Abstract
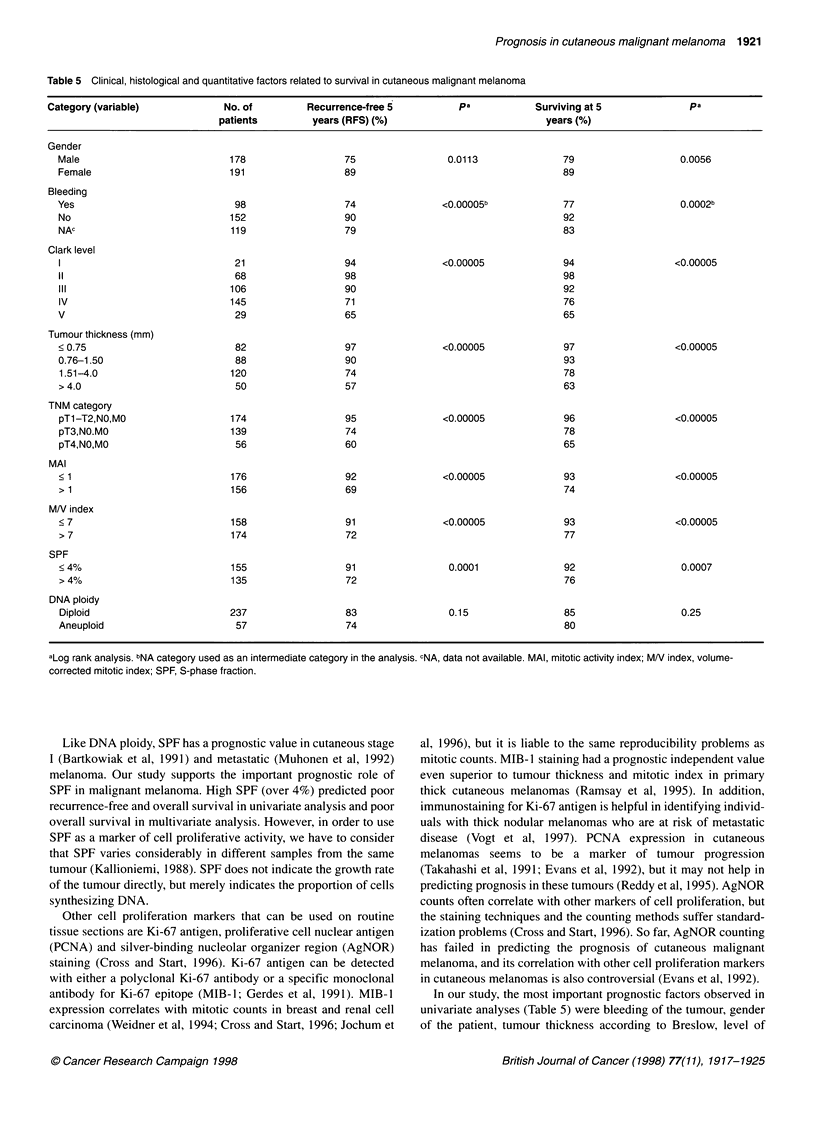
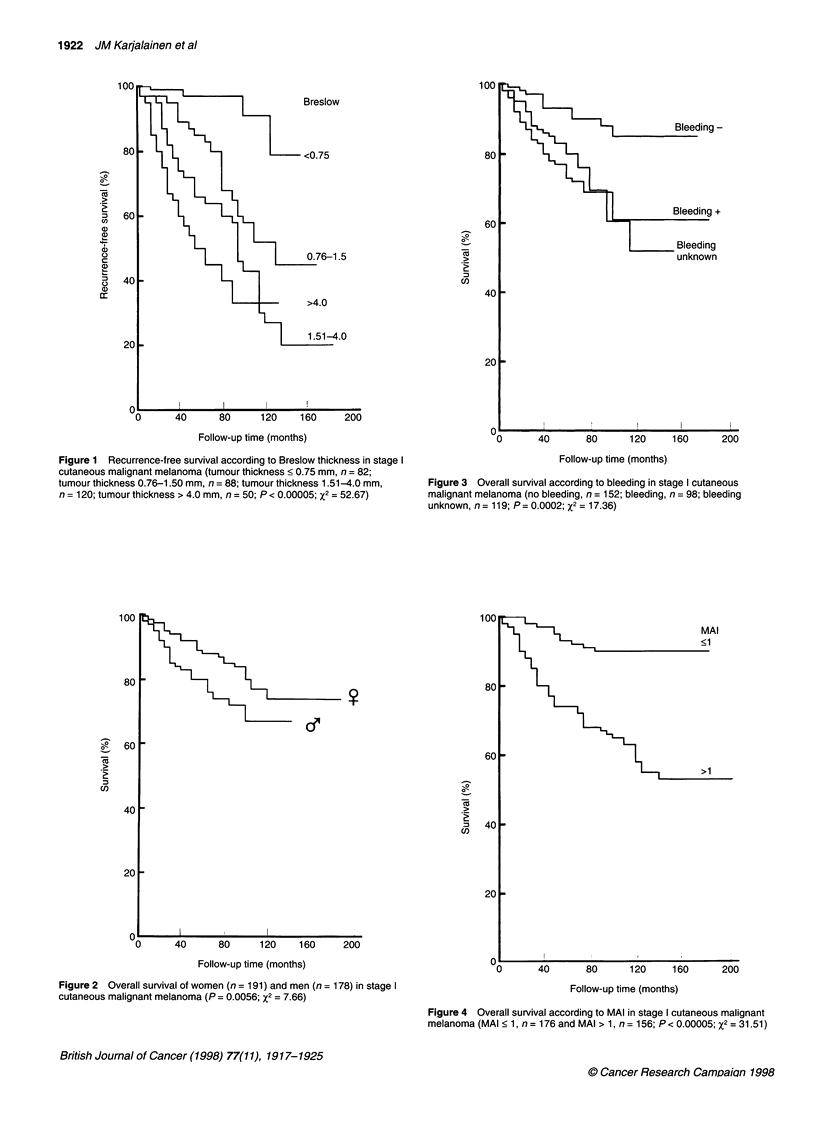
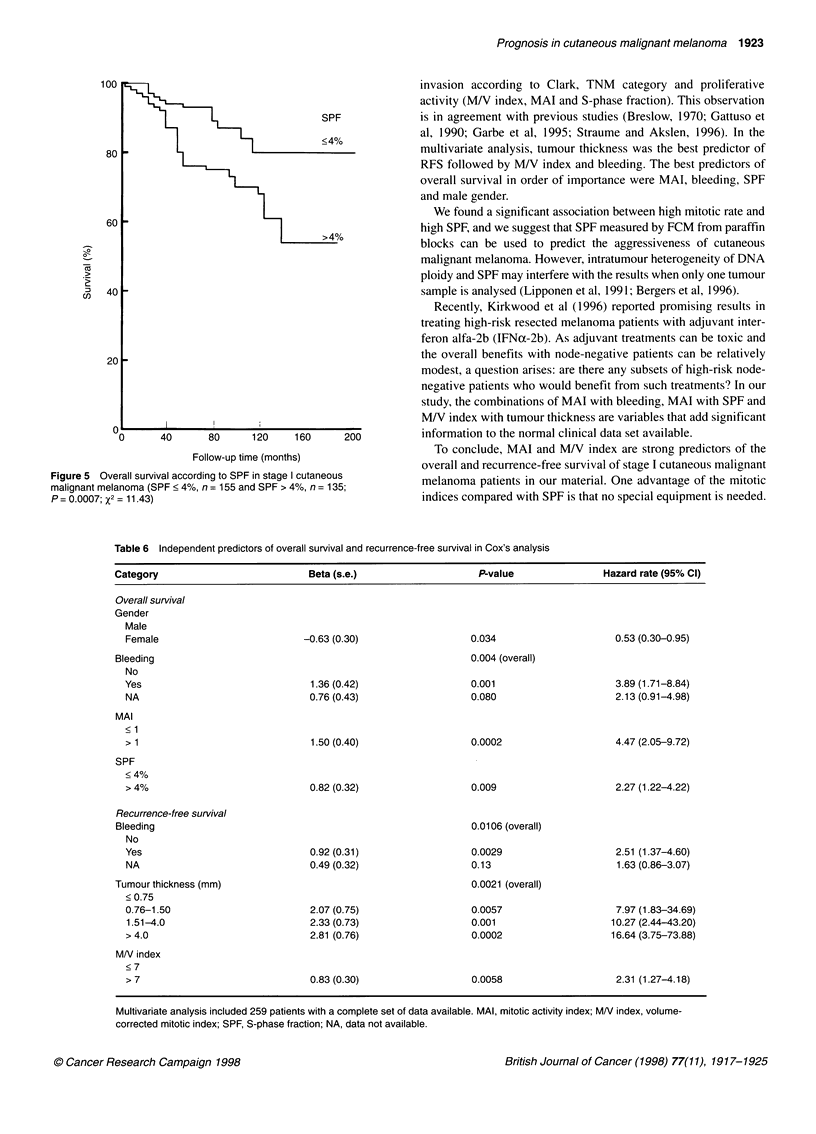
Clinical data from 369 patients with clinical stage I cutaneous malignant melanoma treated in Kuopio University Hospital district between 1974 and 1989 with a mean follow-up of 6.4 years were analysed. Clinical parameters, histology, DNA index, S-phase fraction (SPF) and mitotic indices [mitotic activity index (MAI) and volume-corrected mitotic index (M/V index)] were correlated with the outcome of the disease to establish their value as predictors of stage I cutaneous malignant melanoma. In univariate survival analyses, bleeding, gender, tumour thickness, level of invasion according to Clark, TNM category, MAI, M/V index and SPF were the most significant predictors of recurrence-free (RFS) and overall survival. In Cox's multivariate analysis, tumour thickness (P = 0.0021), bleeding (P = 0.0106) and M/V index (P = 0.0058) predicted poor RFS in the 259 patients available for the analysis. Poor overall survival was predicted by MAI (P = 0.0002), bleeding (P = 0.004), SPF (P = 0.009) and male gender (P = 0.034). The present results indicate that mitotic activity index (MAI), volume-corrected mitotic index (M/V index) and S-phase fraction (SPF) are important prognostic factors in addition to the well-established Breslow thickness in stage I cutaneous malignant melanoma.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baisch H., Göhde W., Linden W. A. Analysis of PCP-data to determine the fraction of cells in the various phases of cell cycle. Radiat Environ Biophys. 1975 Jun 13;12(1):31–39. doi: 10.1007/BF02339807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnhill R. L., Fine J. A., Roush G. C., Berwick M. Predicting five-year outcome for patients with cutaneous melanoma in a population-based study. Cancer. 1996 Aug 1;78(3):427–432. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0142(19960801)78:3<427::AID-CNCR8>3.0.CO;2-G. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartkowiak D., Schumann J., Otto F. J., Lippold A., Drepper H. DNA flow cytometry in the prognosis of primary malignant melanoma. Oncology. 1991;48(1):39–43. doi: 10.1159/000226892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergers E., van Diest P. J., Baak J. P. Tumour heterogeneity of DNA cell cycle variables in breast cancer measured by flow cytometry. J Clin Pathol. 1996 Nov;49(11):931–937. doi: 10.1136/jcp.49.11.931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breslow A. Thickness, cross-sectional areas and depth of invasion in the prognosis of cutaneous melanoma. Ann Surg. 1970 Nov;172(5):902–908. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197011000-00017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camplejohn R. S., Macartney J. C., Morris R. W. Measurement of S-phase fractions in lymphoid tissue comparing fresh versus paraffin-embedded tissue and 4',6'-diamidino-2 phenylindole dihydrochloride versus propidium iodide staining. Cytometry. 1989 Jul;10(4):410–416. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990100408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark W. H., Jr, From L., Bernardino E. A., Mihm M. C. The histogenesis and biologic behavior of primary human malignant melanomas of the skin. Cancer Res. 1969 Mar;29(3):705–727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemente C. G., Mihm M. C., Jr, Bufalino R., Zurrida S., Collini P., Cascinelli N. Prognostic value of tumor infiltrating lymphocytes in the vertical growth phase of primary cutaneous melanoma. Cancer. 1996 Apr 1;77(7):1303–1310. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0142(19960401)77:7<1303::AID-CNCR12>3.0.CO;2-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collan Y. U., Kuopio T., Baak J. P., Becker R., Bogomoletz W. V., Deverell M., van Diest P., van Galen C., Gilchrist K., Javed A. Standardized mitotic counts in breast cancer. Evaluation of the method. Pathol Res Pract. 1996 Sep;192(9):931–941. doi: 10.1016/S0344-0338(96)80075-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross S. S., Start R. D. Estimating mitotic activity in tumours. Histopathology. 1996 Nov;29(5):485–488. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2559.1996.d01-519.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donhuijsen K. Mitosis counts: reproducibility and significance in grading of malignancy. Hum Pathol. 1986 Nov;17(11):1122–1125. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(86)80417-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eastwood J., Baker T. G. Cutaneous malignant melanoma in West Yorkshire: II. A prospective study of recurrence and prediction of lymph nodal metastasis. Br J Cancer. 1984 Jul;50(1):35–43. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1984.137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eskelinen M., Lipponen P., Papinaho S., Aaltomaa S., Kosma V. M., Klemi P., Syrjänen K. DNA flow cytometry, nuclear morphometry, mitotic indices and steroid receptors as independent prognostic factors in female breast cancer. Int J Cancer. 1992 Jun 19;51(4):555–561. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910510409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans A. T., Blessing K., Orrell J. M., Grant A. Mitotic indices, anti-PCNA immunostaining, and AgNORs in thick cutaneous melanomas displaying paradoxical behaviour. J Pathol. 1992 Sep;168(1):15–22. doi: 10.1002/path.1711680104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedlander M. L., Hedley D. W., Taylor I. W. Clinical and biological significance of aneuploidy in human tumours. J Clin Pathol. 1984 Sep;37(9):961–974. doi: 10.1136/jcp.37.9.961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garbe C., Büttner P., Bertz J., Burg G., d'Hoedt B., Drepper H., Guggenmoos-Holzmann I., Lechner W., Lippold A., Orfanos C. E. Primary cutaneous melanoma. Identification of prognostic groups and estimation of individual prognosis for 5093 patients. Cancer. 1995 May 15;75(10):2484–2491. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19950515)75:10<2484::aid-cncr2820751014>3.0.co;2-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gattuso P., Reddy V., Solans E., Kathuria S., Aranha G. V., Jacobs H. K., Walloch J. Is DNA ploidy of prognostic significance in stage I cutaneous melanoma? Surgery. 1990 Oct;108(4):702–709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerdes J., Li L., Schlueter C., Duchrow M., Wohlenberg C., Gerlach C., Stahmer I., Kloth S., Brandt E., Flad H. D. Immunobiochemical and molecular biologic characterization of the cell proliferation-associated nuclear antigen that is defined by monoclonal antibody Ki-67. Am J Pathol. 1991 Apr;138(4):867–873. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haapasalo H., Collan Y., Atkin N. B., Pesonen E., Seppä A. Prognosis of ovarian carcinomas: prediction by histoquantitative methods. Histopathology. 1989 Aug;15(2):167–178. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1989.tb03064.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haapasalo H., Pesonen E., Collan Y. Volume corrected mitotic index (M/V-INDEX). The standard of mitotic activity in neoplasms. Pathol Res Pract. 1989 Nov;185(5):551–554. doi: 10.1016/S0344-0338(89)80191-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedley D. W., Friedlander M. L., Taylor I. W., Rugg C. A., Musgrove E. A. Method for analysis of cellular DNA content of paraffin-embedded pathological material using flow cytometry. J Histochem Cytochem. 1983 Nov;31(11):1333–1335. doi: 10.1177/31.11.6619538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jannink I., Risberg B., Van Diest P. J., Baak J. P. Heterogeneity of mitotic activity in breast cancer. Histopathology. 1996 Nov;29(5):421–428. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2559.1996.d01-509.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jochum W., Schröder S., al-Taha R., August C., Gross A. J., Berger J., Padberg B. C. Prognostic significance of nuclear DNA content and proliferative activity in renal cell carcinomas. A clinicopathologic study of 58 patients using mitotic count, MIB-1 staining, and DNA cytophotometry. Cancer. 1996 Feb 1;77(3):514–521. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0142(19960201)77:3<514::AID-CNCR13>3.0.CO;2-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kallioniemi O. P. Comparison of fresh and paraffin-embedded tissue as starting material for DNA flow cytometry and evaluation of intratumor heterogeneity. Cytometry. 1988 Mar;9(2):164–169. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990090211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keshgegian A. A., Cnaan A. Proliferation markers in breast carcinoma. Mitotic figure count, S-phase fraction, proliferating cell nuclear antigen, Ki-67 and MIB-1. Am J Clin Pathol. 1995 Jul;104(1):42–49. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/104.1.42. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kheir S. M., Bines S. D., Vonroenn J. H., Soong S. J., Urist M. M., Coon J. S. Prognostic significance of DNA aneuploidy in stage I cutaneous melanoma. Ann Surg. 1988 Apr;207(4):455–461. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198804000-00014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkwood J. M., Strawderman M. H., Ernstoff M. S., Smith T. J., Borden E. C., Blum R. H. Interferon alfa-2b adjuvant therapy of high-risk resected cutaneous melanoma: the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Trial EST 1684. J Clin Oncol. 1996 Jan;14(1):7–17. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1996.14.1.7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindholm C., Hofer P. A., Jonsson H., Tribukait B. Flow DNA-cytometric findings of paraffin-embedded primary cutaneous melanomas related to prognosis. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1989;58(2):147–151. doi: 10.1007/BF02890065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipponen P. K., Eskelinen M. J., Nordling S. Intratumoral heterogeneity of DNA indexes in transitional cell bladder cancer: relation to tumor histology. Eur Urol. 1991;20(4):311–314. doi: 10.1159/000471723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipponen P. K., Kosma V. M., Collan Y., Kulju T., Kosunen O., Eskelinen M. Potential of nuclear morphometry and volume-corrected mitotic index in grading transitional cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder. Eur Urol. 1990;17(4):333–337. doi: 10.1159/000464075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montironi R., Collan Y., Scarpelli M., Sisti S., Barbatelli G., Carnevali A., Pisani E., Mariuzzi G. M. Reproducibility of mitotic counts and identification of mitotic figures in malignant glial tumors. Appl Pathol. 1988;6(4):258–265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muhonen T., Pyrhönen S., Laasonen A., Wasenius V. M., Asko-Seljavaara S., Franssila K., Kangas L. Tumour growth rate and DNA flow cytometry parameters as prognostic factors in metastatic melanoma. Br J Cancer. 1992 Sep;66(3):528–532. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1992.307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn C. M., Wright N. A. The clinical assessment of proliferation and growth in human tumours: evaluation of methods and applications as prognostic variables. J Pathol. 1990 Feb;160(2):93–102. doi: 10.1002/path.1711600202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsay J. A., From L., Iscoe N. A., Kahn H. J. MIB-1 proliferative activity is a significant prognostic factor in primary thick cutaneous melanomas. J Invest Dermatol. 1995 Jul;105(1):22–26. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12312431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy V. B., Gattuso P., Aranha G., Carson H. J. Cell proliferation markers in predicting metastases in malignant melanoma. J Cutan Pathol. 1995 Jun;22(3):248–251. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0560.1995.tb00746.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salman S. M., Rogers G. S. Prognostic factors in thin cutaneous malignant melanoma. J Dermatol Surg Oncol. 1990 May;16(5):413–418. doi: 10.1111/j.1524-4725.1990.tb00057.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmoeckel C., Braun-Falco O. Prognostic index in malignant melanoma. Arch Dermatol. 1978 Jun;114(6):871–873. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seckinger D., Sugarbaker E., Frankfurt O. DNA content in human cancer. Application in pathology and clinical medicine. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1989 Jun;113(6):619–626. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straume O., Akslen L. A. Independent prognostic importance of vascular invasion in nodular melanomas. Cancer. 1996 Sep 15;78(6):1211–1219. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0142(19960915)78:6<1211::AID-CNCR7>3.0.CO;2-C. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi H., Strutton G. M., Parsons P. G. Determination of proliferating fractions in malignant melanomas by anti-PCNA/cyclin monoclonal antibody. Histopathology. 1991 Mar;18(3):221–227. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1991.tb00829.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talve L., Kainu J., Collan Y., Ekfors T. Immunohistochemical expression of p53 protein, mitotic index and nuclear morphometry in primary malignant melanoma of the skin. Pathol Res Pract. 1996 Aug;192(8):825–833. doi: 10.1016/S0344-0338(96)80056-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt T., Zipperer K. H., Vogt A., Hölzel D., Landthaler M., Stolz W. p53-protein and Ki-67-antigen expression are both reliable biomarkers of prognosis in thick stage I nodular melanomas of the skin. Histopathology. 1997 Jan;30(1):57–63. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2559.1996.d01-558.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidner N., Moore D. H., 2nd, Vartanian R. Correlation of Ki-67 antigen expression with mitotic figure index and tumor grade in breast carcinomas using the novel "paraffin"-reactive MIB1 antibody. Hum Pathol. 1994 Apr;25(4):337–342. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(94)90140-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Roenn J. H., Kheir S. M., Wolter J. M., Coon J. S. Significance of DNA abnormalities in primary malignant melanoma and nevi, a retrospective flow cytometric study. Cancer Res. 1986 Jun;46(6):3192–3195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


