Abstract
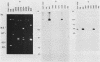
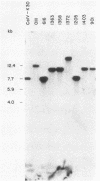
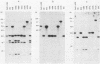
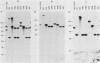
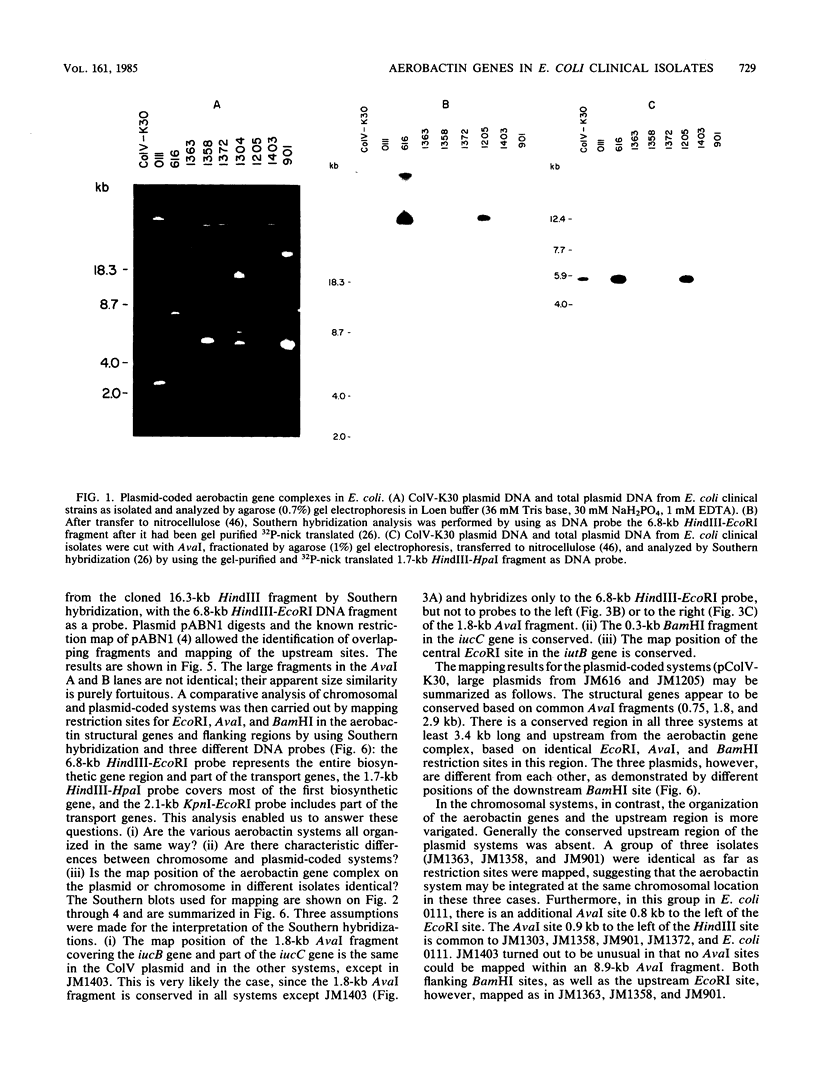
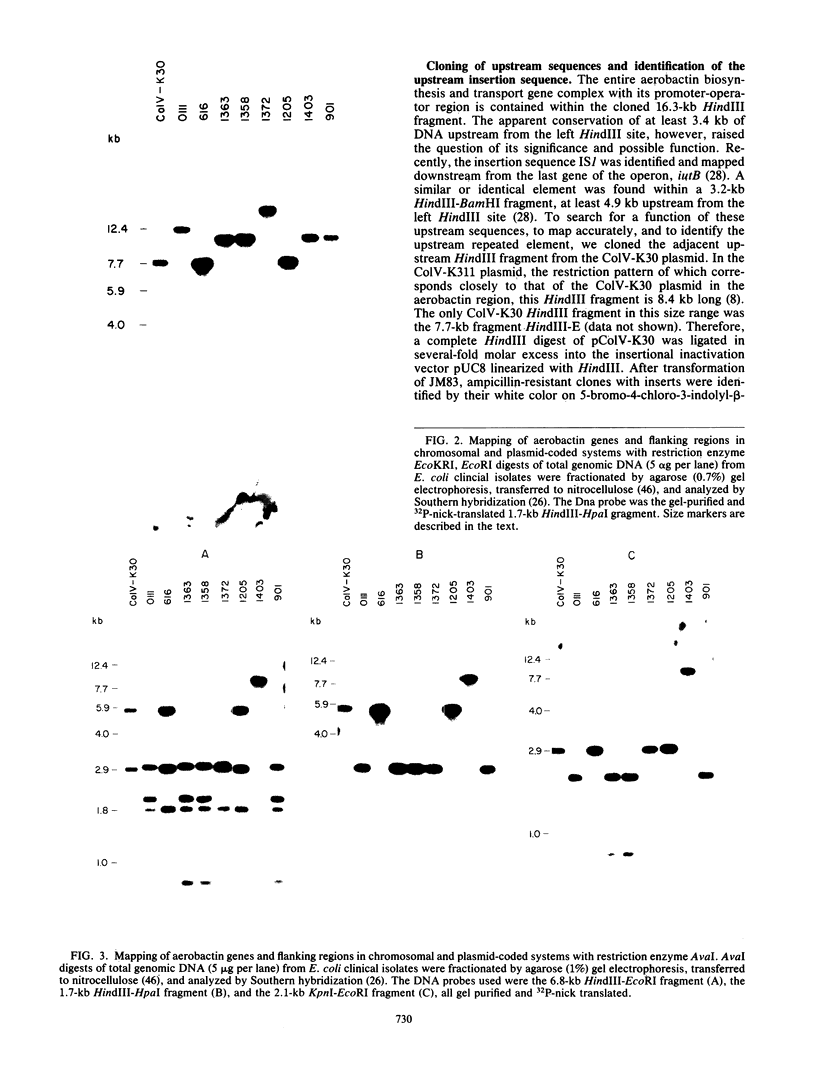
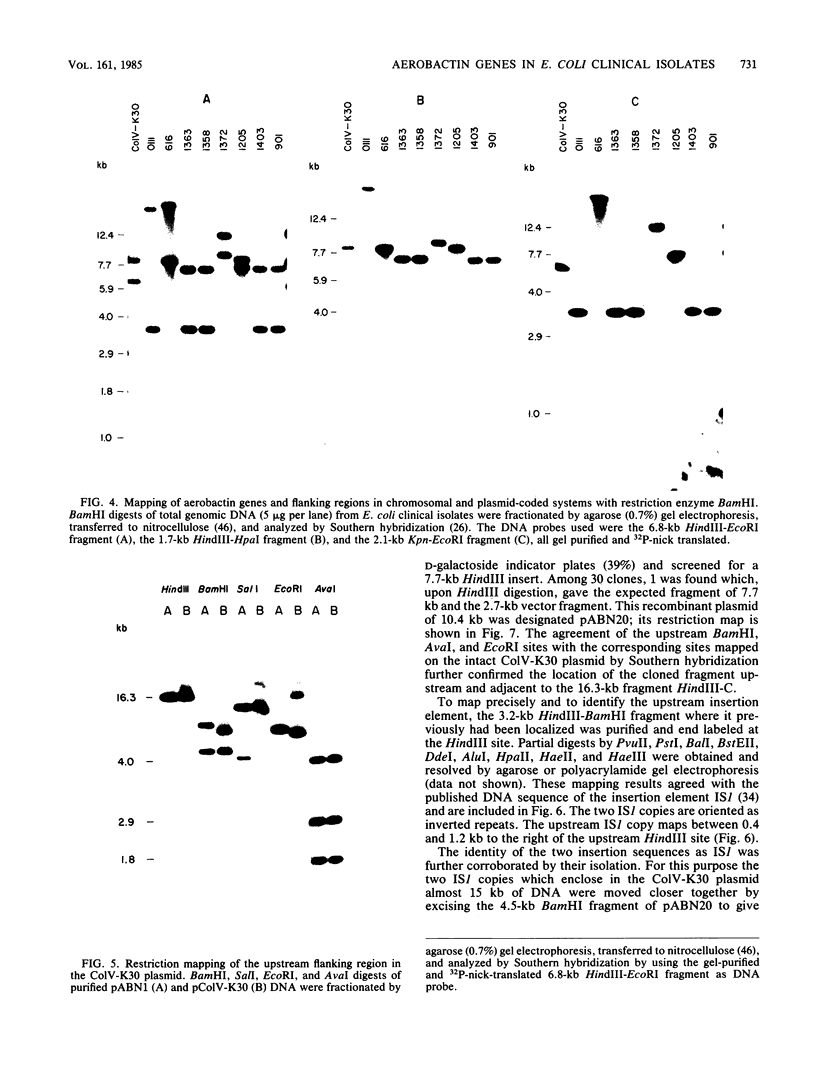
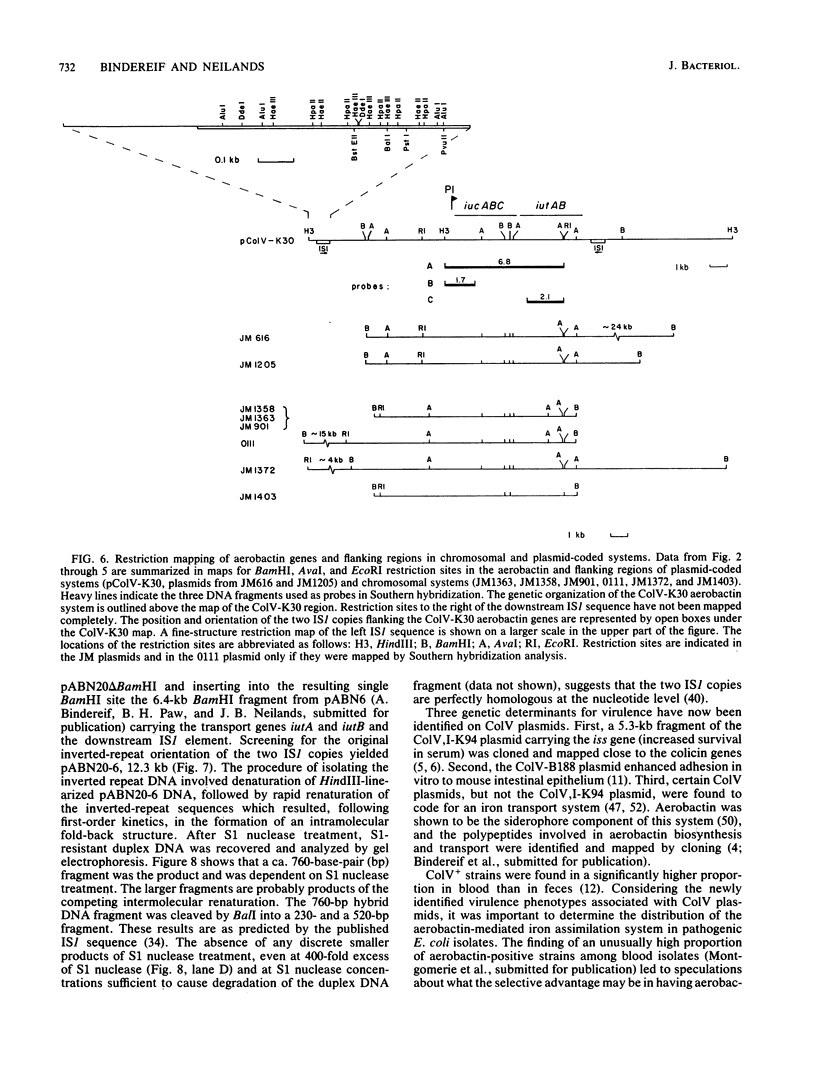
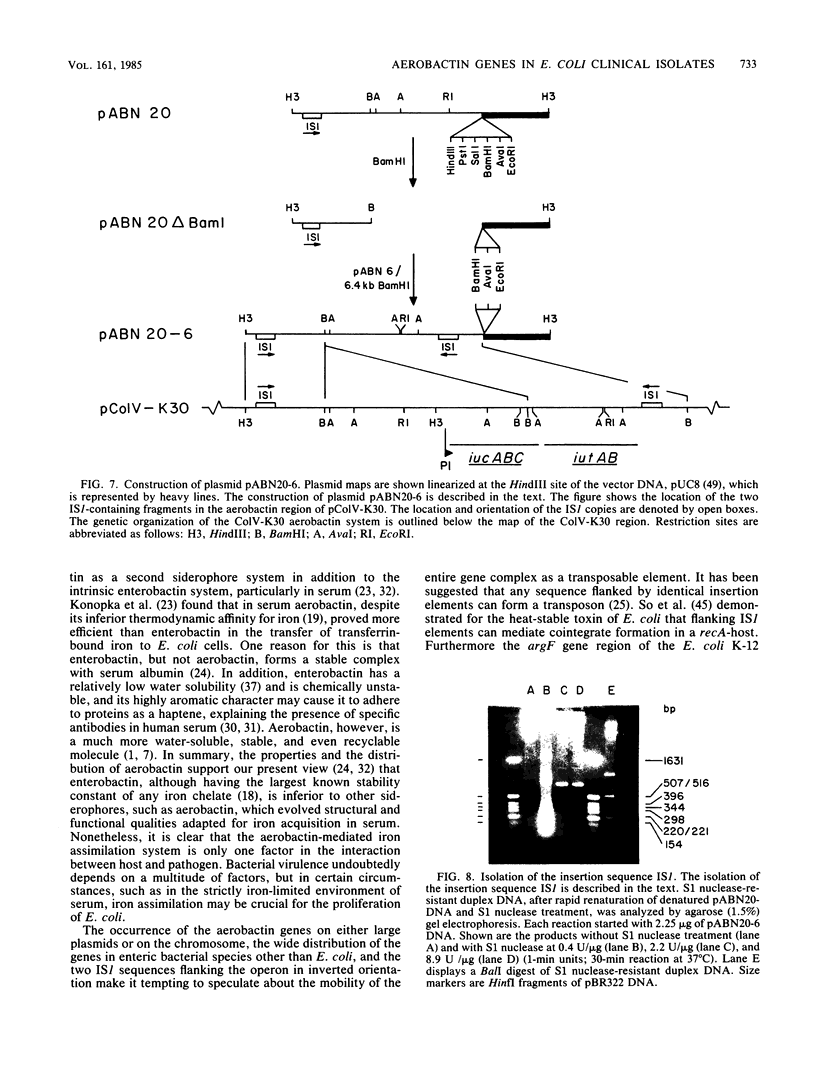
The location of the aerobactin gene complex on either the chromosome or plasmid was determined in eight aerobactin-positive clinical isolates of Escherichia coli by Southern hybridization analysis, using as probes the cloned aerobactin genes from the ColV-K30 plasmid. The aerobactin genes were in two cases detected on large plasmids, whereas in the other strains the aerobactin genes are most likely located on the chromosome. Restriction mapping revealed only slight variations in the structural genes and an at least 3.4-kilobase-long upstream region conserved in all three plasmid-coded systems. A 7.7-kilobase HindIII fragment upstream and adjacent to the 16.3-kilobase HindIII fragment carrying the complete aerobactin system was cloned from the ColV-K30 plasmid. Fine-structure restriction mapping identified the left insertion sequence in the upstream region as IS1, in inverted orientation to the IS1 element downstream from the aerobactin operon. The upstream and downstream sequences of IS1 appear to have perfect homology, as indicated by S1 nuclease resistance of a 760-base-pair DNA duplex formed by both IS1 elements.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arceneaux J. E., Davis W. B., Downer D. N., Haydon A. H., Byers B. R. Fate of labeled hydroxamates during iron transport from hydroxamate-ion chelates. J Bacteriol. 1973 Sep;115(3):919–927. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.3.919-927.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Better M., Lewis B., Corbin D., Ditta G., Helinski D. R. Structural relationships among Rhizobium meliloti symbiotic promoters. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):479–485. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90181-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bindereif A., Braun V., Hantke K. The cloacin receptor of ColV-bearing Escherichia coli is part of the Fe3+-aerobactin transport system. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jun;150(3):1472–1475. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.3.1472-1475.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bindereif A., Neilands J. B. Cloning of the aerobactin-mediated iron assimilation system of plasmid ColV. J Bacteriol. 1983 Feb;153(2):1111–1113. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.2.1111-1113.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binns M. M., Davies D. L., Hardy K. G. Cloned fragments of the plasmid ColV,I-K94 specifying virulence and serum resistance. Nature. 1979 Jun 28;279(5716):778–781. doi: 10.1038/279778a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binns M. M., Mayden J., Levine R. P. Further characterization of complement resistance conferred on Escherichia coli by the plasmid genes traT of R100 and iss of ColV,I-K94. Infect Immun. 1982 Feb;35(2):654–659. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.2.654-659.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun V., Gross R., Köster W., Zimmermann L. Plasmid and chromosomal mutants in the iron(III)-aerobactin transport system of Escherichia coli. Use of streptonigrin for selection. Mol Gen Genet. 1983;192(1-2):131–139. doi: 10.1007/BF00327658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullen J. J., Rogers H. J., Griffiths E. Role of iron in bacterial infection. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1978;80:1–35. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-66956-9_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clancy J., Savage D. C. Another Colicin V phenotype: in vitro adhesion of Escherichia coli to mouse intestinal epithelium. Infect Immun. 1981 Apr;32(1):343–352. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.1.343-352.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies D. L., Falkiner F. R., Hardy K. G. Colicin V production by clinical isolates of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):574–579. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.574-579.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dretzen G., Bellard M., Sassone-Corsi P., Chambon P. A reliable method for the recovery of DNA fragments from agarose and acrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):295–298. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90296-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elledge S. J., Walker G. C. Proteins required for ultraviolet light and chemical mutagenesis. Identification of the products of the umuC locus of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1983 Feb 25;164(2):175–192. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(83)90074-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elwell L. P., Shipley P. L. Plasmid-mediated factors associated with virulence of bacteria to animals. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1980;34:465–496. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.34.100180.002341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson F., Magrath D. I. The isolation and characterization of a hydroxamic acid (aerobactin) formed by Aerobacter aerogenes 62-I. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Nov 18;192(2):175–184. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(69)90353-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu M., Deonier R. C. Mapping of IS1 elements flanking the argF gene region on the Escherichia coli K-12 chromosome. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;181(2):222–229. doi: 10.1007/BF00268430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishiguro N., Sato G., Sasakawa C., Danbara H., Yoshikawa M. Identification of citrate utilization transposon Tn3411 from a naturally occurring citrate utilization plasmid. J Bacteriol. 1982 Mar;149(3):961–968. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.3.961-968.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konopka K., Bindereif A., Neilands J. B. Aerobactin-mediated utilization of transferrin iron. Biochemistry. 1982 Dec 7;21(25):6503–6508. doi: 10.1021/bi00268a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konopka K., Neilands J. B. Effect of serum albumin on siderophore-mediated utilization of transferrin iron. Biochemistry. 1984 May 8;23(10):2122–2127. doi: 10.1021/bi00305a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDougall S., Neilands J. B. Plasmid- and chromosome-coded aerobactin synthesis in enteric bacteria: insertion sequences flank operon in plasmid-mediated systems. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jul;159(1):300–305. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.1.300-305.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekalanos J. J. Duplication and amplification of toxin genes in Vibrio cholerae. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):253–263. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90228-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore D. G., Earhart C. F. Specific inhibition of Escherichia coli ferrienterochelin uptake by a normal human serum immunoglobulin. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):631–635. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.631-635.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore D. G., Yancey R. J., Lankford C. E., Earhart C. F. Bacteriostatic enterochelin-specific immunoglobulin from normal human serum. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):418–423. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.418-423.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohtsubo H., Ohtsubo E. Isolation of inverted repeat sequences, including IS1, IS2, and IS3, in Escherichia coli plasmids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2316–2320. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohtsubo H., Ohtsubo E. Nucleotide sequence of an insertion element, IS1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Feb;75(2):615–619. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.2.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne S. M., Niesel D. W., Peixotto S. S., Lawlor K. M. Expression of hydroxamate and phenolate siderophores by Shigella flexneri. J Bacteriol. 1983 Sep;155(3):949–955. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.3.949-955.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne S. M. Synthesis and utilization of siderophores by Shigella flexneri. J Bacteriol. 1980 Sep;143(3):1420–1424. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.3.1420-1424.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack J. R., Neilands J. B. Enterobactin, an iron transport compound from Salmonella typhimurium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Mar 12;38(5):989–992. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90819-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Moseley S. L., Falkow S. Characterization of plasmids and plasmid-associated determinants of Yersinia enterocolitica pathogenesis. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):775–782. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.775-782.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quackenbush R. L., Falkow S. Relationship between colicin V activity and virulence in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1979 May;24(2):562–564. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.2.562-564.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIMON E. H., TESSMAN I. THYMIDINE-REQUIRING MUTANTS OF PHAGE T4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Sep;50:526–532. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.3.526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenk T. E., Rhodes C., Rigby P. W., Berg P. Biochemical method for mapping mutational alterations in DNA with S1 nuclease: the location of deletions and temperature-sensitive mutations in simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):989–993. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. O., Birnstiel M. L. A simple method for DNA restriction site mapping. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Sep;3(9):2387–2398. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.9.2387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W. A search for transmissible pathogenic characters in invasive strains of Escherichia coli: the discovery of a plasmid-controlled toxin and a plasmid-controlled lethal character closely associated, or identical, with colicine V. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Jul;83(0):95–111. doi: 10.1099/00221287-83-1-95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Huggins M. B. Further observations on the association of the colicine V plasmid of Escherichia coli with pathogenicity and with survival in the alimentary tract. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 Feb;92(2):335–350. doi: 10.1099/00221287-92-2-335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- So M., Heffron F., McCarthy B. J. The E. coli gene encoding heat stable toxin is a bacterial transposon flanked by inverted repeats of IS1. Nature. 1979 Feb 8;277(5696):453–456. doi: 10.1038/277453a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart S. J., Greenwood K. T., Luke R. K. Hydroxamate-mediated transport of iron controlled by ColV plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jul;143(1):35–42. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.1.35-42.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart S. J., Greenwood K. T., Luke R. K. Iron-suppressible production of hydroxamate by Escherichia coli isolates. Infect Immun. 1982 Jun;36(3):870–875. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.3.870-875.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner P. J., Williams P. H., Bindereif A., Neilands J. B. ColV plasmid-specific aerobactin synthesis by invasive strains of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1981 Aug;33(2):540–545. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.2.540-545.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg E. D. Iron withholding: a defense against infection and neoplasia. Physiol Rev. 1984 Jan;64(1):65–102. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1984.64.1.65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams P. H. Novel iron uptake system specified by ColV plasmids: an important component in the virulence of invasive strains of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):925–932. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.925-932.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams P. H., Warner P. J. ColV plasmid-mediated, colicin V-independent iron uptake system of invasive strains of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1980 Aug;29(2):411–416. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.2.411-416.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Yokota T. Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin genes are flanked by repeated deoxyribonucleic acid sequences. J Bacteriol. 1981 Feb;145(2):850–860. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.2.850-860.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- York M. K., Stodolsky M. Characterization of P1argF derivatives from Escherichia coli K12 transduction. I. IS1 elements flank the argF gene segment. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;181(2):230–240. doi: 10.1007/BF00268431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]