Abstract
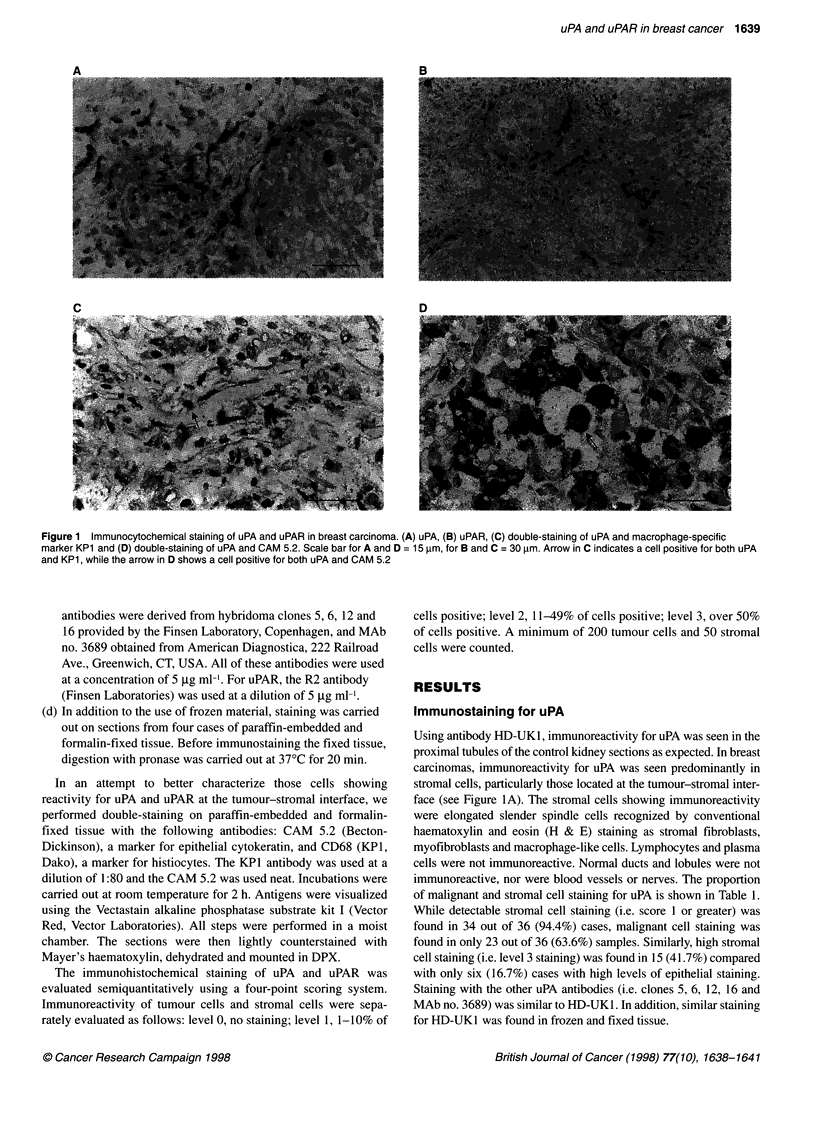
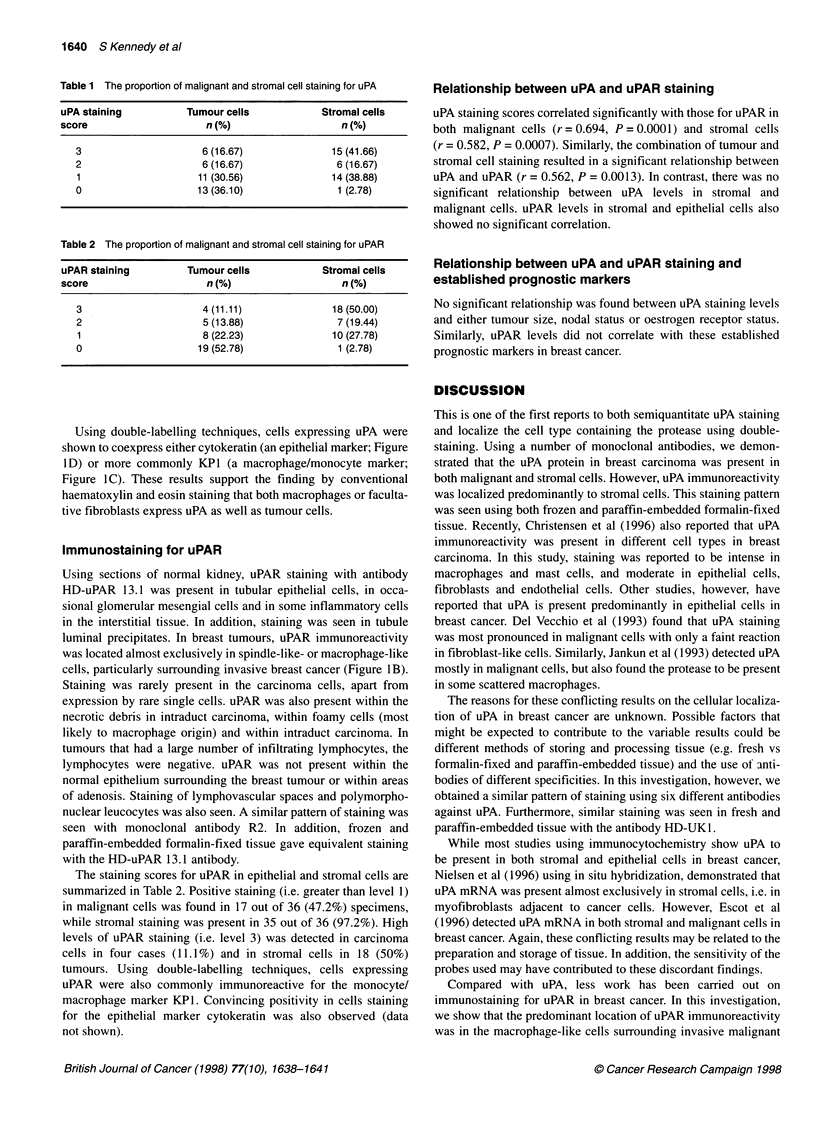
Urokinase plasminogen activator (uPA) is a serine protease involved in cancer invasion and metastasis. uPA acts in vivo by binding to a membrane receptor known as uPAR. In this study, uPA and uPAR levels were semiquantitated by immunocytochemistry in 36 primary breast carcinomas. Using monoclonal antibody HD-UK 1, uPA was detected both in stromal and in malignant cells. However, the predominant location was in the stromal cells. Using double-staining, cells containing uPA were also found to coexpress either cytokeratin (an epithelial cell marker) or more frequently KP1 (a macrophage/monocyte cell marker). With monoclonal antibody HD-uPAR 13.1, uPAR was localized principally to spindle- or macrophage-like stromal cells, especially when these cells surrounded invasive breast cancer. In contrast, uPAR was only rarely detected in cancer cells and was not detected in normal epithelia surrounding tumour or in areas of adenosis. uPA levels in both stromal and epithelial cells were significantly correlated with those for uPAR. We conclude that both uPA and its receptor are mostly present in stromal cells in invasive breast carcinomas. These results suggest that stromal cells collaborate with malignant cells to mediate metastasis.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andreasen P. A., Kjøller L., Christensen L., Duffy M. J. The urokinase-type plasminogen activator system in cancer metastasis: a review. Int J Cancer. 1997 Jul 3;72(1):1–22. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1097-0215(19970703)72:1<1::aid-ijc1>3.0.co;2-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bechtel M. J., Reinartz J., Rox J. M., Inndorf S., Schaefer B. M., Kramer M. D. Upregulation of cell-surface-associated plasminogen activation in cultured keratinocytes by interleukin-1 beta and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Exp Cell Res. 1996 Mar 15;223(2):395–404. doi: 10.1006/excr.1996.0094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi E., Cohen R. L., Thor A. T., Todd R. F., 3rd, Mizukami I. F., Lawrence D. A., Ljung B. M., Shuman M. A., Smith H. S. The urokinase receptor is expressed in invasive breast cancer but not in normal breast tissue. Cancer Res. 1994 Feb 15;54(4):861–866. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boros P., Miller C. M. Hepatocyte growth factor: a multifunctional cytokine. Lancet. 1995 Feb 4;345(8945):293–295. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(95)90279-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carriero M. V., Franco P., Del Vecchio S., Massa O., Botti G., D'Aiuto G., Stoppelli M. P., Salvatore M. Tissue distribution of soluble and receptor-bound urokinase in human breast cancer using a panel of monoclonal antibodies. Cancer Res. 1994 Oct 15;54(20):5445–5454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen L., Wiborg Simonsen A. C., Heegaard C. W., Moestrup S. K., Andersen J. A., Andreasen P. A. Immunohistochemical localization of urokinase-type plasminogen activator, type-1 plasminogen-activator inhibitor, urokinase receptor and alpha(2)-macroglobulin receptor in human breast carcinomas. Int J Cancer. 1996 May 16;66(4):441–452. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0215(19960516)66:4<441::AID-IJC6>3.0.CO;2-W. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Vecchio S., Stoppelli M. P., Carriero M. V., Fonti R., Massa O., Li P. Y., Botti G., Cerra M., D'Aiuto G., Esposito G. Human urokinase receptor concentration in malignant and benign breast tumors by in vitro quantitative autoradiography: comparison with urokinase levels. Cancer Res. 1993 Jul 1;53(13):3198–3206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duffy M. J. Proteases as prognostic markers in cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 1996 Apr;2(4):613–618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duffy M. J. The role of proteolytic enzymes in cancer invasion and metastasis. Clin Exp Metastasis. 1992 May;10(3):145–155. doi: 10.1007/BF00132746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duggan C., Maguire T., McDermott E., O'Higgins N., Fennelly J. J., Duffy M. J. Urokinase plasminogen activator and urokinase plasminogen activator receptor in breast cancer. Int J Cancer. 1995 May 29;61(5):597–600. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910610502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escot C., Zhao Y., Puech C., Rochefort H. Cellular localisation by in situ hybridisation of cathepsin D, stromelysin 3, and urokinase plasminogen activator RNAs in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1996;38(2):217–226. doi: 10.1007/BF01806676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grøndahl-Hansen J., Peters H. A., van Putten W. L., Look M. P., Pappot H., Rønne E., Dano K., Klijn J. G., Brünner N., Foekens J. A. Prognostic significance of the receptor for urokinase plasminogen activator in breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 1995 Oct;1(10):1079–1087. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankun J., Merrick H. W., Goldblatt P. J. Expression and localization of elements of the plasminogen activation system in benign breast disease and breast cancers. J Cell Biochem. 1993 Oct;53(2):135–144. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240530206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jänicke F., Schmitt M., Pache L., Ulm K., Harbeck N., Höfler H., Graeff H. Urokinase (uPA) and its inhibitor PAI-1 are strong and independent prognostic factors in node-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1993;24(3):195–208. doi: 10.1007/BF01833260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mars W. M., Zarnegar R., Michalopoulos G. K. Activation of hepatocyte growth factor by the plasminogen activators uPA and tPA. Am J Pathol. 1993 Sep;143(3):949–958. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen B. S., Sehested M., Timshel S., Pyke C., Danø K. Messenger RNA for urokinase plasminogen activator is expressed in myofibroblasts adjacent to cancer cells in human breast cancer. Lab Invest. 1996 Jan;74(1):168–177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyke C., Graem N., Ralfkiaer E., Rønne E., Høyer-Hansen G., Brünner N., Danø K. Receptor for urokinase is present in tumor-associated macrophages in ductal breast carcinoma. Cancer Res. 1993 Apr 15;53(8):1911–1915. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyke C., Kristensen P., Ralfkiaer E., Grøndahl-Hansen J., Eriksen J., Blasi F., Danø K. Urokinase-type plasminogen activator is expressed in stromal cells and its receptor in cancer cells at invasive foci in human colon adenocarcinomas. Am J Pathol. 1991 May;138(5):1059–1067. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schäfer B. M., Maier K., Eickhoff U., Todd R. F., Kramer M. D. Plasminogen activation in healing human wounds. Am J Pathol. 1994 Jun;144(6):1269–1280. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vries T. J., Quax P. H., Denijn M., Verrijp K. N., Verheijen J. H., Verspaget H. W., Weidle U. H., Ruiter D. J., van Muijen G. N. Plasminogen activators, their inhibitors, and urokinase receptor emerge in late stages of melanocytic tumor progression. Am J Pathol. 1994 Jan;144(1):70–81. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]