Abstract
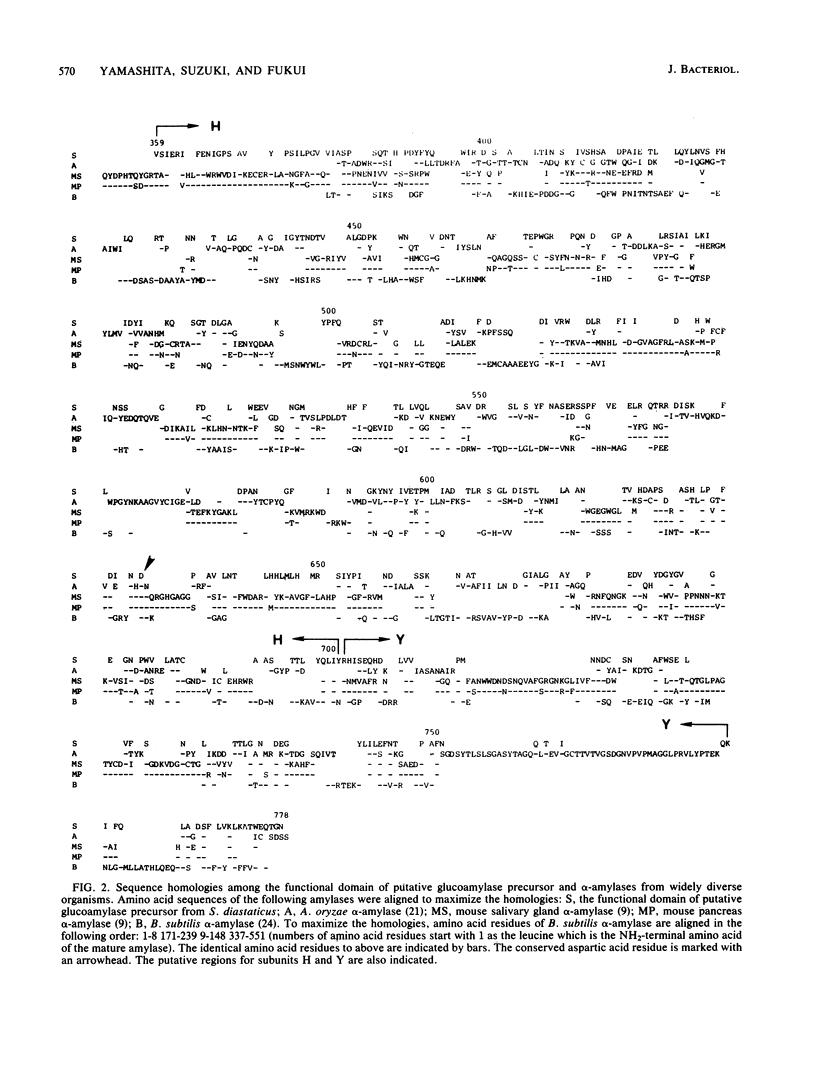
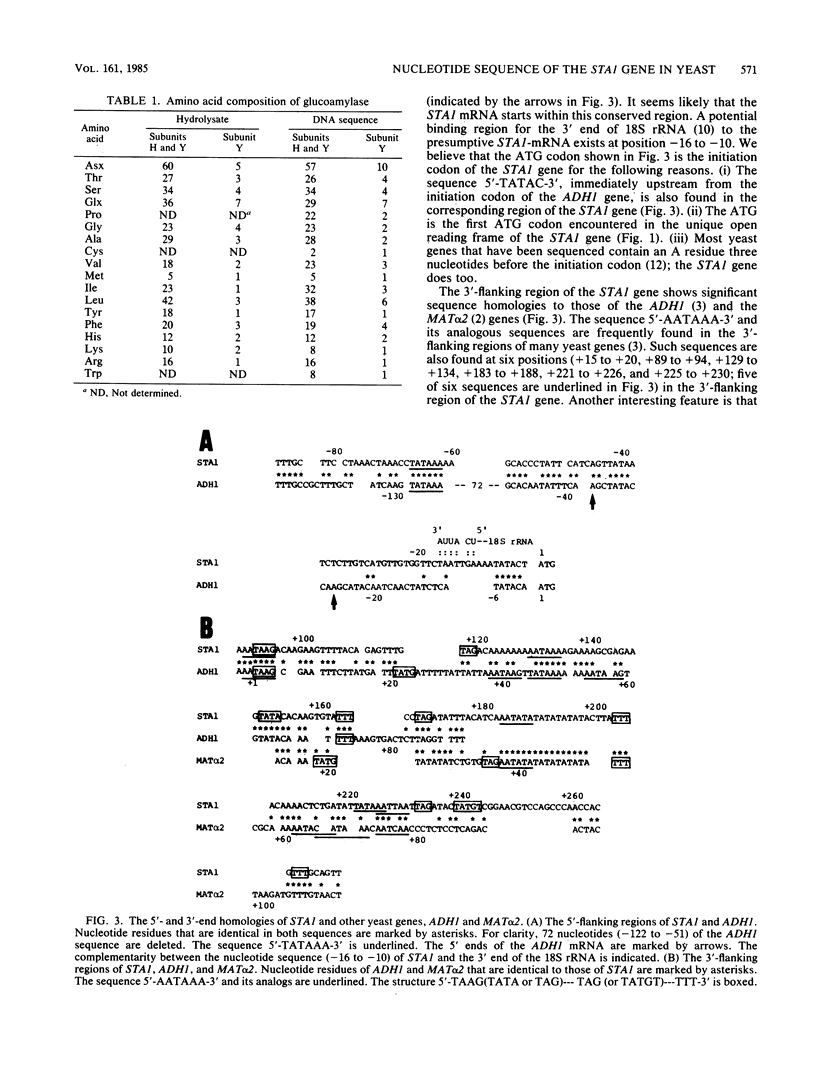
The complete nucleotide sequence of the extracellular glucoamylase gene STA1 from the yeast Saccharomyces diastaticus has been determined. A single open reading frame codes for a 778-amino-acid protein which contains 13 potential N-glycosylation sites. In the 5'- and 3'-flanking regions of the gene, there are striking sequence homologies to the corresponding regions of ADH1 for alcohol dehydrogenase and MAT alpha 2 for mating type control in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The putative precursor begins with a hydrophobic segment that presumably acts as a signal sequence for secretion. The presumptive signal sequence showed a significant homology to that of Bacillus subtilis alpha-amylase precursor. The next segment, of ca. 320 amino acids, contains a threonine-rich tract in which direct repeat sequences of 35 amino acids exist, and is bordered by a pair of basic amino acid residues (Lys-Lys) which may be a proteolytic processing signal. The carboxy-terminal half of the precursor is a presumptive glucoamylase which contains several peptide segments showing a high degree of homology with alpha-amylases from widely diverse organisms including a procaryote (B. subtilis) and eucaryotes (Aspergillus oryzae and mouse). Analysis of both the nucleotide sequence of the STA1 gene and the amino acid composition of the purified glucoamylase suggested that the putative precursor is processed to yield subunits H and Y of mature enzyme by both trypsin-like and chymotrypsin-like cleavages.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arima K., Oshima T., Kubota I., Nakamura N., Mizunaga T., Toh-e A. The nucleotide sequence of the yeast PHO5 gene: a putative precursor of repressible acid phosphatase contains a signal peptide. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 25;11(6):1657–1672. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.6.1657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Astell C. R., Ahlstrom-Jonasson L., Smith M., Tatchell K., Nasmyth K. A., Hall B. D. The sequence of the DNAs coding for the mating-type loci of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):15–23. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90356-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennetzen J. L., Hall B. D. The primary structure of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene for alcohol dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):3018–3025. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bostian K. A., Elliott Q., Bussey H., Burn V., Smith A., Tipper D. J. Sequence of the preprotoxin dsRNA gene of type I killer yeast: multiple processing events produce a two-component toxin. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):741–751. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90354-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Empirical predictions of protein conformation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:251–276. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.001343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colonna W. J., Magee P. T. Glycogenolytic enzymes in sporulating yeast. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):844–853. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.844-853.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comb M., Seeburg P. H., Adelman J., Eiden L., Herbert E. Primary structure of the human Met- and Leu-enkephalin precursor and its mRNA. Nature. 1982 Feb 25;295(5851):663–666. doi: 10.1038/295663a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emr S. D., Silhavy T. J. Importance of secondary structure in the signal sequence for protein secretion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(15):4599–4603. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.15.4599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagenbüchle O., Bovey R., Young R. A. Tissue-specific expression of mouse-alpha-amylase genes: nucleotide sequence of isoenzyme mRNAs from pancreas and salivary gland. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):179–187. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90125-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagenbüchle O., Santer M., Steitz J. A., Mans R. J. Conservation of the primary structure at the 3' end of 18S rRNA from eucaryotic cells. Cell. 1978 Mar;13(3):551–563. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90328-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius D., Schekman R., Thorner J. Glycosylation and processing of prepro-alpha-factor through the yeast secretory pathway. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):309–318. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90224-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurjan J., Herskowitz I. Structure of a yeast pheromone gene (MF alpha): a putative alpha-factor precursor contains four tandem copies of mature alpha-factor. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):933–943. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90298-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langford C. J., Klinz F. J., Donath C., Gallwitz D. Point mutations identify the conserved, intron-contained TACTAAC box as an essential splicing signal sequence in yeast. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):645–653. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90344-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuura Y., Kusunoki M., Harada W., Tanaka N., Iga Y., Yasuoka N., Toda H., Narita K., Kakudo M. Molecular structure of taka-amylase A. I. Backbone chain folding at 3 A resolution. J Biochem. 1980 May;87(5):1555–1558. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakanishi S., Inoue A., Kita T., Nakamura M., Chang A. C., Cohen S. N., Numa S. Nucleotide sequence of cloned cDNA for bovine corticotropin-beta-lipotropin precursor. Nature. 1979 Mar 29;278(5703):423–427. doi: 10.1038/278423a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spicer E. K., Noble J. A. Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin. Nucleotide sequence of the A subunit gene. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 25;257(10):5716–5721. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern A. S., Jones B. N., Shively J. E., Stein S., Undenfriend S. Two adrenal opioid polypeptides: proposed intermediates in the processing of proenkephalin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1962–1966. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struck D. K., Lennarz W. J., Brew K. Primary structural requirements for the enzymatic formation of the N-glycosidic bond in glycoproteins. Studies with alpha-lactalbumin. J Biol Chem. 1978 Aug 25;253(16):5786–5794. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takkinen K., Pettersson R. F., Kalkkinen N., Palva I., Söderlund H., Käriäinen L. Amino acid sequence of alpha-amylase from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens deduced from the nucleotide sequence of the cloned gene. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 25;258(2):1007–1013. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlasuk G. P., Inouye S., Ito H., Itakura K., Inouye M. Effects of the complete removal of basic amino acid residues from the signal peptide on secretion of lipoprotein in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 10;258(11):7141–7148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita I., Maemura T., Hatano T., Fukui S. Polymorphic extracellular glucoamylase genes and their evolutionary origin in the yeast Saccharomyces diastaticus. J Bacteriol. 1985 Feb;161(2):574–582. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.2.574-582.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamazaki H., Ohmura K., Nakayama A., Takeichi Y., Otozai K., Yamasaki M., Tamura G., Yamane K. Alpha-amylase genes (amyR2 and amyE+) from an alpha-amylase-hyperproducing Bacillus subtilis strain: molecular cloning and nucleotide sequences. J Bacteriol. 1983 Oct;156(1):327–337. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.1.327-337.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaret K. S., Sherman F. DNA sequence required for efficient transcription termination in yeast. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):563–573. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90211-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



