Abstract
Enhanced sensitivity to the chromosome-damaging effects of ionizing radiation is a feature of many cancer-predisposing conditions. We previously showed that 42% of an unselected series of breast cancer patients and 9% of healthy control subjects showed elevated chromosomal radiosensitivity of lymphocytes irradiated in the G2 phase of the cell cycle. We suggested that, in addition to the highly penetrant genes BRCA1 and BRCA2, which confer a very high risk of breast cancer and are carried by about 5% of all breast cancer patients, there are also low-penetrance predisposing genes carried by a much higher proportion of breast cancer patients, a view supported by recent epidemiological studies. Ideally, testing for the presence of these putative genes should involve the use of simpler methods than the G2 assay, which requires metaphase analysis of chromosome damage. Here we report on the use of a simple, rapid micronucleus assay in G0 lymphocytes exposed to high dose rate (HDR) or low dose rate gamma-irradiation, with delayed mitogenic stimulation. Good assay reproducibility was obtained, particularly with the HDR protocol, which identified 31% (12 out of 39) of breast cancer patients compared with 5% (2 out of 42) of healthy controls as having elevated radiation sensitivity. In the long term, such cytogenetic assays may have the potential for selecting women for intensive screening for breast cancer.
Full text
PDF

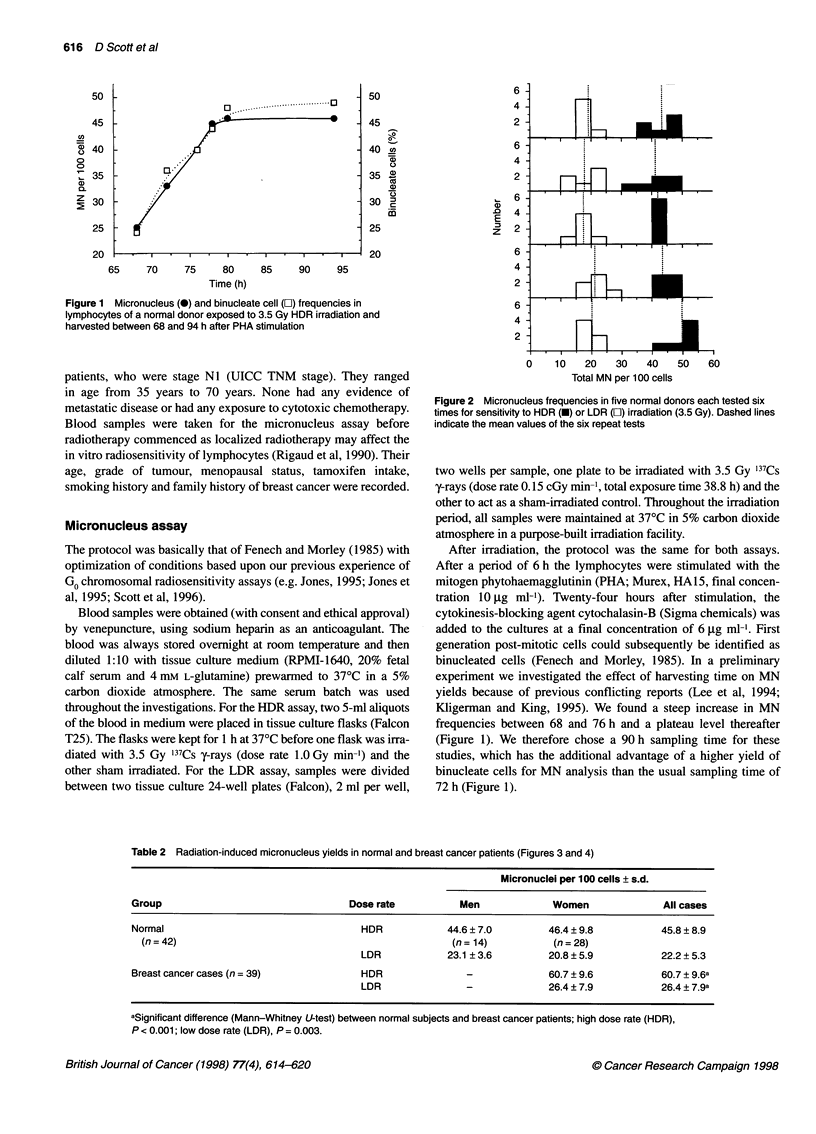
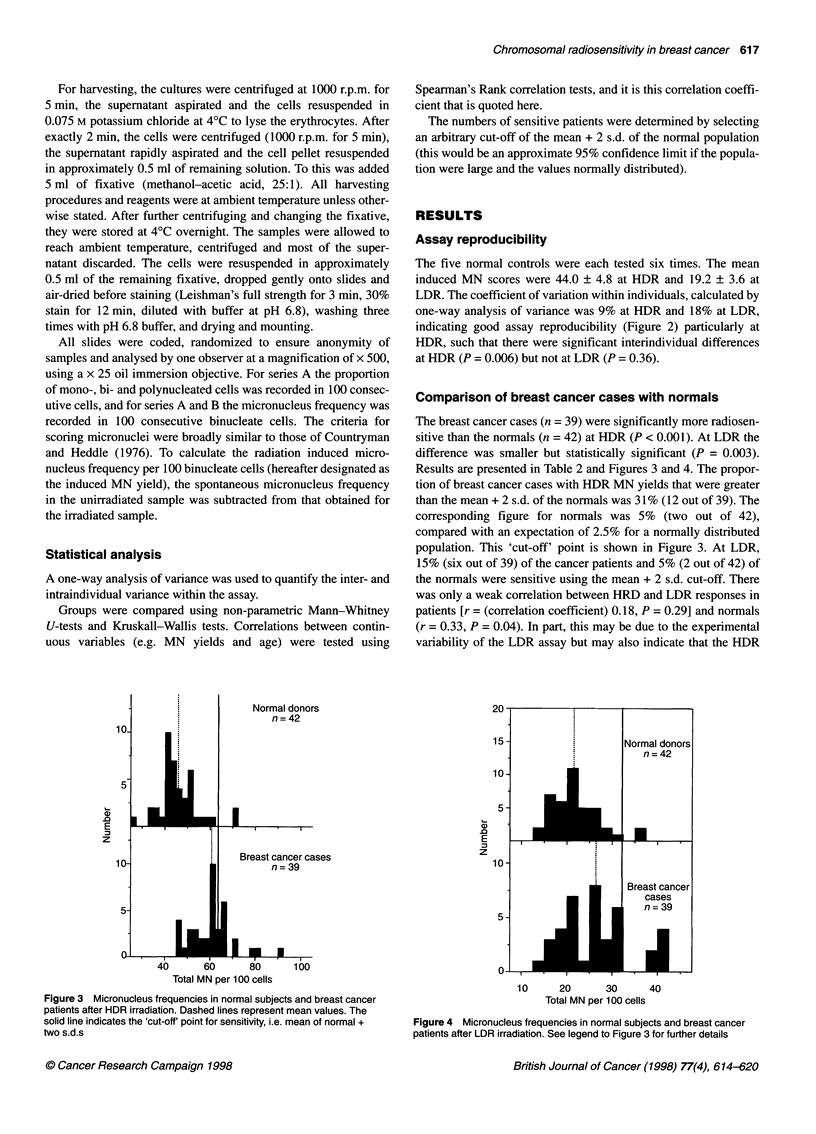
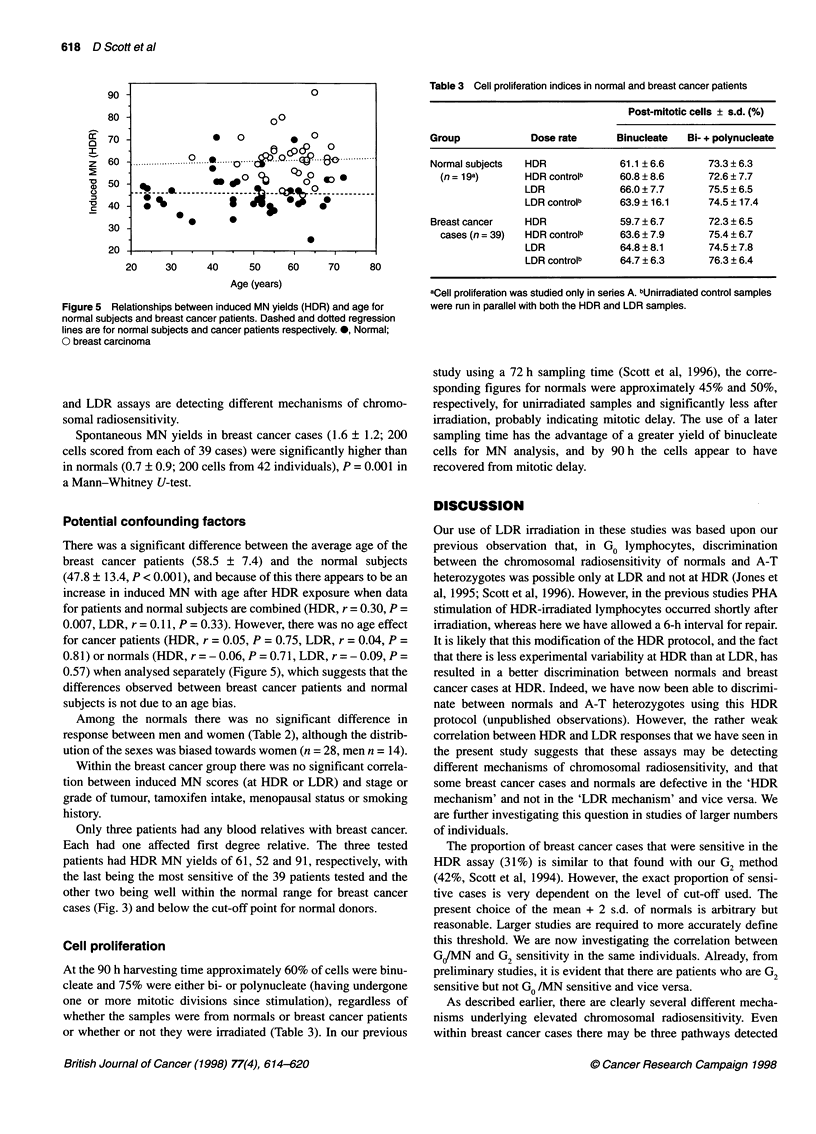


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Böcker W., Müller W. U., Streffer C. Image processing algorithms for the automated micronucleus assay in binucleated human lymphocytes. Cytometry. 1995 Apr 1;19(4):283–294. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990190402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen P. L., Sellers T. A., Rich S. S., Potter J. D., Folsom A. R. Segregation analysis of breast cancer in a population-based sample of postmenopausal probands: The Iowa Women's Health Study. Genet Epidemiol. 1995;12(4):401–415. doi: 10.1002/gepi.1370120408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Countryman P. I., Heddle J. A., Crawford E. The repair of X-ray induced chromosomal damage in trisomy 2-and normal diploid lymphocytes. Cancer Res. 1977 Jan;37(1):52–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Countryman P. I., Heddle J. A. The production of micronuclei from chromosome aberrations in irradiated cultures of human lymphocytes. Mutat Res. 1976 Dec;41(2-3):321–332. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(76)90105-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeBauche D. M., Pai G. S., Stanley W. S. Enhanced G2 chromatid radiosensitivity in dyskeratosis congenita fibroblasts. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Feb;46(2):350–357. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duckworth-Rysiecki G., Taylor A. M. Effects of ionizing radiation on cells from Fanconi's anemia patients. Cancer Res. 1985 Jan;45(1):416–420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabry L., Coton C. Study on the repair of the radioinduced lesions involved in the formation of chromosomal aberrations in G0 human lymphocytes after exposure to gamma-rays and fast neutrons. Mutat Res. 1985 May;149(3):475–483. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(85)90166-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Featherstone T., Taylor A. M., Harnden D. G. Studies on the radiosensitivity of cells from patients with basal cell naevus syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 1983 Jan;35(1):58–66. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons B., Scott D., Hungerford J. L., Cheung K. L., Harrison C., Attard-Montalto S., Evans M., Birch J. M., Kingston J. E. Retinoblastoma in association with the chromosome breakage syndromes Fanconi's anaemia and Bloom's syndrome: clinical and cytogenetic findings. Clin Genet. 1995 Jun;47(6):311–317. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1995.tb03971.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heddle J. A., Lue C. B., Saunders E. F., Benz R. D. Sensitivity to five mutagens in Fanconi's anemia as measured by the micronucleus method. Cancer Res. 1978 Sep;38(9):2983–2988. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaspers N. G., Gatti R. A., Baan C., Linssen P. C., Bootsma D. Genetic complementation analysis of ataxia telangiectasia and Nijmegen breakage syndrome: a survey of 50 patients. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1988;49(4):259–263. doi: 10.1159/000132673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones L. A., Scott D., Cowan R., Roberts S. A. Abnormal radiosensitivity of lymphocytes from breast cancer patients with excessive normal tissue damage after radiotherapy: chromosome aberrations after low dose-rate irradiation. Int J Radiat Biol. 1995 May;67(5):519–528. doi: 10.1080/09553009514550631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr B., Ashcroft G. S., Scott D., Horan M. A., Ferguson M. W., Donnai D. Rothmund-Thomson syndrome: two case reports show heterogeneous cutaneous abnormalities, an association with genetically programmed ageing changes, and increased chromosomal radiosensitivity. J Med Genet. 1996 Nov;33(11):928–934. doi: 10.1136/jmg.33.11.928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. Cancer-susceptibility genes. Gatekeepers and caretakers. Nature. 1997 Apr 24;386(6627):761–763. doi: 10.1038/386761a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kligerman A. D., King S. C. Frequency of micronucleated-binucleated lymphocytes is not significantly affected by the harvest time following G0 exposure to X-radiation. Int J Radiat Biol. 1995 Jul;68(1):19–23. doi: 10.1080/09553009514550871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight R. D., Parshad R., Price F. M., Tarone R. E., Sanford K. K. X-ray-induced chromatid damage in relation to DNA repair and cancer incidence in family members. Int J Cancer. 1993 Jun 19;54(4):589–593. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910540412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn E. M. Effects of X-irradiation in G1 and G2 on Bloom's Syndrome and normal chromosomes. Hum Genet. 1980;54(3):335–341. doi: 10.1007/BF00291579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavin M. F., Bennett I., Ramsay J., Gardiner R. A., Seymour G. J., Farrell A., Walsh M. Identification of a potentially radiosensitive subgroup among patients with breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1994 Nov 2;86(21):1627–1634. doi: 10.1093/jnci/86.21.1627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavin M. F., Le Poidevin P., Bates P. Enhanced levels of radiation-induced G2 phase delay in ataxia telangiectasia heterozygotes. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1992 Jun;60(2):183–187. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(92)90014-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. K., Wiley A. L., Jr, Esinhart J. D., Blackburn L. D. Radiation dose-dependent variations of micronuclei production in cytochalasin B-blocked human lymphocytes. Teratog Carcinog Mutagen. 1994;14(1):1–12. doi: 10.1002/tcm.1770140102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little J. B., Nagasawa H. Effect of confluent holding on potentially lethal damage repair, cell cycle progression, and chromosomal aberrations in human normal and ataxia-telangiectasia fibroblasts. Radiat Res. 1985 Jan;101(1):81–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morten J. E., Harnden D. G., Taylor A. M. Chromosome damage in G0 X-irradiated lymphocytes from patients with hereditary retinoblastoma. Cancer Res. 1981 Sep;41(9 Pt 1):3635–3638. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mozdarani H., Bryant P. E. Kinetics of chromatid aberrations in G2 ataxia-telangiectasia cells exposed to X-rays and ara A. Int J Radiat Biol. 1989 Jan;55(1):71–84. doi: 10.1080/09553008914550081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parshad R., Price F. M., Bohr V. A., Cowans K. H., Zujewski J. A., Sanford K. K. Deficient DNA repair capacity, a predisposing factor in breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 1996 Jul;74(1):1–5. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1996.307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parshad R., Price F. M., Pirollo K. F., Chang E. H., Sanford K. K. Cytogenetic response to G2-phase X irradiation in relation to DNA repair and radiosensitivity in a cancer-prone family with Li-Fraumeni syndrome. Radiat Res. 1993 Nov;136(2):236–240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parshad R., Sanford K. K., Jones G. M. Chromatid damage after G2 phase x-irradiation of cells from cancer-prone individuals implicates deficiency in DNA repair. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5612–5616. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston R. J. DNA repair and chromosome aberrations: the effect of cytosine arabinoside on the frequency of chromosome aberrations induced by radiation and chemicals. Teratog Carcinog Mutagen. 1980;1(2):147–159. doi: 10.1002/tcm.1770010204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price F. M., Parshad R., Tarone R. E., Sanford K. K. Radiation-induced chromatid aberrations in Cockayne syndrome and xeroderma pigmentosum group C fibroblasts in relation to cancer predisposition. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1991 Nov;57(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(91)90183-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigaud O., Guedeney G., Duranton I., Leroy A., Doloy M. T., Magdelenat H. Genotoxic effects of radiotherapy and chemotherapy on the circulating lymphocytes of breast cancer patients. I. Chromosome aberrations induced in vivo. Mutat Res. 1990 Sep;242(1):17–23. doi: 10.1016/0165-1218(90)90095-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanford K. K., Parshad R., Gantt R., Tarone R. E., Jones G. M., Price F. M. Factors affecting and significance of G2 chromatin radiosensitivity in predisposition to cancer. Int J Radiat Biol. 1989 Jun;55(6):963–981. doi: 10.1080/09553008914551001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanford K. K., Parshad R., Price F. M., Jones G. M., Tarone R. E., Eierman L., Hale P., Waldmann T. A. Enhanced chromatid damage in blood lymphocytes after G2 phase x irradiation, a marker of the ataxia-telangiectasia gene. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1990 Jun 20;82(12):1050–1054. doi: 10.1093/jnci/82.12.1050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanford K. K., Parshad R., Price F. M., Tarone R. E., Benedict W. F. Cytogenetic responses to G2 phase x-irradiation of cells from retinoblastoma patients. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1996 May;88(1):43–48. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(95)00279-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanford K. K., Tarone R. E., Parshad R., Tucker M. A., Greene M. H., Jones G. M. Hypersensitivity to G2 chromatid radiation damage in familial dysplastic naevus syndrome. Lancet. 1987 Nov 14;2(8568):1111–1116. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91546-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki M. S., Tonomura A., Matsubara S. Chromosome constitution and its bearing on the chromosomal radiosensitivity in man. Mutat Res. 1970 Dec;10(6):617–633. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(70)90089-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz J. L., Jordan R., Sedita B. A., Swenningson M. J., Banáth J. P., Olive P. L. Different sensitivity to cell killing and chromosome mutation induction by gamma rays in two human lymphoblastoid cell lines derived from a single donor: possible role of apoptosis. Mutagenesis. 1995 May;10(3):227–233. doi: 10.1093/mutage/10.3.227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott D., Hu Q., Roberts S. A. Dose-rate sparing for micronucleus induction in lymphocytes of controls and ataxia-telangiectasia heterozygotes exposed to 60Co gamma-irradiation in vitro. Int J Radiat Biol. 1996 Nov;70(5):521–527. doi: 10.1080/095530096144725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott D., Spreadborough A., Levine E., Roberts S. A. Genetic predisposition in breast cancer. Lancet. 1994 Nov 19;344(8934):1444–1444. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)90615-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taalman R. D., Hustinx T. W., Weemaes C. M., Seemanová E., Schmidt A., Passarge E., Scheres J. M. Further delineation of the Nijmegen breakage syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1989 Mar;32(3):425–431. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320320332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taalman R. D., Jaspers N. G., Scheres J. M., de Wit J., Hustinx T. W. Hypersensitivity to ionizing radiation, in vitro, in a new chromosomal breakage disorder, the Nijmegen Breakage Syndrome. Mutat Res. 1983 Feb;112(1):23–32. doi: 10.1016/0167-8817(83)90021-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeshita T., Higurashi M., Ariizumi-Shibusawa C., Shimizu K., Iijima S., Yamagata Z., Asaka A., Morimoto K., Ishibashi Y., Otsuka F. Elevated chromosome aberration frequency after X-ray exposure of cultured fibroblasts derived from patients with porokeratosis. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1994 Apr;73(2):161–164. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(94)90202-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor A. M., Metcalfe J. A., Oxford J. M., Harnden D. G. Is chromatid-type damage in ataxia telangiectasia after irradiation at G0 a consequence of defective repair? Nature. 1976 Apr 1;260(5550):441–443. doi: 10.1038/260441a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teare M. D., Wallace S. A., Harris M., Howell A., Birch J. M. Cancer experience in the relatives of an unselected series of breast cancer patients. Br J Cancer. 1994 Jul;70(1):102–111. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1994.257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verhaegen F., Vral A., Seuntjens J., Schipper N. W., de Ridder L., Thierens H. Scoring of radiation-induced micronuclei in cytokinesis-blocked human lymphocytes by automated image analysis. Cytometry. 1994 Oct 1;17(2):119–127. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990170203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vorechovský I., Scott D., Haeney M. R., Webster D. A. Chromosomal radiosensitivity in common variable immune deficiency. Mutat Res. 1993 Dec;290(2):255–264. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(93)90166-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waghray M., al-Sedairy S., Ozand P. T., Hannan M. A. Cytogenetic characterization of ataxia telangiectasia (AT) heterozygotes using lymphoblastoid cell lines and chronic gamma-irradiation. Hum Genet. 1990 May;84(6):532–534. doi: 10.1007/BF00210804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L., Cui Y., Lord B. I., Roberts S. A., Potten C. S., Hendry J. H., Scott D. Gamma-ray-induced cell killing and chromosome abnormalities in the bone marrow of p53-deficient mice. Radiat Res. 1996 Sep;146(3):259–266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward J. F. The complexity of DNA damage: relevance to biological consequences. Int J Radiat Biol. 1994 Nov;66(5):427–432. doi: 10.1080/09553009414551401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe R., Ishibashi Y., Otsuka F. Chromosomal instability and cellular hypersensitivity to X-radiation of cultured fibroblasts derived from porokeratosis patients' skin. Mutat Res. 1990 Jun;230(2):273–278. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(90)90065-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams K. J., Boyle J. M., Birch J. M., Norton J. D., Scott D. Cell cycle arrest defect in Li-Fraumeni Syndrome: a mechanism of cancer predisposition? Oncogene. 1997 Jan 23;14(3):277–282. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1200838. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Zein R., Shaw P., Tyring S. K., Au W. W. Chromosomal radiosensitivity of lymphocytes from skin cancer-prone patients. Mutat Res. 1995 Oct;335(2):143–149. doi: 10.1016/0165-1161(95)90050-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


