Abstract
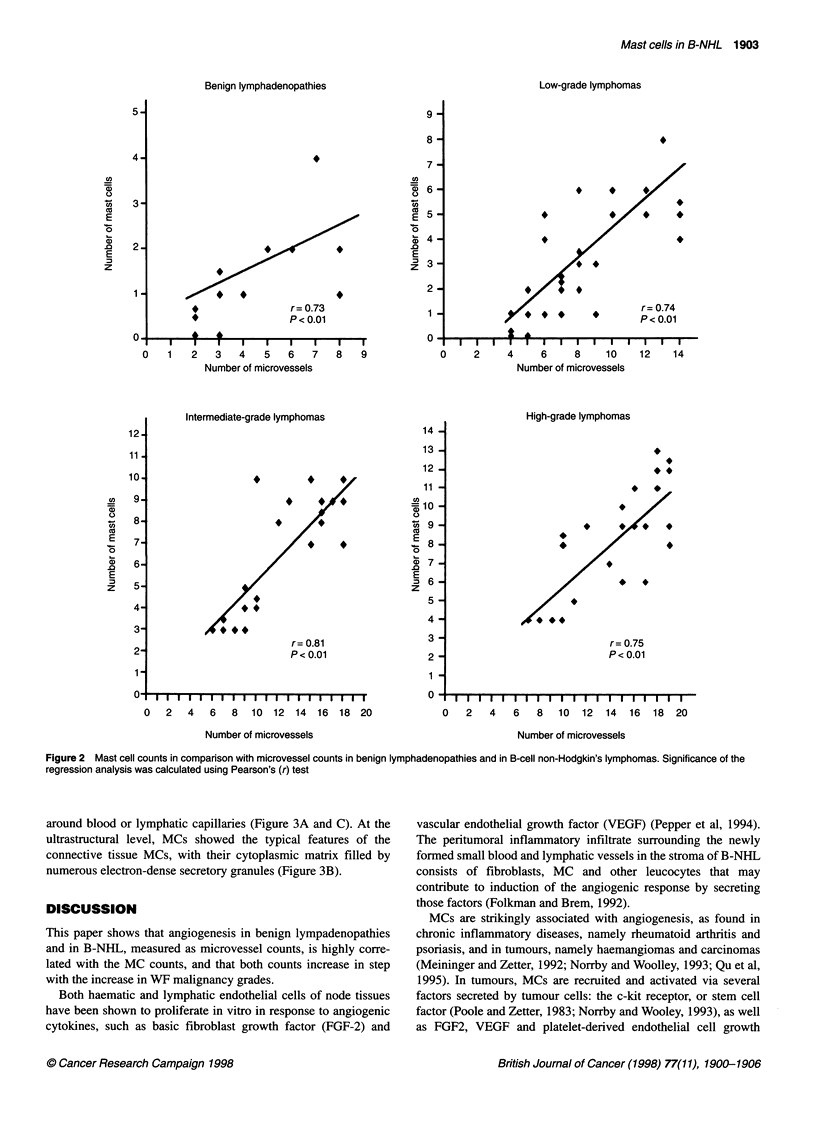
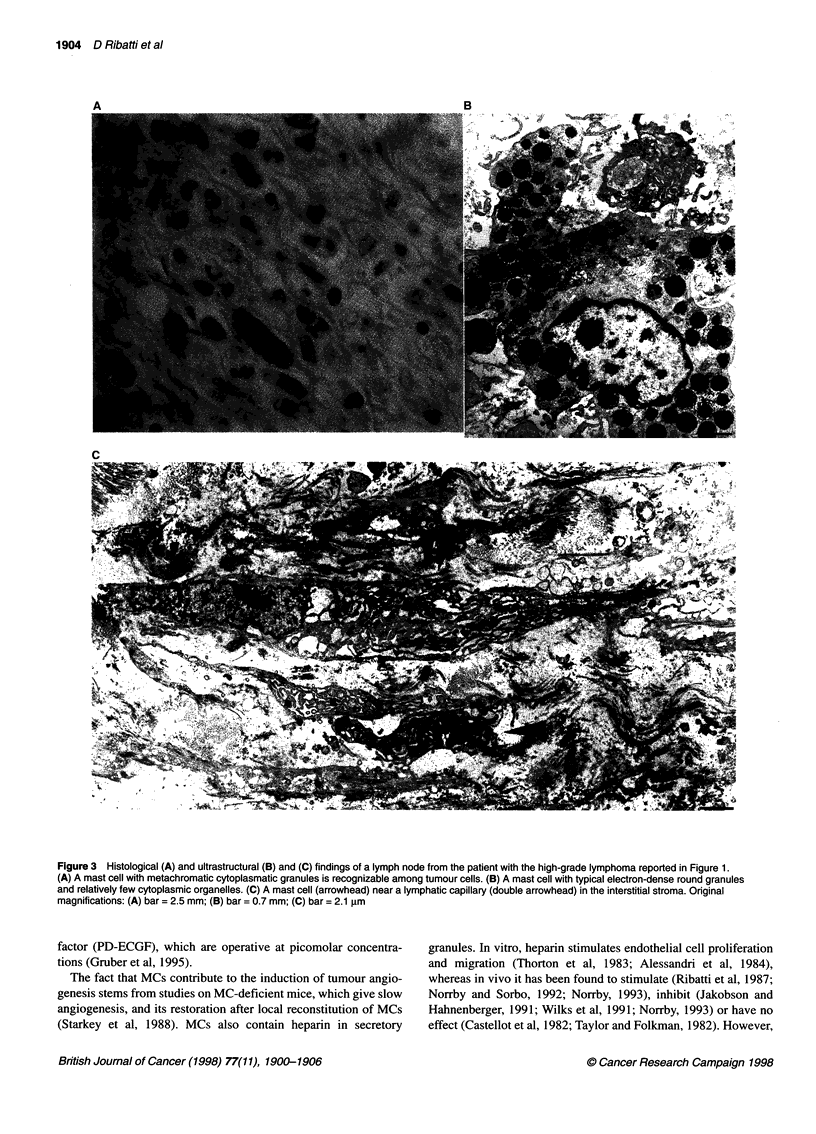
Morphological and morphometric data showing a higher number of mast cells (MCs) in the stroma of B-cell non-Hodgkin's lymphomas (B-NHL) than in benign lymphadenopathies are presented in support of the suggestion that angiogenesis during the progression of B-NHL may be partly mediated by angiogenic factors in their secretory granules.
Keywords: angiogenesis, mast cell, B-cell non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, tumour progression
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aznavoorian S., Murphy A. N., Stetler-Stevenson W. G., Liotta L. A. Molecular aspects of tumor cell invasion and metastasis. Cancer. 1993 Feb 15;71(4):1368–1383. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19930215)71:4<1368::aid-cncr2820710432>3.0.co;2-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beil W. J., Login G. R., Galli S. J., Dvorak A. M. Ultrastructural immunogold localization of tumor necrosis factor-alpha to the cytoplasmic granules of rat peritoneal mast cells with rapid microwave fixation. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1994 Sep;94(3 Pt 1):531–536. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(94)90210-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair R. J., Meng H., Marchese M. J., Ren S., Schwartz L. B., Tonnesen M. G., Gruber B. L. Human mast cells stimulate vascular tube formation. Tryptase is a novel, potent angiogenic factor. J Clin Invest. 1997 Jun 1;99(11):2691–2700. doi: 10.1172/JCI119458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bussolino F., Ziche M., Wang J. M., Alessi D., Morbidelli L., Cremona O., Bosia A., Marchisio P. C., Mantovani A. In vitro and in vivo activation of endothelial cells by colony-stimulating factors. J Clin Invest. 1991 Mar;87(3):986–995. doi: 10.1172/JCI115107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbone P. P., Kaplan H. S., Musshoff K., Smithers D. W., Tubiana M. Report of the Committee on Hodgkin's Disease Staging Classification. Cancer Res. 1971 Nov;31(11):1860–1861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castellot J. J., Jr, Karnovsky M. J., Spiegelman B. M. Differentiation-dependent stimulation of neovascularization and endothelial cell chemotaxis by 3T3 adipocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5597–5601. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dethlefsen S. M., Matsuura N., Zetter B. R. Mast cell accumulation at sites of murine tumor implantation: implications for angiogenesis and tumor metastasis. Invasion Metastasis. 1994;14(1-6):395–408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedorocko P., Macková O. Radioprotective effects of combination broncho-vaxom, a macrophage activator, and indomethacin, an inhibitor of prostaglandin production: relationship to myelopoiesis. Eur J Haematol. 1996 Jan-Feb;56(1-2):54–61. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1996.tb00294.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J. Angiogenesis in cancer, vascular, rheumatoid and other disease. Nat Med. 1995 Jan;1(1):27–31. doi: 10.1038/nm0195-27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J., Shing Y. Angiogenesis. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 5;267(16):10931–10934. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J., Watson K., Ingber D., Hanahan D. Induction of angiogenesis during the transition from hyperplasia to neoplasia. Nature. 1989 May 4;339(6219):58–61. doi: 10.1038/339058a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruber B. L., Marchese M. J., Kew R. Angiogenic factors stimulate mast-cell migration. Blood. 1995 Oct 1;86(7):2488–2493. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada J., Cavanaugh P. G., Lotan O., Nicolson G. L. Separable growth and migration factors for large-cell lymphoma cells secreted by microvascular endothelial cells derived from target organs for metastasis. Br J Cancer. 1992 Aug;66(2):349–354. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1992.269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishai-Michaeli R., Svahn C. M., Weber M., Chajek-Shaul T., Korner G., Ekre H. P., Vlodavsky I. Importance of size and sulfation of heparin in release of basic fibroblast growth factor from the vascular endothelium and extracellular matrix. Biochemistry. 1992 Feb 25;31(7):2080–2088. doi: 10.1021/bi00122a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakobson A. M., Hahnenberger R. Antiangiogenic effect of heparin and other sulphated glycosaminoglycans in the chick embryo chorioallantoic membrane. Pharmacol Toxicol. 1991 Aug;69(2):122–126. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1991.tb01284.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joensuu H., Klemi P. J., Jalkanen S. Biologic progression in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. A flow cytometric study. Cancer. 1990 Jun 1;65(11):2564–2571. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19900601)65:11<2564::aid-cncr2820651128>3.0.co;2-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler D. A., Langer R. S., Pless N. A., Folkman J. Mast cells and tumor angiogenesis. Int J Cancer. 1976 Nov 15;18(5):703–709. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910180520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kittas C., Hansmann M. L., Borisch B., Feller A. C., Lennert K. The blood microvasculature in T-cell lymphomas. A morphological, ultrastructural and immunohistochemical study. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol. 1985;405(4):439–452. doi: 10.1007/BF00737170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meininger C. J., Zetter B. R. Mast cells and angiogenesis. Semin Cancer Biol. 1992 Apr;3(2):73–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mignatti P., Rifkin D. B. Biology and biochemistry of proteinases in tumor invasion. Physiol Rev. 1993 Jan;73(1):161–195. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1993.73.1.161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles S. A., Rezai A. R., Salazar-González J. F., Vander Meyden M., Stevens R. H., Logan D. M., Mitsuyasu R. T., Taga T., Hirano T., Kishimoto T. AIDS Kaposi sarcoma-derived cells produce and respond to interleukin 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(11):4068–4072. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrby K. Heparin and angiogenesis: a low-molecular-weight fraction inhibits and a high-molecular-weight fraction stimulates angiogenesis systemically. Haemostasis. 1993 Mar;23 (Suppl 1):141–149. doi: 10.1159/000216923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepper M. S., Wasi S., Ferrara N., Orci L., Montesano R. In vitro angiogenic and proteolytic properties of bovine lymphatic endothelial cells. Exp Cell Res. 1994 Feb;210(2):298–305. doi: 10.1006/excr.1994.1042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poole T. J., Zetter B. R. Stimulation of rat peritoneal mast cell migration by tumor-derived peptides. Cancer Res. 1983 Dec;43(12 Pt 1):5857–5861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qu Z., Liebler J. M., Powers M. R., Galey T., Ahmadi P., Huang X. N., Ansel J. C., Butterfield J. H., Planck S. R., Rosenbaum J. T. Mast cells are a major source of basic fibroblast growth factor in chronic inflammation and cutaneous hemangioma. Am J Pathol. 1995 Sep;147(3):564–573. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raju K. S., Alessandri G., Gullino P. M. Characterization of a chemoattractant for endothelium induced by angiogenesis effectors. Cancer Res. 1984 Apr;44(4):1579–1584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribatti D., Roncali L., Nico B., Bertossi M. Effects of exogenous heparin on the vasculogenesis of the chorioallantoic membrane. Acta Anat (Basel) 1987;130(3):257–263. doi: 10.1159/000146454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts A. B., Sporn M. B., Assoian R. K., Smith J. M., Roche N. S., Wakefield L. M., Heine U. I., Liotta L. A., Falanga V., Kehrl J. H. Transforming growth factor type beta: rapid induction of fibrosis and angiogenesis in vivo and stimulation of collagen formation in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4167–4171. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starkey J. R., Crowle P. K., Taubenberger S. Mast-cell-deficient W/Wv mice exhibit a decreased rate of tumor angiogenesis. Int J Cancer. 1988 Jul 15;42(1):48–52. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910420110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sörbo J., Jakobsson A., Norrby K. Mast-cell histamine is angiogenic through receptors for histamine1 and histamine2. Int J Exp Pathol. 1994 Feb;75(1):43–50. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S., Folkman J. Protamine is an inhibitor of angiogenesis. Nature. 1982 May 27;297(5864):307–312. doi: 10.1038/297307a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornton S. C., Mueller S. N., Levine E. M. Human endothelial cells: use of heparin in cloning and long-term serial cultivation. Science. 1983 Nov 11;222(4624):623–625. doi: 10.1126/science.6635659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
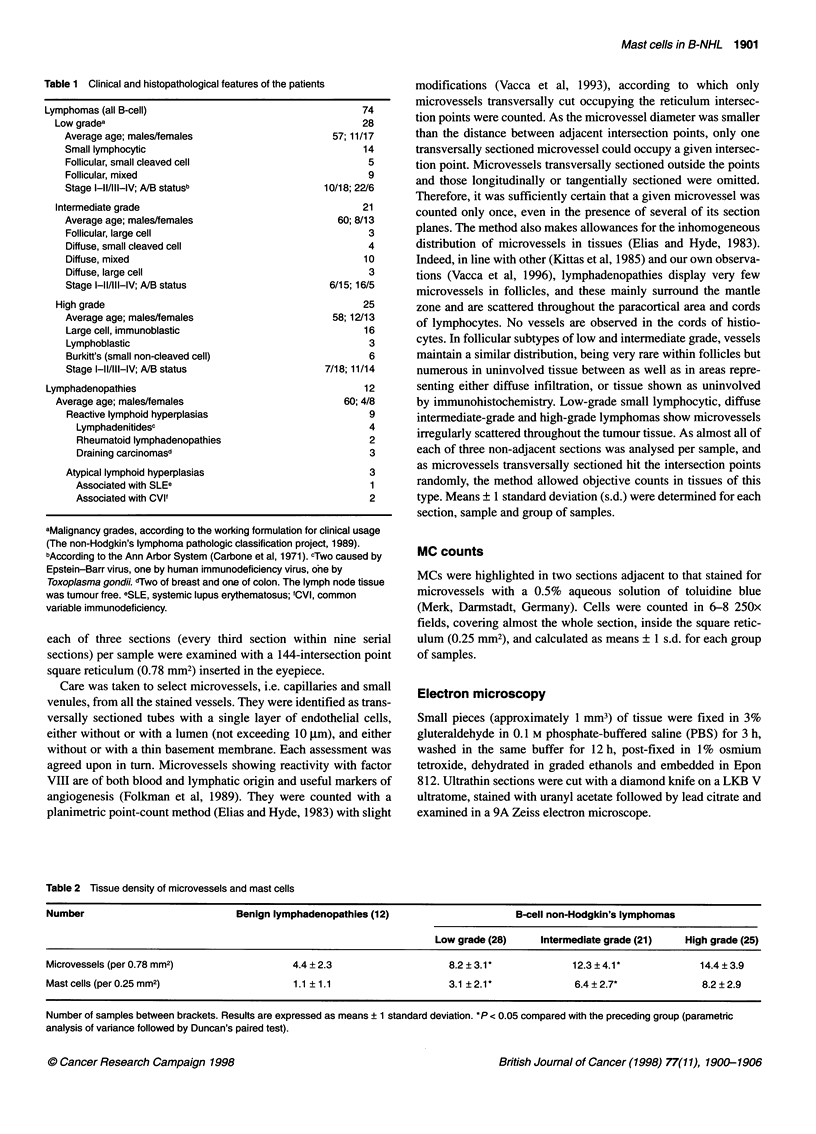
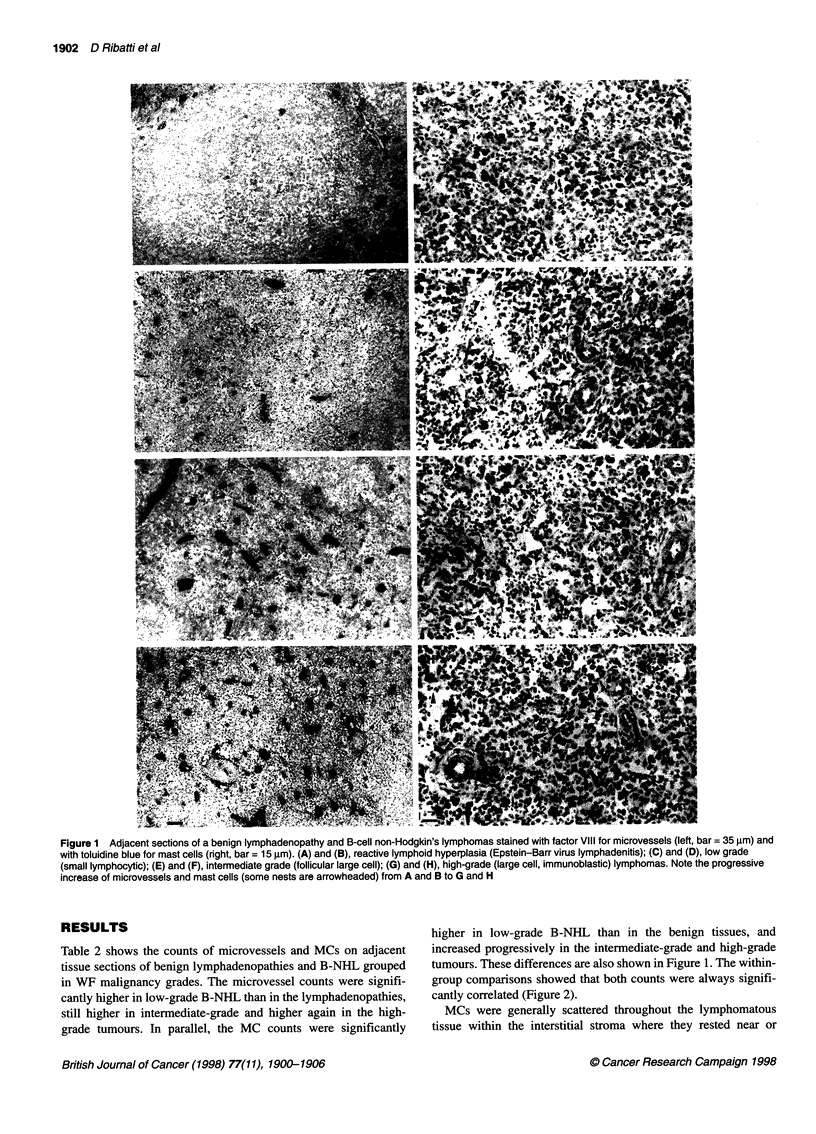
- Vacca A., Ranieri G., Ribatti D., Di Stefano R., Caloro D., Serio G., Di Loreto M., Silvestris F., Dammacco F. Differential expression of two ICAM-1 epitopes and LFA-1 chains in B-cell non-Hodgkin's lymphomas. Eur J Haematol. 1994 Aug;53(2):85–92. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1994.tb01870.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vacca A., Ribatti D., Fanelli M., Costantino F., Nico B., Di Stefano R., Serio G., Dammacco F. Expression of tenascin is related to histologic malignancy and angiogenesis in b-cell non-Hodgkin's lymphomas. Leuk Lymphoma. 1996 Aug;22(5-6):473–481. doi: 10.3109/10428199609054786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vacca A., Ribatti D., Roncali L., Lospalluti M., Serio G., Carrel S., Dammacco F. Melanocyte tumor progression is associated with changes in angiogenesis and expression of the 67-kilodalton laminin receptor. Cancer. 1993 Jul 15;72(2):455–461. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19930715)72:2<455::aid-cncr2820720222>3.0.co;2-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wain S. L., Braylan R. C., Borowitz M. J. Correlation of monoclonal antibody phenotyping and cellular DNA content in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. The Southeastern Cancer Study Group experience. Cancer. 1987 Nov 15;60(10):2403–2411. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19871115)60:10<2403::aid-cncr2820601009>3.0.co;2-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilks J. W., Scott P. S., Vrba L. K., Cocuzza J. M. Inhibition of angiogenesis with combination treatments of angiostatic steroids and suramin. Int J Radiat Biol. 1991 Jul-Aug;60(1-2):73–77. doi: 10.1080/09553009114551581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yayon A., Klagsbrun M., Esko J. D., Leder P., Ornitz D. M. Cell surface, heparin-like molecules are required for binding of basic fibroblast growth factor to its high affinity receptor. Cell. 1991 Feb 22;64(4):841–848. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90512-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]