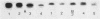Abstract
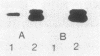
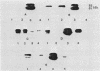
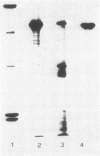
Exoprotease of Serratia marcescens ATCC 25419 is exceptional among members of the family Enterobacteriaceae in that it is secreted in large amounts by viable cells into the culture medium. Labeling of cells with radioactive amino acids revealed no intracellular protein that could be precipitated with antibodies raised against purified exoproteases. With substances known to interfere with the excretion of some proteins--tosyl-L-lysine chloromethyl ketone, phenethyl alcohol, procaine, and sodium azide--and with rifampin, an intracellular form (apparent molecular weight, 52,000) larger than the major exoform (molecular weight, 51,000) was identified. Moreover, the 52,000-molecular-weight form was the main protein in immunoprecipitates of a cysteine-auxotrophic mutant starved for cysteine. Beside the major exoform, protease I, two additional exoproteases, termed II and III, appeared in the medium of stationary cultures. They were precipitated by antibodies against protease I, were identical in the Ouchterlony double-diffusion assay, and exhibited only a small difference, if any at all, in the peptide pattern after partial hydrolysis with protease V8 of Staphylococcus aureus. The amino- and carboxy-terminal amino acid sequences of protease I and II were determined and found to be identical, NH2-Ala-Ala-Thr-Gly-Gly-Tyr-Asp-Ala-Val-Asp and Phe-Ile-Val-COOH, respectively. The microheterogeneity of the isolated exoforms revealed by anion-exchange chromatography and sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis was also observed in samples pulse-labeled with radioactive amino acids. It remains to be determined whether the different protease forms are the result of processing (modification) reactions or whether they constitute isoenzymes encoded by very similar genes.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aiyappa P. S., Harris J. O. The extracellular metalloprotease of Serratia marcescens: I. Purification and characterization. Mol Cell Biochem. 1976 Nov 30;13(2):95–100. doi: 10.1007/BF01837059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun V., Schmitz G. Excretion of a protease by Serratia marcescens. Arch Microbiol. 1980 Jan;124(1):55–61. doi: 10.1007/BF00407028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bromke B. J., Hammel J. M. Regulation of extracellular protease formation by Serratia marcescens. Can J Microbiol. 1979 Jan;25(1):47–52. doi: 10.1139/m79-008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CASTANEDA-AGULLO M. Studies on the biosynthesis of extracellular proteases by bacteria. I. Serratia marcescens, synthetic and gelatin media. J Gen Physiol. 1956 Jan 20;39(3):369–375. doi: 10.1085/jgp.39.3.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decedue C. J., Broussard E. A., 2nd, Larson A. D., Braymer H. D. Purification and characterization of the extracellular proteinase of Serratia marcescens. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Aug 15;569(2):293–301. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(79)90065-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enequist H. G., Hirst T. R., Harayama S., Hardy S. J., Randall L. L. Energy is required for maturation of exported proteins in Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1981 May 15;116(2):227–233. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05323.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gayda R. C., Henderson G. W., Markovitz A. Neuroactive drugs inhibit trypsin and outer membrane protein processing in Escherichia coli K-12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 May;76(5):2138–2142. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.5.2138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRS C. H. The oxidation of ribonuclease with performic acid. J Biol Chem. 1956 Apr;219(2):611–621. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halegoua S., Inouye M. Translocation and assembly of outer membrance proteins of Escherichia coli. Selective accumulation of precursors and novel assembly intermediates caused by phenethyl alcohol. J Mol Biol. 1979 May 5;130(1):39–61. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90551-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirashima A., Childs G., Inouye M. Differential inhibitory effects of antibiotics on the biosynthesis of envelope proteins of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1973 Sep 15;79(2):373–389. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90012-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito K. Effects of a protease inhibitor on biosynthesis of Escherichia coli proteins. J Bacteriol. 1977 Dec;132(3):1021–1023. doi: 10.1128/jb.132.3.1021-1023.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izui K., Nielsen J. B., Caulfield M. P., Lampen J. O. Large exopenicillinase, initial extracellular form detected in cultures of Bacillus licheniformis. Biochemistry. 1980 Apr 29;19(9):1882–1886. doi: 10.1021/bi00550a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazdunski C., Baty D., Pagès J. M. Procaine, a local anesthetic interacting with the cell membrane, inhibits the processing of precursor forms of periplasmic proteins in Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1979 May 2;96(1):49–57. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13012.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loriia Zh K., Briukner B., Egorov N. S. O prirode istinnogo induktora sinteza vnekletochnoi proteazy Serratia marcescens. Mikrobiologiia. 1977 May-Jun;46(3):440–446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg B., Meijers J., Peters R., van der Hoek P., van Alphen L. Electrophoretic resolution of the "major outer membrane protein" of Escherichia coli K12 into four bands. FEBS Lett. 1975 Oct 15;58(1):254–258. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80272-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg B., Van Alphen L. Molecular architecture and functioning of the outer membrane of Escherichia coli and other gram-negative bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Mar 21;737(1):51–115. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(83)90014-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyerly D. M., Kreger A. S. Importance of serratia protease in the pathogenesis of experimental Serratia marcescens pneumonia. Infect Immun. 1983 Apr;40(1):113–119. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.1.113-119.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyerly D., Kreger A. Purification and characterization of a Serratia marcescens metalloprotease. Infect Immun. 1979 May;24(2):411–421. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.2.411-421.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaelis S., Beckwith J. Mechanism of incorporation of cell envelope proteins in Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1982;36:435–465. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.36.100182.002251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami M., Fukunaga K., Matsuhashi M., Ono M. Stimulative effect of proteins on protease formation by Serratia sp. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Nov 18;192(2):378–380. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(69)90385-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noel D., Nikaido K., Ames G. F. A single amino acid substitution in a histidine-transport protein drastically alters its mobility in sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Biochemistry. 1979 Sep 18;18(19):4159–4165. doi: 10.1021/bi00586a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver D. B., Beckwith J. E. coli mutant pleiotropically defective in the export of secreted proteins. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):765–772. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90184-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rydén A. C., von Hofsten B. Some properties of the extracellular proteinase and the cell-bound peptidase of Serratia. Acta Chem Scand. 1968;22(9):2803–2808. doi: 10.3891/acta.chem.scand.22-2803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnaitman C. A. Effect of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, Triton X-100, and lysozyme on the morphology and chemical composition of isolate cell walls of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1971 Oct;108(1):553–563. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.1.553-563.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silhavy T. J., Benson S. A., Emr S. D. Mechanisms of protein localization. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Sep;47(3):313–344. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.3.313-344.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons K., Sarvas M., Garoff H., Helenius A. Membrane-bound and secreted forms of penicillinase from Bacillus licheniformis. J Mol Biol. 1978 Dec 25;126(4):673–690. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90015-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udenfriend S., Stein S., Böhlen P., Dairman W., Leimgruber W., Weigele M. Fluorescamine: a reagent for assay of amino acids, peptides, proteins, and primary amines in the picomole range. Science. 1972 Nov 24;178(4063):871–872. doi: 10.1126/science.178.4063.871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner W., Vogel M., Goebel W. Transport of hemolysin across the outer membrane of Escherichia coli requires two functions. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):200–210. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.200-210.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler U., Heller K. B., Folle B. Pleiotropic consequences of mutations towards antibiotic-hypersensitivity in Serratia marcescens. Arch Microbiol. 1978 Mar;116(3):259–268. doi: 10.1007/BF00417849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young M. E., Carroad P. A. Dependence of extracellular chitinase activity of Serratia marcescens QMB1466 on continuous culture dilution rate. Can J Microbiol. 1981 Jan;27(1):142–144. doi: 10.1139/m81-022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]