Abstract
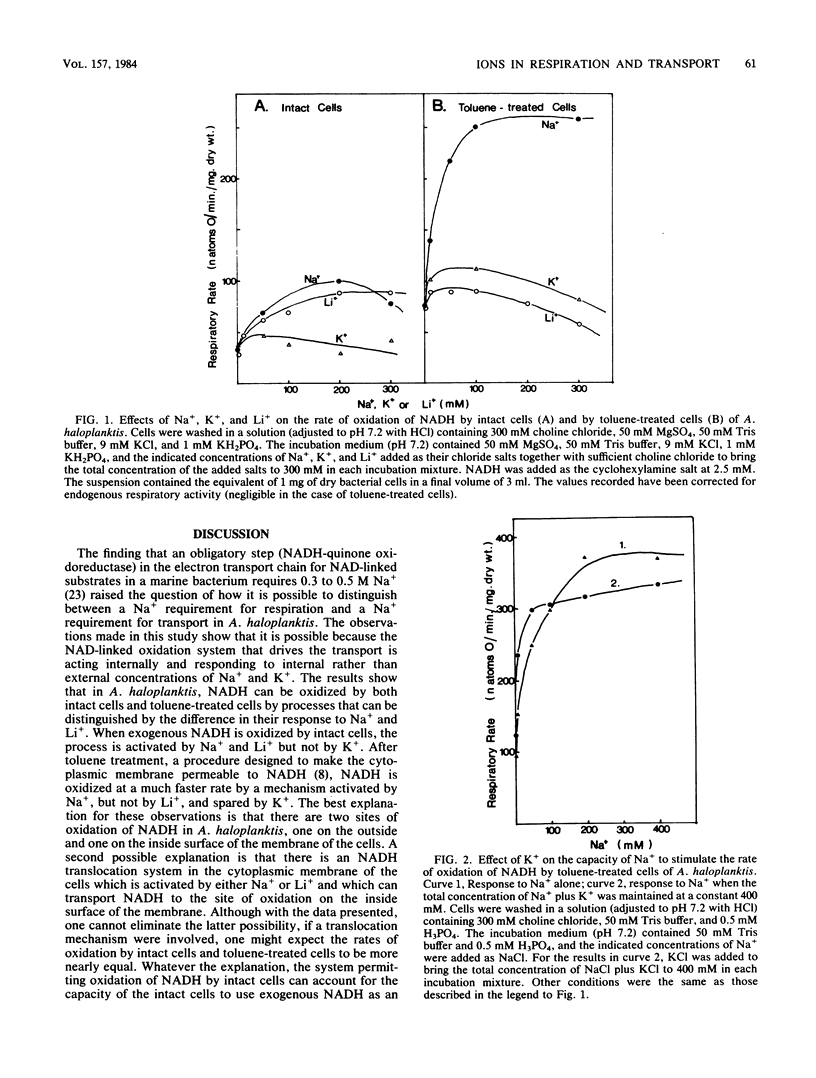
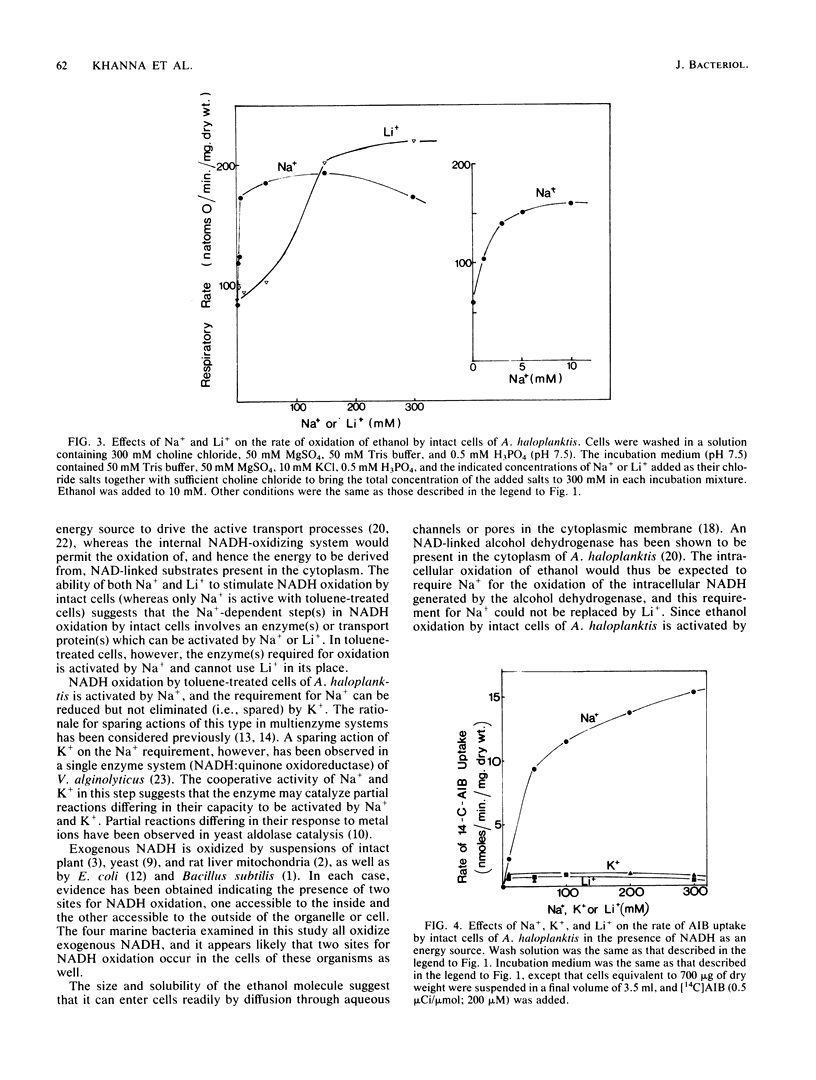
Intact cells of the marine bacterium Alteromonas haloplanktis 214 oxidized NADH, added to the suspending medium, by a process which was stimulated by Na+ or Li+ but not K+. Toluene-treated cells oxidized NADH at three times the rate of untreated cells by a mechanism activated by Na+ but not by Li+ or K+. In the latter reaction, K+ spared the requirement for Na+. Intact cells of A. haloplanktis oxidized ethanol by a mechanism stimulated by either Na+ or Li+. The uptake of alpha-aminoisobutyric acid by intact cells of A. haloplanktis in the presence of either NADH or ethanol as an oxidizable substrate required Na+, and neither Li+ nor K+ could replace it. The results indicate that exogenous and endogenous NADH and ethanol are oxidized by A. haloplanktis by processes distinguishable from one another by their requirements for alkali metal ions and from the ion requirements for membrane transport. Intact cells of Vibrio natriegens and Photobacterium phosphoreum oxidized NADH, added externally, by an Na+-activated process, and intact cells of Vibrio fischeri oxidized NADH, added externally, by a K+-activated process. Toluene treatment caused the cells of all three organisms to oxidize NADH at much faster rates than untreated cells by mechanisms which were activated by Na+ and spared by K+.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bergsma J., Strijker R., Alkema J. Y., Seijen H. G., Konings W. N. NADH dehydrogenase and NADH oxidation in membrane vesicle from Bacillus subtilis. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Dec;120(3):599–606. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05742.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernardi P., Azzone G. F. ATP synthesis during exogenous NADH oxidation. A reappraisal. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Jan 20;679(1):19–27. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(82)90250-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douce R., Mannella C. A., Bonner W. D., Jr The external NADH dehydrogenases of intact plant mitochondria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jan 18;292(1):105–116. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(73)90255-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drapeau G. R., Matula T. I., MacLeod R. A. Nutrition and metabolism of marine bacteria. XV. Relation of Na+-activated transport to the Na+ requirement of a marine pseudomonad for growth. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jul;92(1):63–71. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.1.63-71.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fein J. E., MacLeod R. A. Characterization of neutral amino acid transport in a marine pseudomonad. J Bacteriol. 1975 Dec;124(3):1177–1190. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.3.1177-1190.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassan H. M., MacLeod R. A. Kinetics of Na+-dependent K+ ion transport in a marine pseudomonad. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jan;121(1):160–164. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.1.160-164.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R. W., DeMoss J. A. Effects of toluene on Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1965 Nov;90(5):1420–1425. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.5.1420-1425.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadonaga J. T., Knowles J. R. Role of mono- and divalent metal cations in the catalysis by yeast aldolase. Biochemistry. 1983 Jan 4;22(1):130–136. doi: 10.1021/bi00270a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lombardi F. J., Reeves J. P., Short S. A., Kaback H. R. Evaluation of the chemiosmotic interpretation of active transport in bacterial membrane vesicles. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974 Feb 18;227:312–327. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb14396.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLEOD R. A., SNELL E. E. The relation of ion antagonism to the inorganic nutrition of lactic acid bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1950 Jun;59(6):783–792. doi: 10.1128/jb.59.6.783-792.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niven D. F., MacLeod R. A. Sodium ion-proton antiport in a marine bacterium. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):737–743. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.737-743.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niven D. F., MacLeod R. A. Sodium ion-substrate symport in a marine bacterium. J Bacteriol. 1980 May;142(2):603–607. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.2.603-607.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Keefe D. T., Anthony C. The microbial metabolism of Cl compounds. The stoicheiometry of respiration-driven proton translocation in Pseudomonas AM1 and in a mutant lacking cytochrome c. Biochem J. 1978 Mar 15;170(3):561–567. doi: 10.1042/bj1700561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprott G. D., Drozdowski J. P., Martin E. L., MacLeod R. A. Kinetics of Naplus-dependent amino acid transport using cells and membrane vesicles of a marine pseudomonad. Can J Microbiol. 1975 Jan;21(1):43–50. doi: 10.1139/m75-006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprott G. D., MacLeod R. A. Nature of the specificity of alcohol coupling to L-alanine transport into isolated membrane vesicles of a marine pseudomonad. J Bacteriol. 1974 Mar;117(3):1043–1054. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.3.1043-1054.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J., MacLeod R. A. Na+ and K+ gradients and alpha-aminoisobutyric acid transport in a marine pseudomonad. J Biol Chem. 1973 Oct 25;248(20):7106–7111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J., MacLeod R. A. Specific electron donor-energized transport of alpha-aminoisobutyric acid and K+ into intact cells of a marine pseudomonad. J Bacteriol. 1974 Mar;117(3):1055–1064. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.3.1055-1064.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unemoto T., Hayashi M., Hayashi M. Na+-dependent activation of NADH oxidase in membrane fractions from halophilic Vibrio alginolyticus and V. costicolus. J Biochem. 1977 Nov;82(5):1389–1395. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131826. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unemoto T., Hayashi M. NADH: quinone oxidoreductase as a site of Na+-dependent activation in the respiratory chain of marine Vibrio alginolyticus. J Biochem. 1979 Jun;85(6):1461–1467. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Jagow G., Klingenberg M. Pathways of hydrogen in mitochondria of Saccharomyces carlsbergensis. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Feb;12(3):583–592. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb00890.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



