Abstract
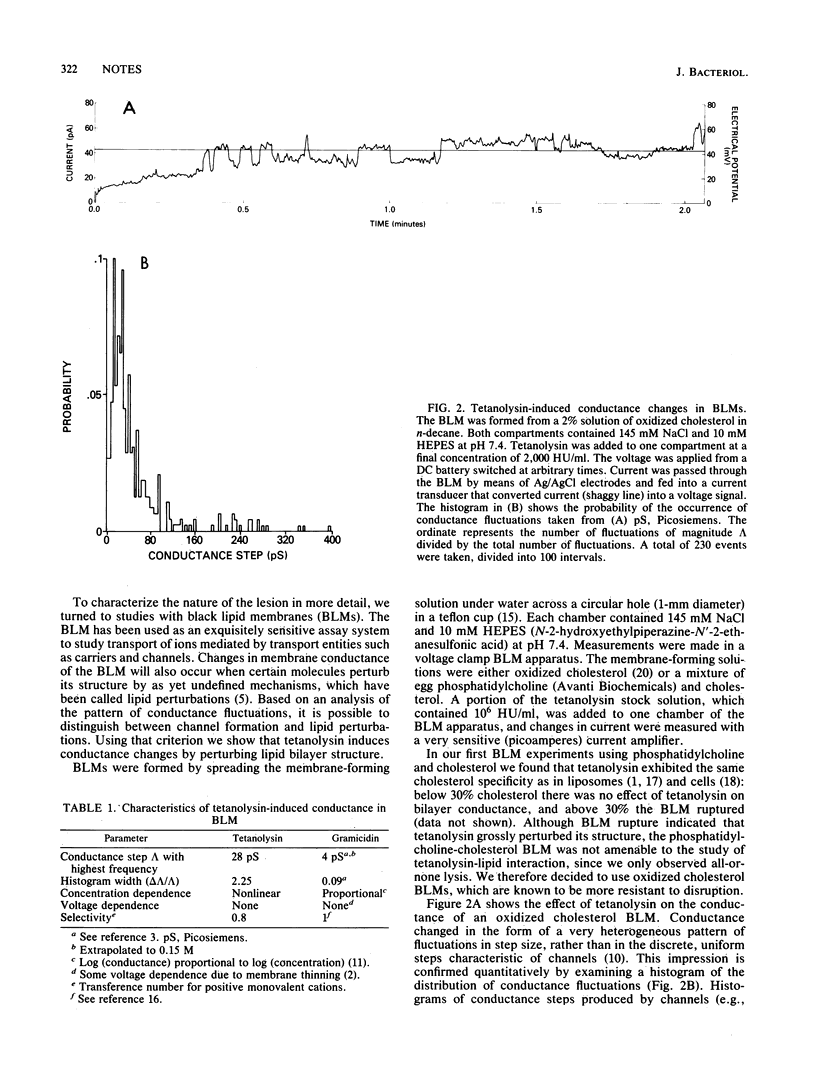
Tetanolysin produced similar rates of leakage of K+ and hemoglobin from erythrocytes. When studied by using cholesterol-containing black lipid membranes, this hemolysin induced conductance steps with a broad frequency distribution. These findings are inconsistent with the formation of structural channels and suggest that tetanolysin acts by causing lipid perturbations.
Full text
PDF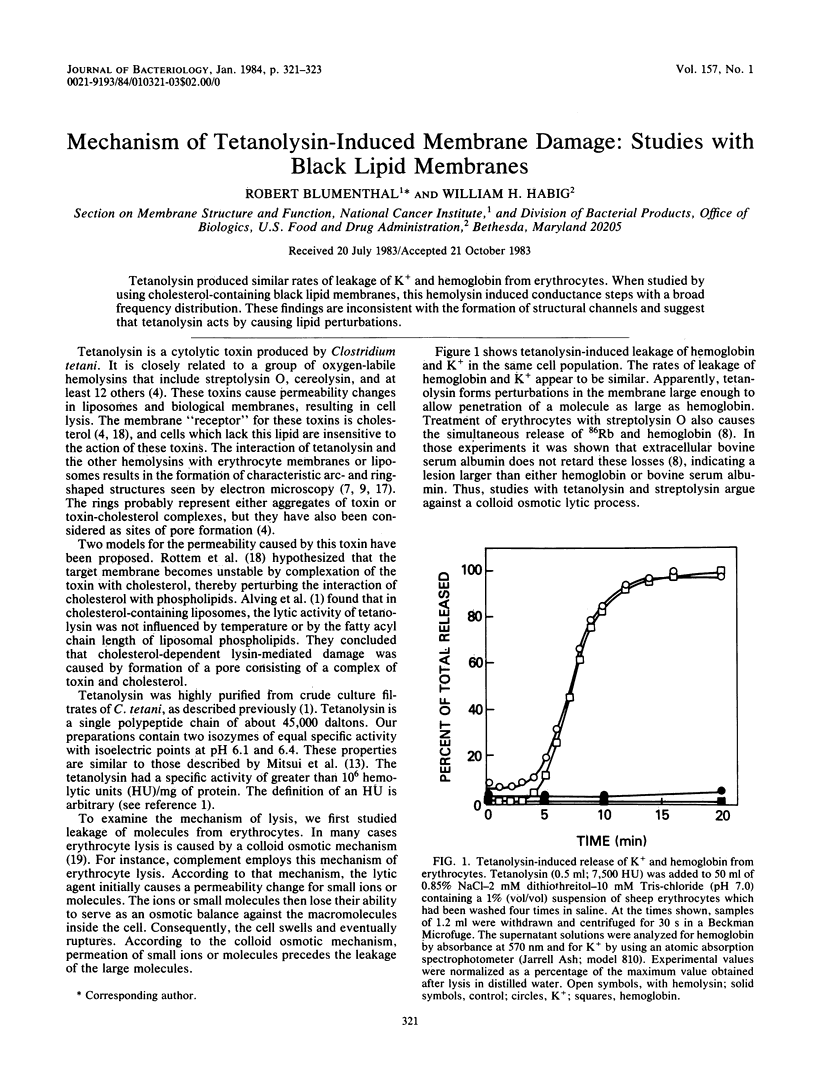

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alving C. R., Habig W. H., Urban K. A., Hardegree M. C. Cholesterol-dependent tetanolysin damage to liposomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Feb 20;551(1):224–228. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90368-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bamberg E., Läuger P. Channel formation kinetics of gramicidin A in lipid bilayer membranes. J Membr Biol. 1973;11(2):177–194. doi: 10.1007/BF01869820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bamberg E., Noda K., Gross E., Läuger P. Single-channel parameters of gramicidin A,B, and C. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jan 21;419(2):223–228. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90348-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenthal R., Klausner R. D., Weinstein J. N. Voltage-dependent translocation of the asialoglycoprotein receptor across lipid membranes. Nature. 1980 Nov 27;288(5789):333–338. doi: 10.1038/288333a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowell J. L., Kim K. S., Bernheimer A. W. Alteration by cereolysin of the structure of cholesterol-containing membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Feb 21;507(2):230–241. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90419-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan J. L. Characteristics of streptolysin O hemolysis: kinetics of hemoglobin and 86rubidium release. Infect Immun. 1974 Jun;9(6):1022–1027. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.6.1022-1027.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan J. L., Schlegel R. Effect of streptolysin O on erythrocyte membranes, liposomes, and lipid dispersions. A protein-cholesterol interaction. J Cell Biol. 1975 Oct;67(1):160–174. doi: 10.1083/jcb.67.1.160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrenstein G., Lecar H. Electrically gated ionic channels in lipid bilayers. Q Rev Biophys. 1977 Feb;10(1):1–34. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500000123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodall M. C. Structural effects in the action of antibiotics on the ion permeability of lipid bilayers. 3. Gramicidins "A" and "S", and lipid specificity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Dec 1;219(2):471–478. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(70)90225-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kempf C., Klausner R. D., Weinstein J. N., Van Renswoude J., Pincus M., Blumenthal R. Voltage-dependent trans-bilayer orientation of melittin. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 10;257(5):2469–2476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUELLER P., RUDIN D. O., TIEN H. T., WESCOTT W. C. Reconstitution of cell membrane structure in vitro and its transformation into an excitable system. Nature. 1962 Jun 9;194:979–980. doi: 10.1038/194979a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsui K., Sekiya T., Nozawa Y., Hase J. Alteration of human erythrocyte plasma membranes by perfringolysin O as revealed by freeze-fracture electron microscopy. Studies on Clostridium perfringens exotoxins V. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jun 13;554(1):68–75. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90007-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsui N., Mitsui K., Hase J. Purification and some properties of tetanolysin. Microbiol Immunol. 1980;24(7):575–584. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1980.tb02860.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers V. B., Haydon D. A. Ion transfer across lipid membranes in the presence of gramicidin A. II. The ion selectivity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Aug 9;274(2):313–322. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90179-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottem S., Cole R. M., Habig W. H., Barile M. F., Hardegree M. C. Structural characteristics of tetanolysin and its binding to lipid vesicles. J Bacteriol. 1982 Nov;152(2):888–892. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.2.888-892.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottem S., Hardegree M. C., Grabowski M. W., Fornwald R., Barile M. F. Interaction between tetanolysin and Mycoplasma cell membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Dec 14;455(3):876–888. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90057-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeman P. Ultrastructure of membrane lesions in immune lysis, osmotic lysis and drug-induced lysis. Fed Proc. 1974 Oct;33(10):2116–2124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



