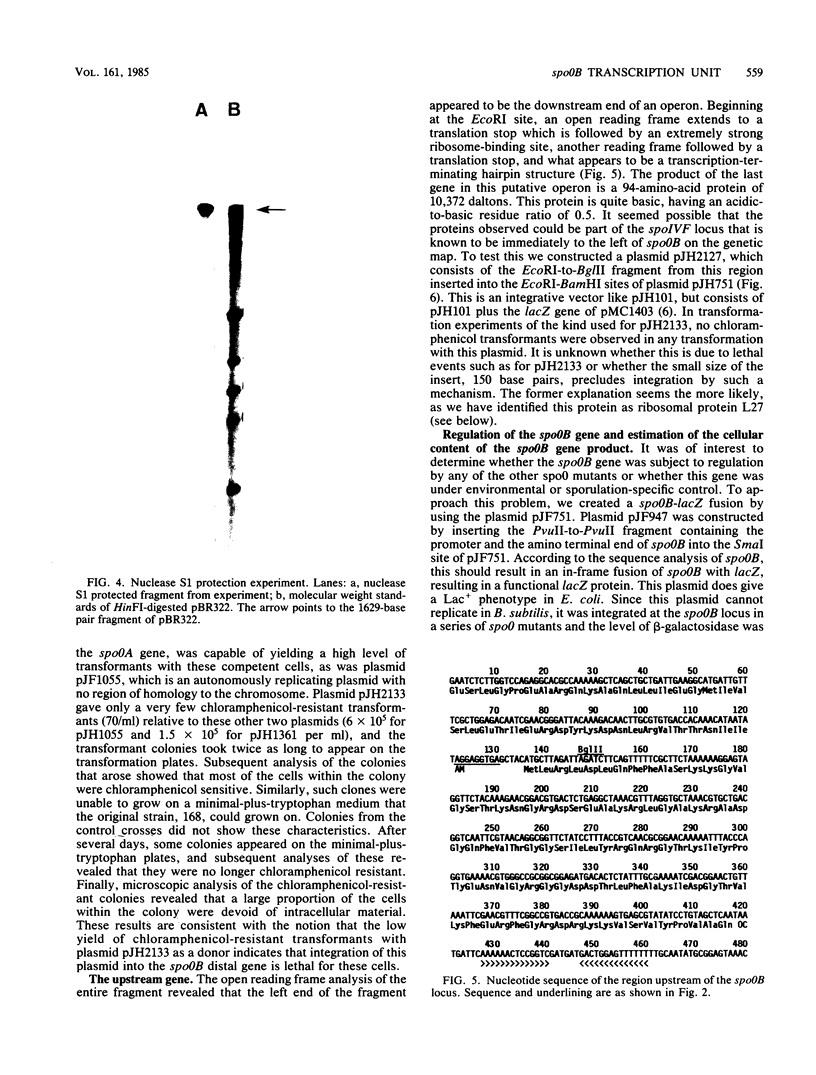
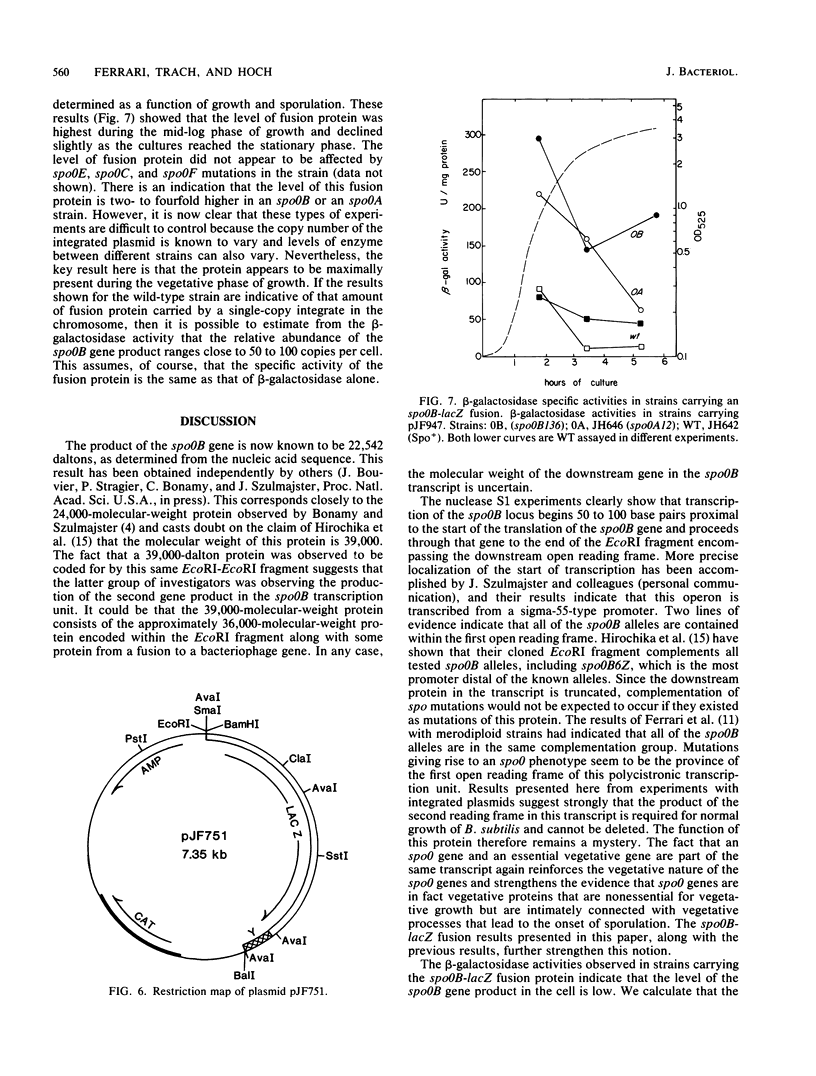
A 2.3-kilobase pair EcoRI fragment containing the spo0B locus has been sequenced. The spo0B locus was shown to code for a protein of 22,542 daltons. Promoter distal to the spo0B locus, an open reading frame was uncovered which was preceded by a strong ribosome-binding site. S1 nuclease protection experiments revealed that both the spo0B locus and this open reading frame were part of the same transcript. A portion of the middle of the open reading frame was cloned in the integrative vector pJH101. Transformation of this plasmid into Bacillus subtilis 168 was only rarely successful, and those few colonies that arose consisted of cells that had lost the plasmid. The results suggested that the product of this open reading frame is essential for the growth of the bacterium. The regulation of the spo0B locus was studied by using translational spo0B-lacZ fusions in an integrative vector. These studies revealed that the spo0B locus was maximally expressed during vegetative growth. It was estimated that 50 to 100 copies of the protein are present during this period. Sequence analysis of the region upstream from the spo0B locus revealed another operon that contained a gene coding for a protein homologous to ribosomal protein L27 of Escherichia coli.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anagnostopoulos C., Spizizen J. REQUIREMENTS FOR TRANSFORMATION IN BACILLUS SUBTILIS. J Bacteriol. 1961 May;81(5):741–746. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.5.741-746.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonamy C., Szulmajster J. Cloning and expression of Bacillus subtilis spore genes. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;188(2):202–210. doi: 10.1007/BF00332676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brehm S. P., Staal S. P., Hoch J. A. Phenotypes of pleiotropic-negative sporulation mutants of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1973 Sep;115(3):1063–1070. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.3.1063-1070.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadaban M. J., Chou J., Cohen S. N. In vitro gene fusions that join an enzymatically active beta-galactosidase segment to amino-terminal fragments of exogenous proteins: Escherichia coli plasmid vectors for the detection and cloning of translational initiation signals. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):971–980. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.971-980.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen R., Mende L., Arfsten U. The primary structure of protein L27 from the peptidyl-tRNA binding site of Escherichia coli ribosomes. FEBS Lett. 1975 Nov 1;59(1):96–99. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80349-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dabbs E. R. A pair of Bacillus subtilis ribosomal protein genes mapping outside the principal ribosomal protein cluster. J Bacteriol. 1983 Nov;156(2):966–969. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.2.966-969.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dagert M., Ehrlich S. D. Prolonged incubation in calcium chloride improves the competence of Escherichia coli cells. Gene. 1979 May;6(1):23–28. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90082-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari E., Henner D. J., Hoch J. A. Isolation of Bacillus subtilis genes from a charon 4A library. J Bacteriol. 1981 Apr;146(1):430–432. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.1.430-432.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari F. A., Lang D., Ferrari E., Hoch J. A. Molecular cloning of the spo0B sporulation locus in bacteriophage lambda. J Bacteriol. 1982 Nov;152(2):809–814. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.2.809-814.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari F. A., Nguyen A., Lang D., Hoch J. A. Construction and properties of an integrable plasmid for Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jun;154(3):1513–1515. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.3.1513-1515.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman M. Z., Chamberlin M. J. Developmental and genetic regulation of Bacillus subtilis genes transcribed by sigma 28-RNA polymerase. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):285–293. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90231-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heiland I., Wittmann-Liebold B. Amino acid sequence of the ribosomal protein L21 of Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1979 Oct 16;18(21):4605–4612. doi: 10.1021/bi00588a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirochika H., Kobayashi Y., Kawamura F., Saito H. Cloning of sporulation gene spoOB of Bacillus subtilis and its genetic and biochemical analysis. J Bacteriol. 1981 May;146(2):494–505. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.2.494-505.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoch J. A. Genetics of bacterial sporulation. Adv Genet. 1976;18:69–98. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2660(08)60437-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoch J. A., Trach K., Kawamura F., Saito H. Identification of the transcriptional suppressor sof-1 as an alteration in the spo0A protein. J Bacteriol. 1985 Feb;161(2):552–555. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.2.552-555.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran C. P., Jr, Lang N., Banner C. D., Haldenwang W. G., Losick R. Promoter for a developmentally regulated gene in Bacillus subtilis. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):783–791. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90186-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ollington J. F., Haldenwang W. G., Huynh T. V., Losick R. Developmentally regulated transcription in a cloned segment of the Bacillus subtilis chromosome. J Bacteriol. 1981 Aug;147(2):432–442. doi: 10.1128/jb.147.2.432-442.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramakrishna N., Dubnau E., Smith I. The complete DNA sequence and regulatory regions of the Bacillus licheniformis spoOH gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Feb 24;12(4):1779–1790. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.4.1779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer P., Millet J., Aubert J. P. Catabolic repression of bacterial sporulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Sep;54(3):704–711. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.3.704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimotsu H., Kawamura F., Kobayashi Y., Saito H. Early sporulation gene spo0F: nucleotide sequence and analysis of gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):658–662. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]