Abstract
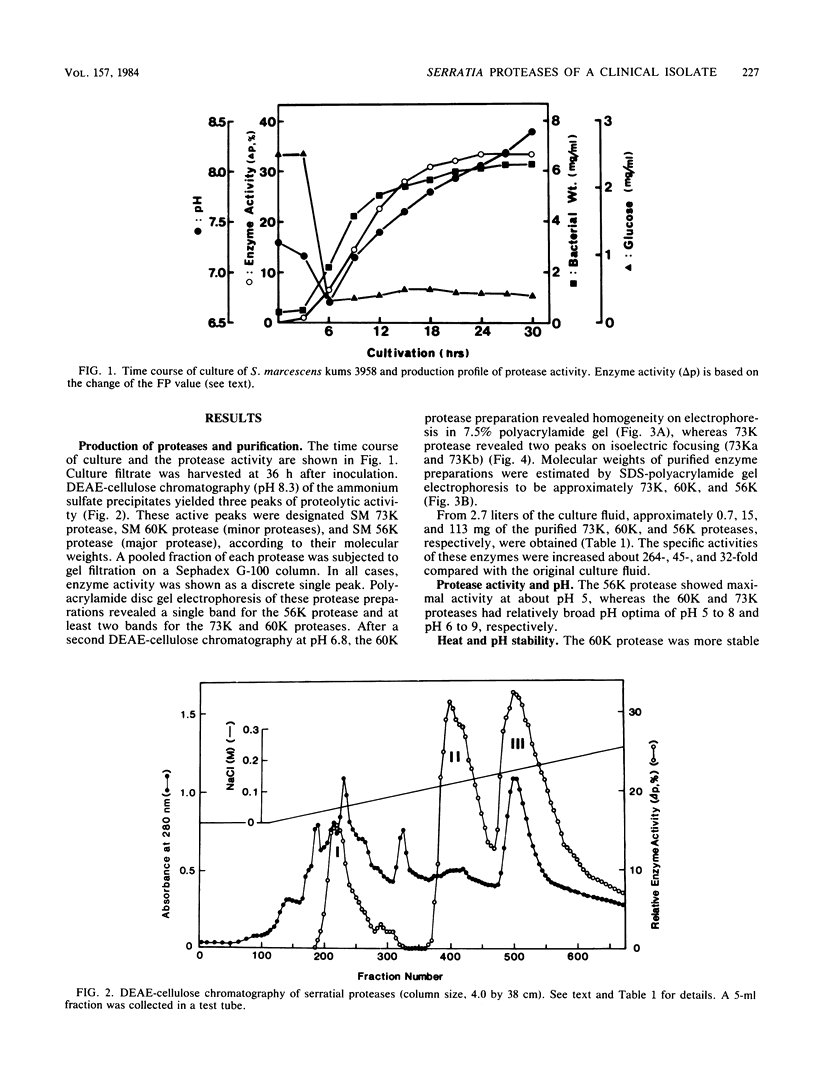
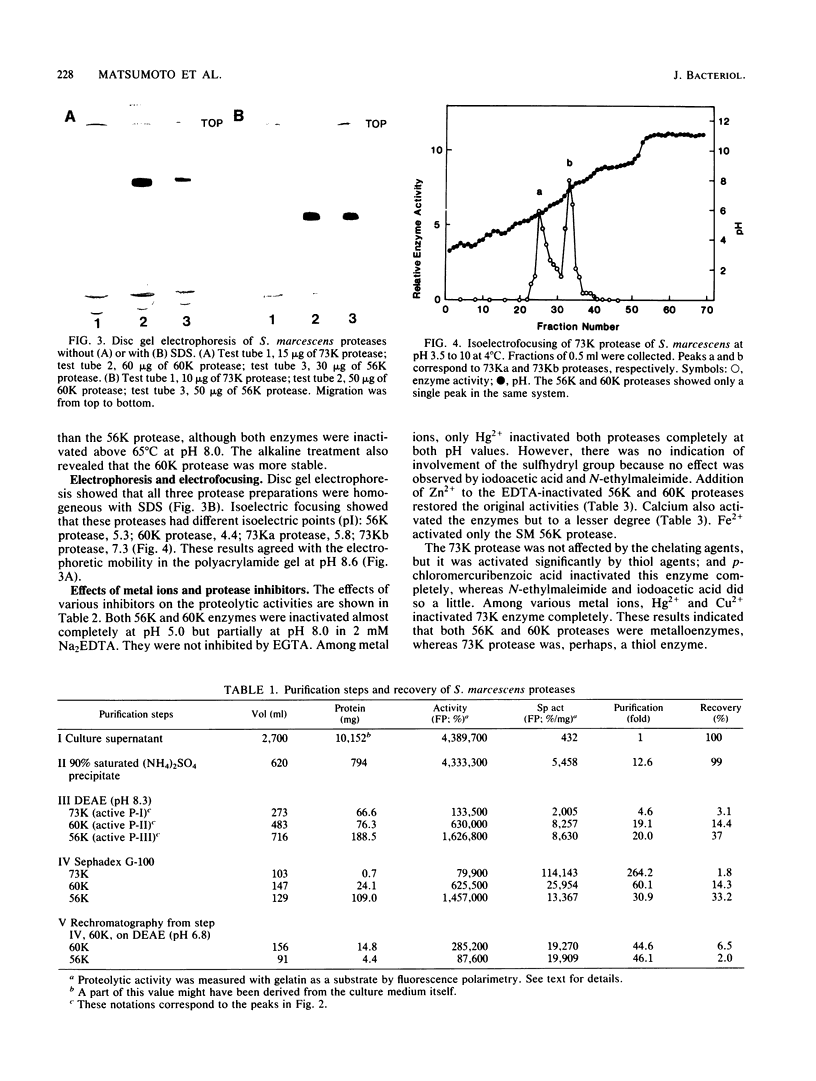
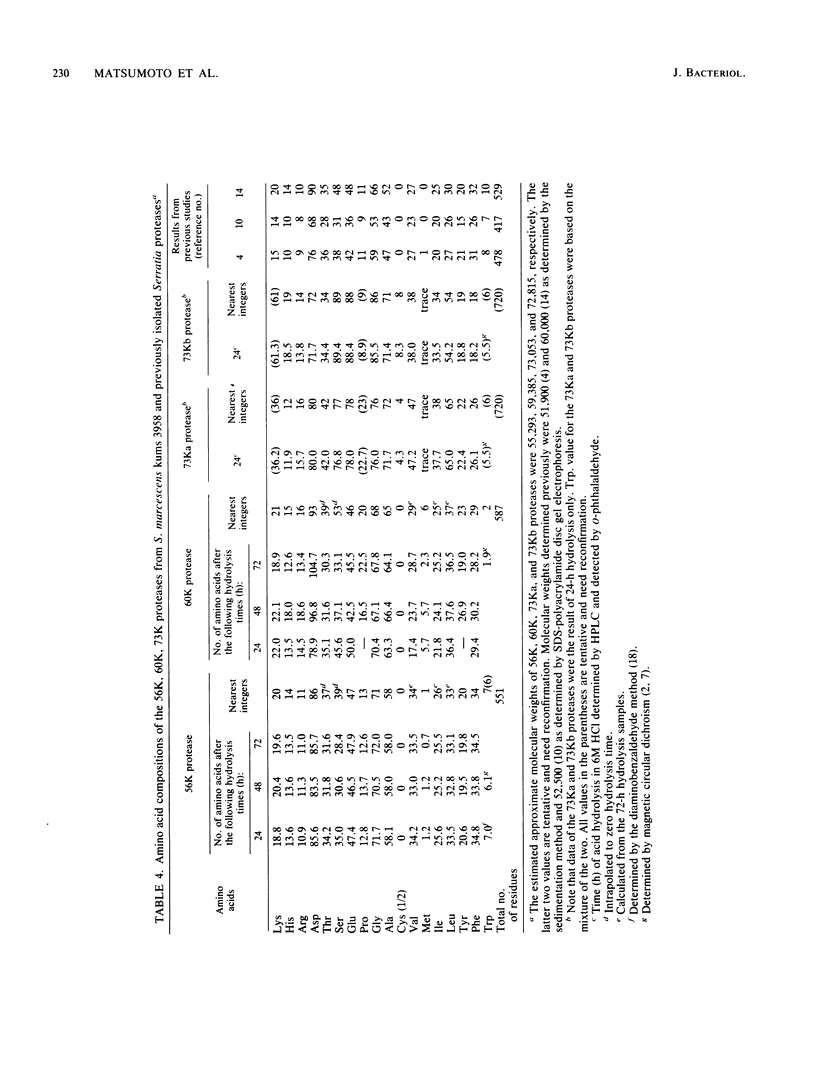
Four distinct proteases were purified to homogeneity from culture filtrates of Serratia marcescens kums 3958, a fresh isolate from a patient with a severe corneal ulcer. Purification was achieved by ammonium sulfate precipitation, DEAE-cellulose ion-exchange chromatography, and Sephadex gel filtration chromatography. The proteases were differentiated from each other by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis with or without sodium dodecyl sulfate and by immunodiffusion in agarose gels. The molecular weights of these purified proteases were estimated to be 56 X 10(3), 60 X 10(3), and 73 X 10(3) (hereafter designated 56K, 60K, and 73K proteases, respectively). The 73K protease was separated into 73Ka and 73Kb upon isoelectricfocusing. The isoelectric points of the 56K (major) and 60K, 73Ka, and 73Kb proteases (minors) were approximately 5.3, 4.4, 5.8, and 7.3, respectively. Both 56K and 60K enzymes were completely inactivated by EDTA at pH 5.0 and were reactivated by zinc ion; thus, they are metalloenzymes, whereas 73K (73Ka and 73Kb) enzymes appear to be thiol proteases. Carbohydrate, cysteine, and cystine were not detected in the 56K and 60K proteases. Amino acid compositions, partial amino acid sequence, and enzymological and immunological properties revealed that these four enzymes are distinct from each other.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aiyappa P. S., Harris J. O. The extracellular metalloprotease of Serratia marcescens: I. Purification and characterization. Mol Cell Biochem. 1976 Nov 30;13(2):95–100. doi: 10.1007/BF01837059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barth G., Records R., Bunnenberg E., Djerassi C., Voelter W. Magnetic circular dichroism studies. XII. The determination of tryptophan in proteins. J Am Chem Soc. 1971 May 19;93(10):2545–2547. doi: 10.1021/ja00739a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decedue C. J., Broussard E. A., 2nd, Larson A. D., Braymer H. D. Purification and characterization of the extracellular proteinase of Serratia marcescens. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Aug 15;569(2):293–301. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(79)90065-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLMAN G. L. Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1959 May;82(1):70–77. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(59)90090-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmquist B., Vallee B. L. Tryptophan quantitation by magnetic circular dichroism in native and modified proteins. Biochemistry. 1973 Oct 23;12(22):4409–4417. doi: 10.1021/bi00746a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIU P. V. Observations on the specificities of extracellular antigens of the genera Aeromonas and Serratia. J Gen Microbiol. 1961 Jan;24:145–154. doi: 10.1099/00221287-24-1-145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyerly D., Gray L., Kreger A. Characterization of rabbit corneal damage produced by Serratia keratitis and by a serratia protease. Infect Immun. 1981 Sep;33(3):927–932. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.3.927-932.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyerly D., Kreger A. Purification and characterization of a Serratia marcescens metalloprotease. Infect Immun. 1979 May;24(2):411–421. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.2.411-421.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda H. Assay of proteolytic enzymes by the fluorescence polarization technique. Anal Biochem. 1979 Jan 1;92(1):222–227. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90649-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda H., Kawauchi H. A new method for the determination of N-terminus of peptides chain with fluorescein-isothiocyanate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Apr 19;31(2):188–192. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90728-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McQuade A. B., Crewther W. G. Activity against a synthetic substrate by a preparation of extracellular proteinase from Serratia marcescens. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969;191(3):762–764. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(69)90382-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Pringle J. R., Osborn M. Measurement of molecular weights by electrophoresis on SDS-acrylamide gel. Methods Enzymol. 1972;26:3–27. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(72)26003-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods K. R., Wang K. T. Separation of dansyl-amino acids by polyamide layer chromatography. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Feb 21;133(2):369–370. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(67)90078-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]