Abstract
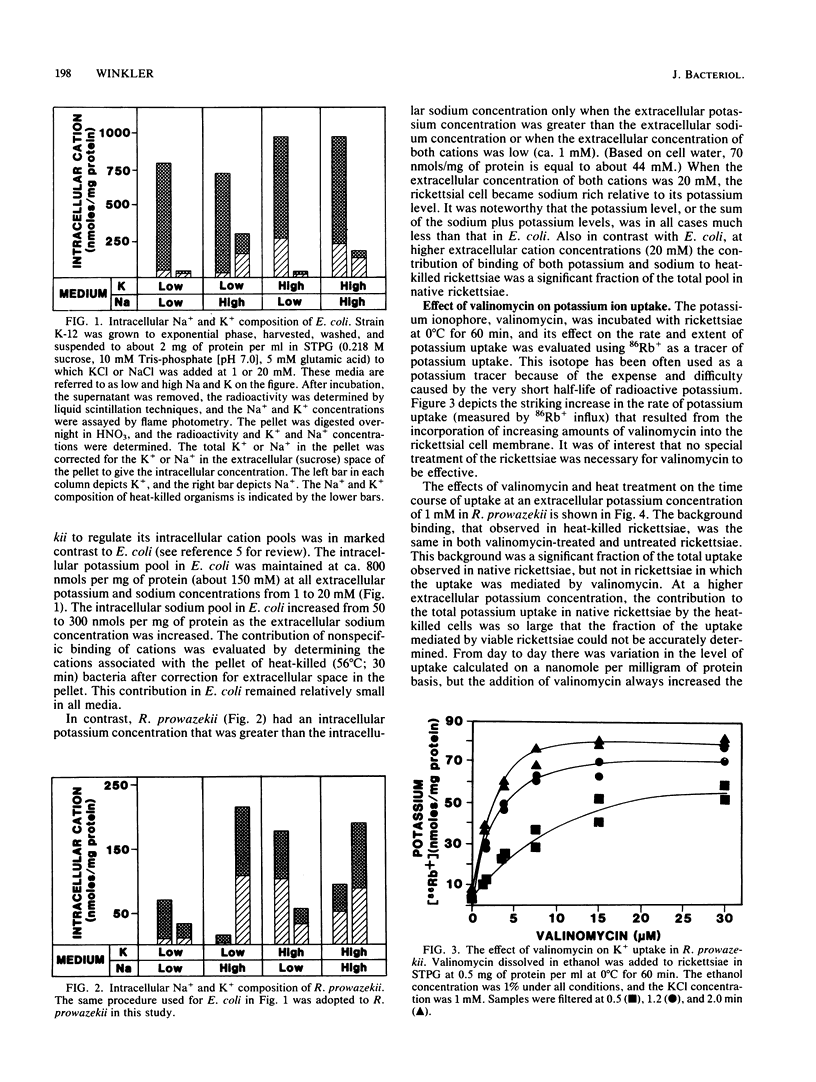
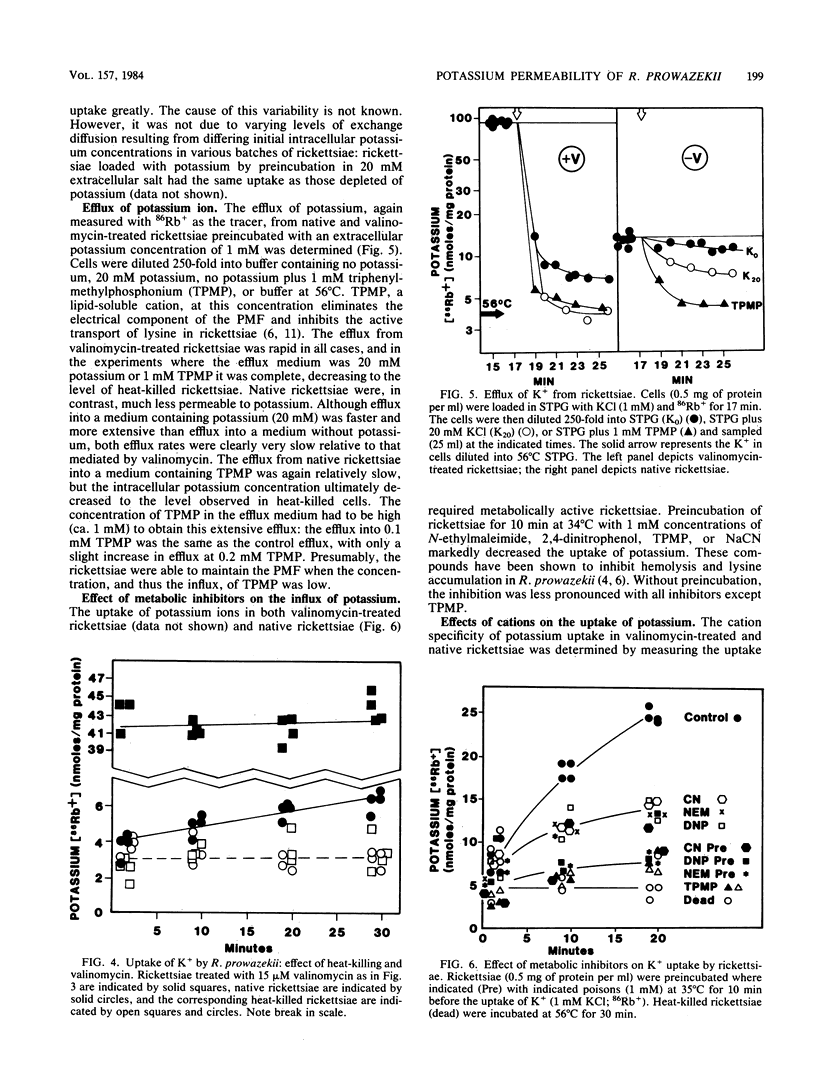
The potassium permeability of Rickettsia prowazekii was characterized by chemical measurement of the intracellular sodium and potassium pools and isotopic flux measurements with 86Rb+ as a tracer. R. prowazekii, in contrast to Escherichia coli, did not maintain a high potassium-to-sodium ratio in their cytoplasm except when the potassium-to-sodium ratio in the extracellular medium was high or when the extracellular concentrations of both cations were low (ca. 1 mM). Both influx and efflux assays with 86Rb+ demonstrated that the rickettsial membrane had limited permeability to potassium and that incorporation of valinomycin into these cells increased these fluxes at least 10-fold. The transport of potassium showed specificity and dependence on rickettsial metabolism. The increased flux of potassium which results from the incorporation of valinomycin into the rickettsial membrane was detrimental to both lysine transport and lysis of erythrocytes by the rickettsiae.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOVARNICK M. R., MILLER J. C., SNYDER J. C. The influence of certain salts, amino acids, sugars, and proteins on the stability of rickettsiae. J Bacteriol. 1950 Apr;59(4):509–522. doi: 10.1128/jb.59.4.509-522.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers W. F., Provost P. J., Wisseman C. L., Jr Permeability properties of Rickettsia mooseri. J Bacteriol. 1967 Mar;93(3):950–960. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.3.950-960.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramm L. E., Winkler H. H. Rickettsial hemolysis: effect of metabolic inhibitors upon hemolysis and adsorption. Infect Immun. 1973 Apr;7(4):550–555. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.4.550-555.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. K., Winkler H. H. Characterization of a lysine-specific active transport system in Rickettsia prowazeki. J Bacteriol. 1977 Mar;129(3):1349–1355. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.3.1349-1355.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WISSEMAN C. L., Jr, JACKSON E. B., HAHN F. E., LEY A. C., SMADEL J. E. Metabolic studies of rickettsiae. I. The effects of antimicrobial substances and enzyme inhibitors on the oxidation of glutamate by purified rickettsiae. J Immunol. 1951 Aug;67(2):123–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H. H., Miller E. T. Phospholipase A and the interaction of Rickettsia prowazekii and mouse fibroblasts (L-929 cells). Infect Immun. 1982 Oct;38(1):109–113. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.1.109-113.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H. H. Rickettsial permeability. An ADP-ATP transport system. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jan 25;251(2):389–396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahorchak R. J., Winkler H. H. Transmembrane electrical potential in Rickettsia prowazekii and its relationship to lysine transport. J Bacteriol. 1983 Feb;153(2):665–671. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.2.665-671.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



