Abstract
Bovine seminal ribonuclease (BSRNase) is an unusual member of the ribonuclease superfamily, because of its remarkable anti-tumour and immunosuppressive properties. We describe here the construction, expression, purification and characterization of a panel of six immunotoxins based upon this enzyme and show that we can increase its anti-tumour activity by over 2 x 10(4)-fold. This is achieved by improving tumour cell targeting using a single-chain Fv (scFv) directed against the oncofetal antigen placental alkaline phosphatase. As well as the simple scFv-BSRNase fusion protein, we have constructed five other derivatives with additional peptides designed to improve folding and intracellular trafficking and delivery. We find that the molecule most cytotoxic to antigen (PLAP)-positive cells in vitro is one that contains a C-terminal 'KDEL' endoplasmic reticulum retention signal and a peptide sequence derived from diphtheria toxin. All these molecules are produced in Escherichia coli (E. coli) as insoluble inclusion bodies and require extensive in vitro processing to recover antigen binding and ribonuclease activity. Despite incomplete ribonuclease activity and quaternary assembly, these molecules are promising reagents for specific chemotherapy of cancer and are potentially less harmful and immunogenic than current immunotoxins.
Full text
PDF

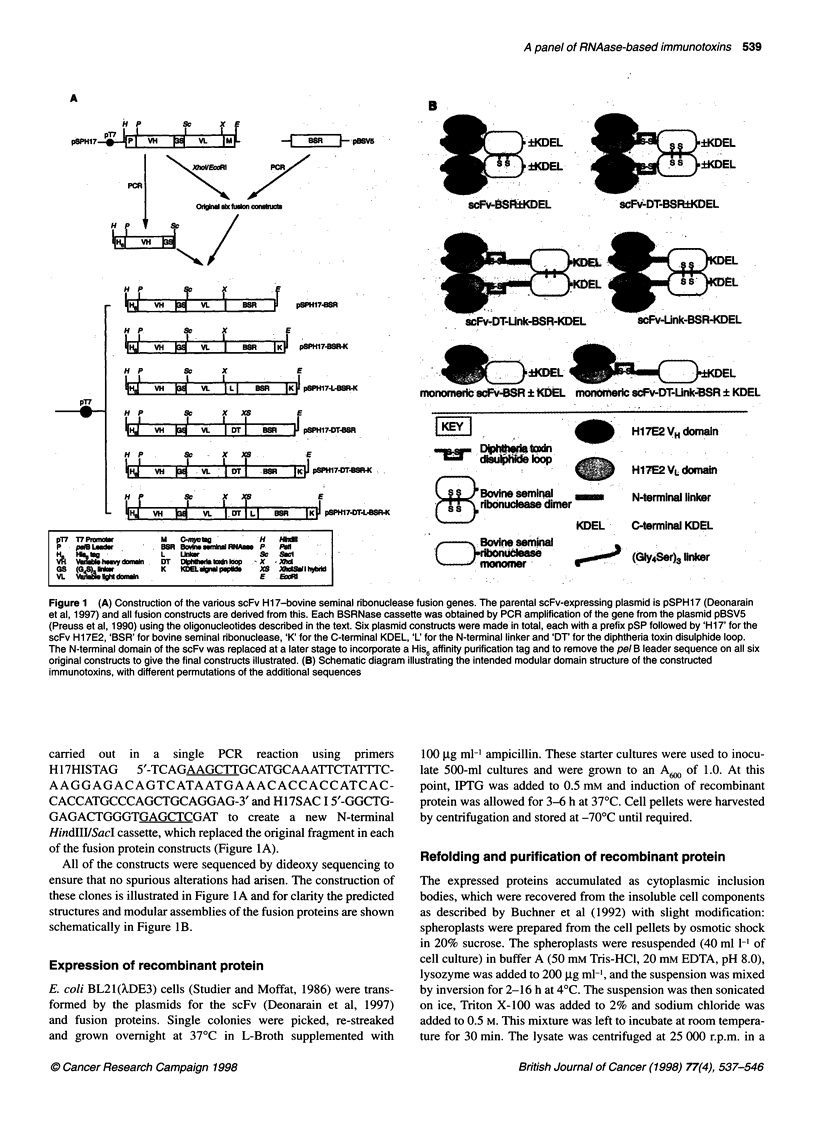

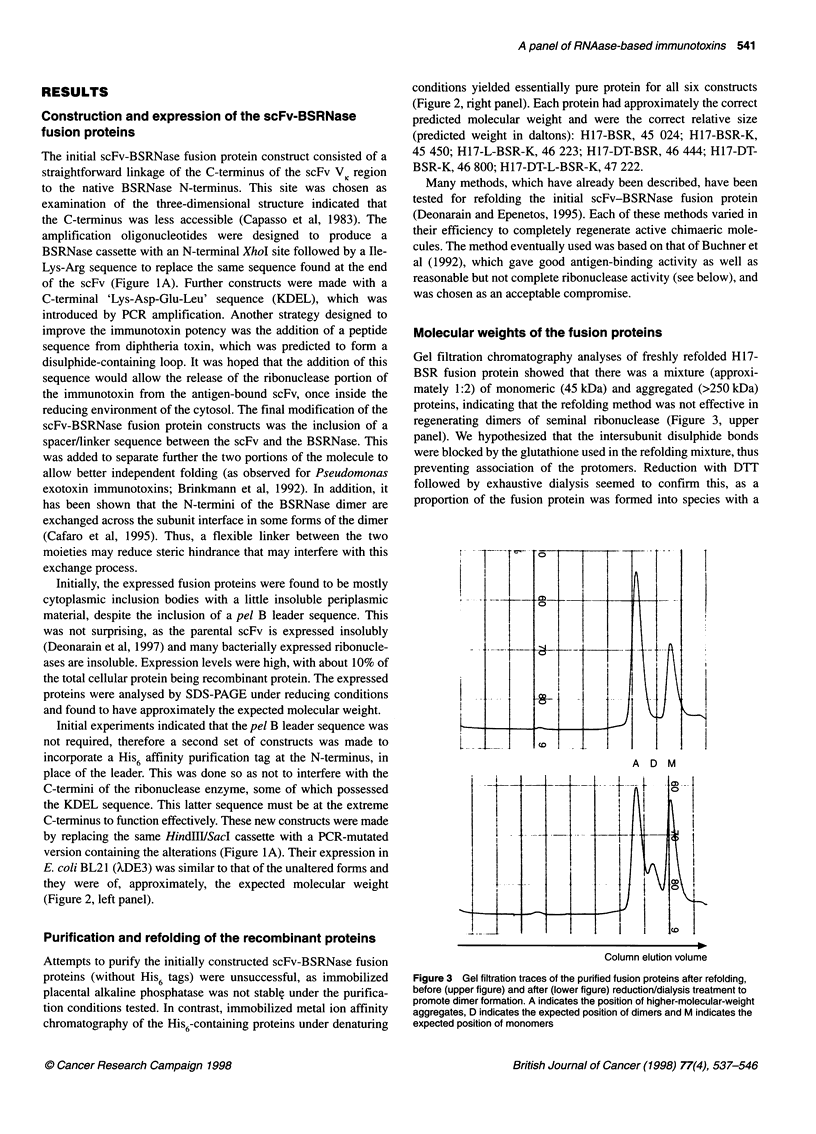
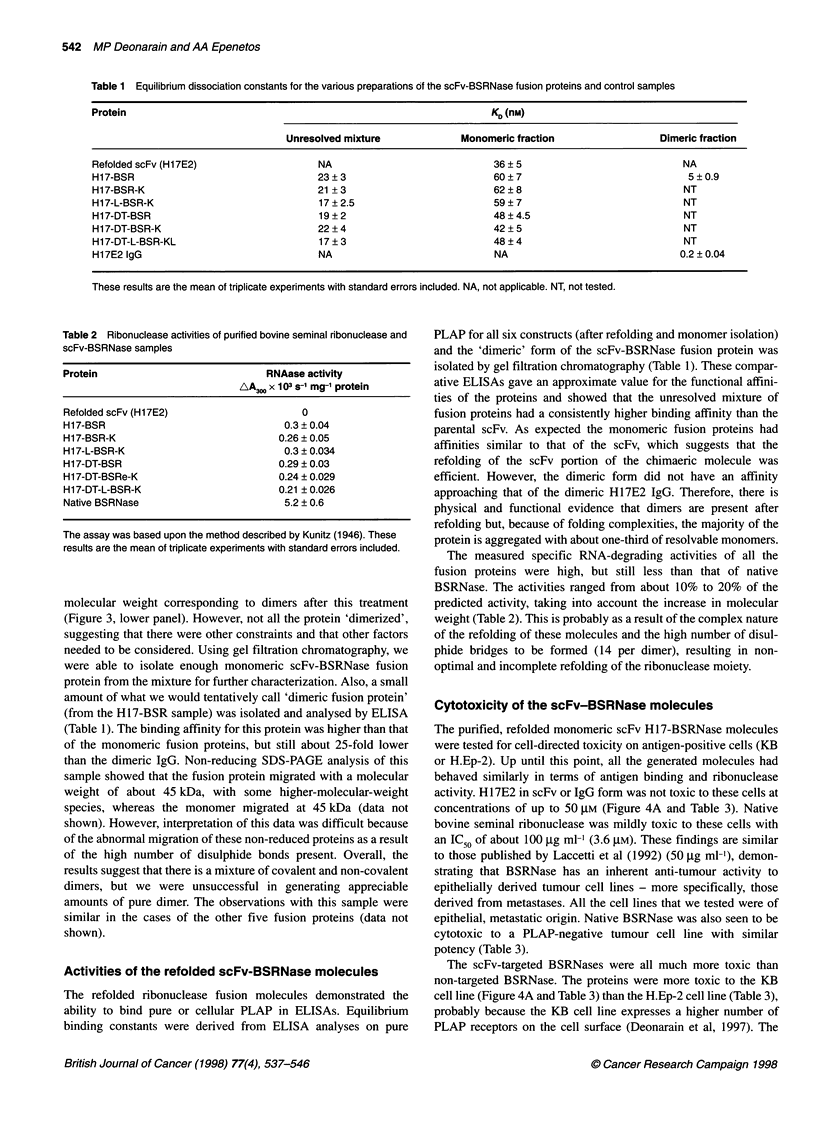
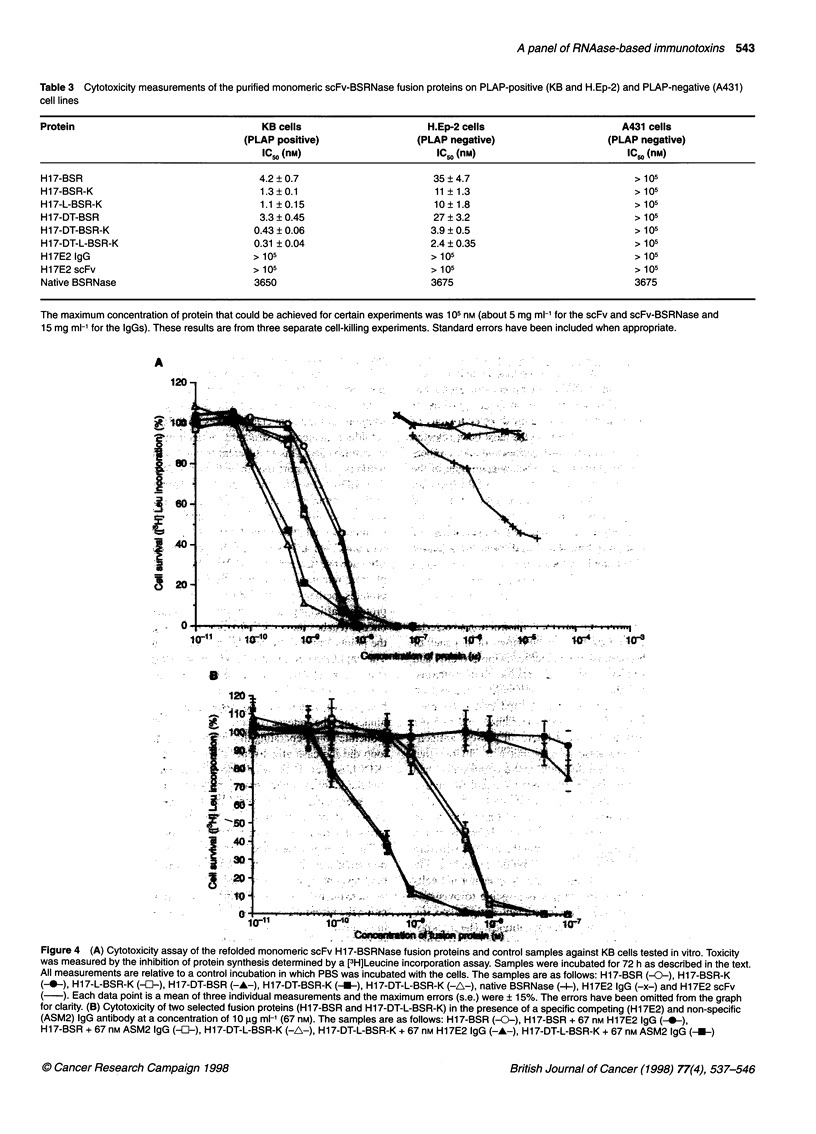



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adinolfi B. S., Cafaro V., D'Alessio G., Di Donato A. Full antitumor action of recombinant seminal ribonuclease depends on the removal of its N-terminal methionine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1995 Aug 15;213(2):525–532. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1995.2163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boleti E., Deonarain M. P., Spooner R. A., Smith A. J., Epenetos A. A., George A. J. Construction, expression and characterisation of a single chain anti-tumour antibody (scFv)-IL-2 fusion protein. Ann Oncol. 1995 Nov;6(9):945–947. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.annonc.a059364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinkmann U., Buchner J., Pastan I. Independent domain folding of Pseudomonas exotoxin and single-chain immunotoxins: influence of interdomain connections. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):3075–3079. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.3075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinkmann U., Pai L. H., FitzGerald D. J., Willingham M., Pastan I. B3(Fv)-PE38KDEL, a single-chain immunotoxin that causes complete regression of a human carcinoma in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8616–8620. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinkmann U., Reiter Y., Jung S. H., Lee B., Pastan I. A recombinant immunotoxin containing a disulfide-stabilized Fv fragment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 15;90(16):7538–7542. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.16.7538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchner J., Pastan I., Brinkmann U. A method for increasing the yield of properly folded recombinant fusion proteins: single-chain immunotoxins from renaturation of bacterial inclusion bodies. Anal Biochem. 1992 Sep;205(2):263–270. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(92)90433-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cafaro V., De Lorenzo C., Piccoli R., Bracale A., Mastronicola M. R., Di Donato A., D'Alessio G. The antitumor action of seminal ribonuclease and its quaternary conformations. FEBS Lett. 1995 Feb 6;359(1):31–34. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)01450-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhary V. K., Queen C., Junghans R. P., Waldmann T. A., FitzGerald D. J., Pastan I. A recombinant immunotoxin consisting of two antibody variable domains fused to Pseudomonas exotoxin. Nature. 1989 Jun 1;339(6223):394–397. doi: 10.1038/339394a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Alessio G., Di Donato A., Parente A., Piccoli R. Seminal RNase: a unique member of the ribonuclease superfamily. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Mar;16(3):104–106. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90042-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deonarain M. P., Epenetos A. A. Targeting enzymes for cancer therapy: old enzymes in new roles. Br J Cancer. 1994 Nov;70(5):786–794. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1994.400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deonarain M. P., Rowlinson-Busza G., George A. J., Epenetos A. A. Redesigned anti-human placental alkaline phosphatase single-chain Fv: soluble expression, characterization and in vivo tumour targeting. Protein Eng. 1997 Jan;10(1):89–98. doi: 10.1093/protein/10.1.89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EAGLE H. Propagation in a fluid medium of a human epidermoid carcinoma, strain KB. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1955 Jul;89(3):362–364. doi: 10.3181/00379727-89-21811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epenetos A. A., Carr D., Johnson P. M., Bodmer W. F., Lavender J. P. Antibody-guided radiolocalisation of tumours in patients with testicular or ovarian cancer using two radioiodinated monoclonal antibodies to placental alkaline phosphatase. Br J Radiol. 1986 Feb;59(698):117–125. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-59-698-117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epenetos A. A., Travers P., Gatter K. C., Oliver R. D., Mason D. Y., Bodmer W. F. An immunohistological study of testicular germ cell tumours using two different monoclonal antibodies against placental alkaline phosphatase. Br J Cancer. 1984 Jan;49(1):11–15. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1984.3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghetie V., Vitetta E. Immunotoxins in the therapy of cancer: from bench to clinic. Pharmacol Ther. 1994 Sep;63(3):209–234. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(94)90025-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glukhov B. N., Jerusalimsky A. P., Canter V. M., Salganik R. I. Ribonuclease treatment of tick-borne encephalitis. Arch Neurol. 1976 Sep;33(9):598–603. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1976.00500090004002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huston J. S., McCartney J., Tai M. S., Mottola-Hartshorn C., Jin D., Warren F., Keck P., Oppermann H. Medical applications of single-chain antibodies. Int Rev Immunol. 1993;10(2-3):195–217. doi: 10.3109/08830189309061696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iles R. K., Ind T. E., Chard T. Production of placental alkaline phosphatase (PLAP) and PLAP-like material by epithelial germ cell and non-germ cell tumours in vitro. Br J Cancer. 1994 Feb;69(2):274–278. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1994.51. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jost C. R., Kurucz I., Jacobus C. M., Titus J. A., George A. J., Segal D. M. Mammalian expression and secretion of functional single-chain Fv molecules. J Biol Chem. 1994 Oct 21;269(42):26267–26273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kihara A., Pastan I. Small chimeric toxins containing only transforming growth factor alpha and domain III of Pseudomonas exotoxin with good antitumor activity in mice. Cancer Res. 1994 Oct 1;54(19):5154–5159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J. S., Soucek J., Matousek J., Raines R. T. Catalytic activity of bovine seminal ribonuclease is essential for its immunosuppressive and other biological activities. Biochem J. 1995 Jun 1;308(Pt 2):547–550. doi: 10.1042/bj3080547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J. S., Soucek J., Matousek J., Raines R. T. Structural basis for the biological activities of bovine seminal ribonuclease. J Biol Chem. 1995 May 5;270(18):10525–10530. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.18.10525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laccetti P., Portella G., Mastronicola M. R., Russo A., Piccoli R., D'Alessio G., Vecchio G. In vivo and in vitro growth-inhibitory effect of bovine seminal ribonuclease on a system of rat thyroid epithelial transformed cells and tumors. Cancer Res. 1992 Sep 1;52(17):4582–4586. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laccetti P., Spalletti-Cernia D., Portella G., De Corato P., D'Alessio G., Vecchio G. Seminal ribonuclease inhibits tumor growth and reduces the metastatic potential of Lewis lung carcinoma. Cancer Res. 1994 Aug 15;54(16):4253–4256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancheño J. M., Gasset M., Oñaderra M., Gavilanes J. G., D'Alessio G. Bovine seminal ribonuclease destabilizes negatively charged membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Feb 28;199(1):119–124. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.1202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matousek J., Soucek J., Ríha J., Zankel T. R., Benner S. A. Immunosuppressive activity of angiogenin in comparison with bovine seminal ribonuclease and pancreatic ribonuclease. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol. 1995 Oct;112(2):235–241. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(95)00075-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murthy B. S., Sirdeshmukh R. Sensitivity of monomeric and dimeric forms of bovine seminal ribonuclease to human placental ribonuclease inhibitor. Biochem J. 1992 Jan 15;281(Pt 2):343–348. doi: 10.1042/bj2810343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newton D. L., Ilercil O., Laske D. W., Oldfield E., Rybak S. M., Youle R. J. Cytotoxic ribonuclease chimeras. Targeted tumoricidal activity in vitro and in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 25;267(27):19572–19578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newton D. L., Nicholls P. J., Rybak S. M., Youle R. J. Expression and characterization of recombinant human eosinophil-derived neurotoxin and eosinophil-derived neurotoxin-anti-transferrin receptor sFv. J Biol Chem. 1994 Oct 28;269(43):26739–26745. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare M., Brown A. N., Hussain K., Gebhardt A., Watson G., Roberts L. M., Vitetta E. S., Thorpe P. E., Lord J. M. Cytotoxicity of a recombinant ricin-A-chain fusion protein containing a proteolytically-cleavable spacer sequence. FEBS Lett. 1990 Oct 29;273(1-2):200–204. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81084-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parente A., D'Alessio G. Reacquisition of quaternary structure by fully reduced and denatured seminal ribonuclease. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Jun 3;149(2):381–387. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08936.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastan I., Chaudhary V., FitzGerald D. J. Recombinant toxins as novel therapeutic agents. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:331–354. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.001555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preuss K. D., Wagner S., Freudenstein J., Scheit K. H. Cloning of cDNA encoding the complete precursor for bovine seminal ribonuclease. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 25;18(4):1057–1057. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.4.1057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russo N., De Nigris M., Di Donato A., D'Alessio G. Expression of native dimers of bovine seminal ribonuclease in a eukaryotic cell system. FEBS Lett. 1993 Mar 8;318(3):242–244. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80520-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rybak S. M., Hoogenboom H. R., Meade H. M., Raus J. C., Schwartz D., Youle R. J. Humanization of immunotoxins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3165–3169. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rybak S. M., Pearson J. W., Fogler W. E., Volker K., Spence S. E., Newton D. L., Mikulski S. M., Ardelt W., Riggs C. W., Kung H. F. Enhancement of vincristine cytotoxicity in drug-resistant cells by simultaneous treatment with onconase, an antitumor ribonuclease. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1996 Jun 5;88(11):747–753. doi: 10.1093/jnci/88.11.747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rybak S. M., Saxena S. K., Ackerman E. J., Youle R. J. Cytotoxic potential of ribonuclease and ribonuclease hybrid proteins. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 5;266(31):21202–21207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage P., Rowlinson-Busza G., Verhoeyen M., Spooner R. A., So A., Windust J., Davis P. J., Epenetos A. A. Construction, characterisation and kinetics of a single chain antibody recognising the tumour associated antigen placental alkaline phosphatase. Br J Cancer. 1993 Oct;68(4):738–742. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1993.420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spooner R. A., Murray S., Rowlinson-Busza G., Deonarain M. P., Chu A., Epenetos A. A. Genetically engineered antibodies for diagnostic pathology. Hum Pathol. 1994 Jun;25(6):606–614. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(94)90228-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Moffatt B. A. Use of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase to direct selective high-level expression of cloned genes. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):113–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOOLAN H. W. Transplantable human neoplasms maintained in cortisone-treated laboratory animals: H.S. No. 1; H.Ep. No. 1; H.Ep. No. 2; H.Ep. No. 3; and H.Emb.Rh. No. 1. Cancer Res. 1954 Oct;14(9):660–666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travers P., Bodmer W. Preparation and characterization of monoclonal antibodies against placental alkaline phosphatase and other human trophoblast-associated determinants. Int J Cancer. 1984 May 15;33(5):633–641. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910330514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vescia S., Tramontano D., Augusti-Tocco G., D'Alessio G. In vitro studies on selective inhibition of tumor cell growth by seminal ribonuclease. Cancer Res. 1980 Oct;40(10):3740–3744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wales R., Roberts L. M., Lord J. M. Addition of an endoplasmic reticulum retrieval sequence to ricin A chain significantly increases its cytotoxicity to mammalian cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 15;268(32):23986–23990. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winter G., Griffiths A. D., Hawkins R. E., Hoogenboom H. R. Making antibodies by phage display technology. Annu Rev Immunol. 1994;12:433–455. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.12.040194.002245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youle R. J., Wu Y. N., Mikulski S. M., Shogen K., Hamilton R. S., Newton D., D'Alessio G., Gravell M. RNase inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus infection of H9 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jun 21;91(13):6012–6016. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.13.6012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



