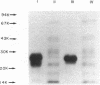
Abstract
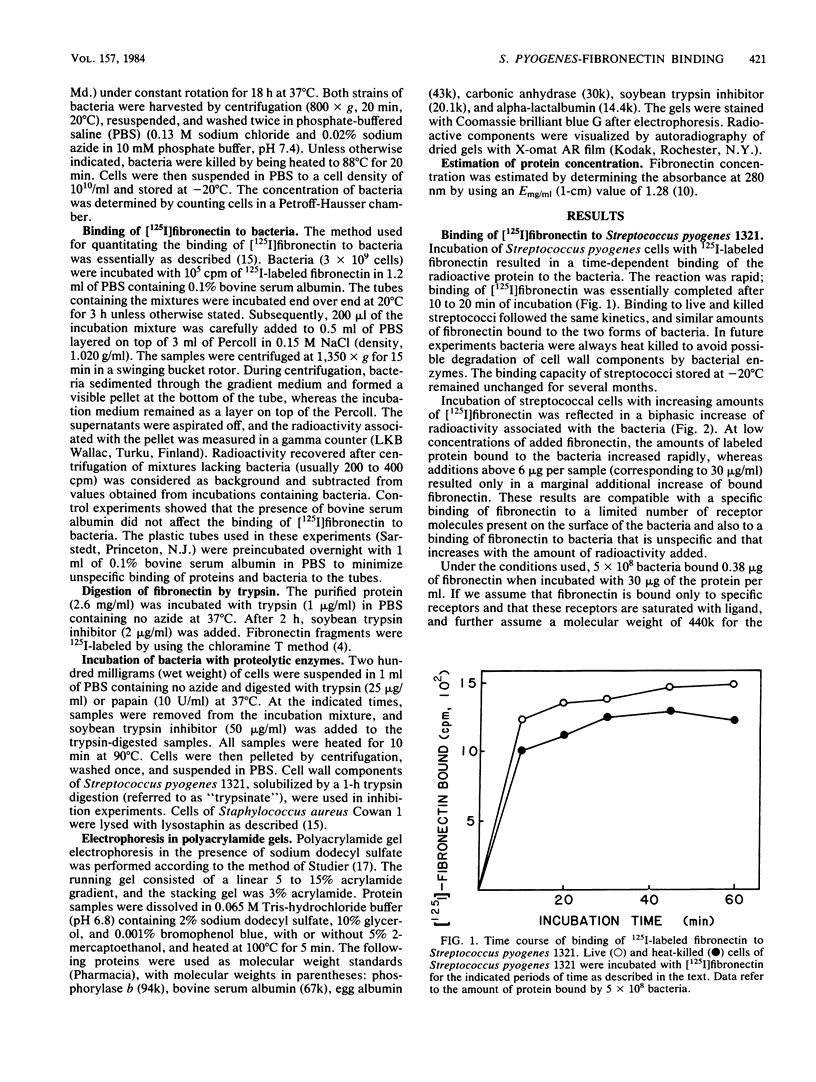
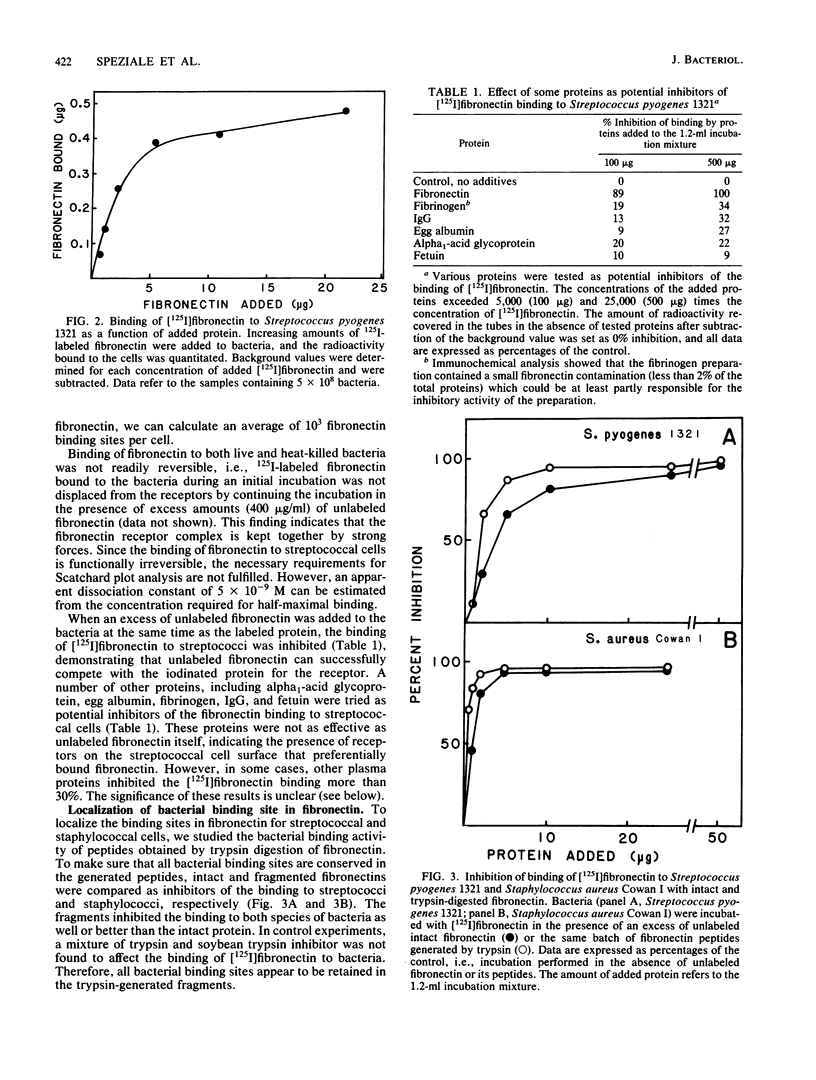
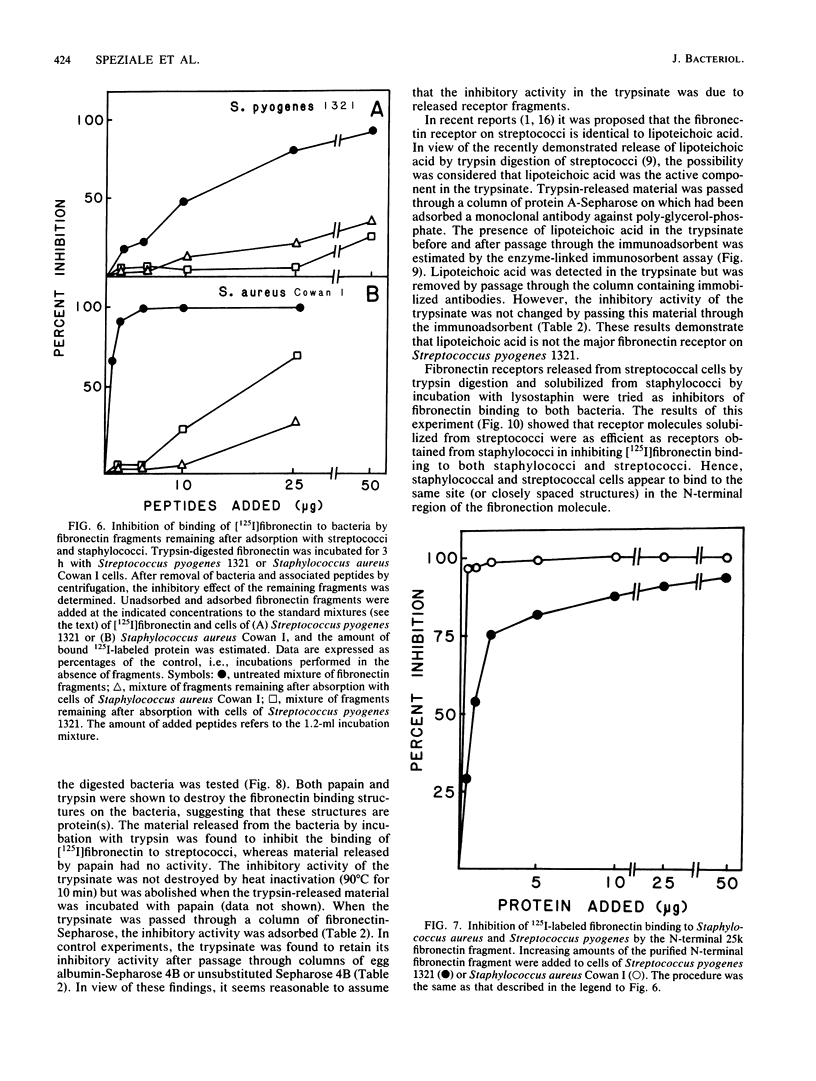
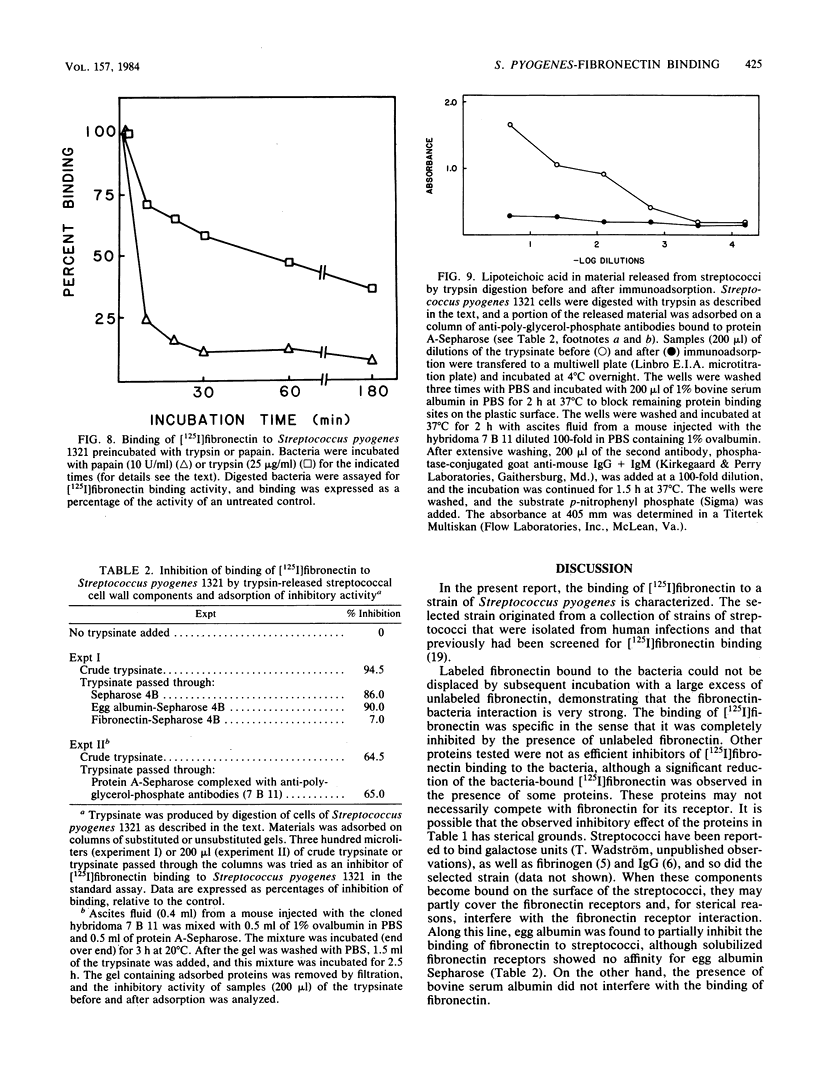
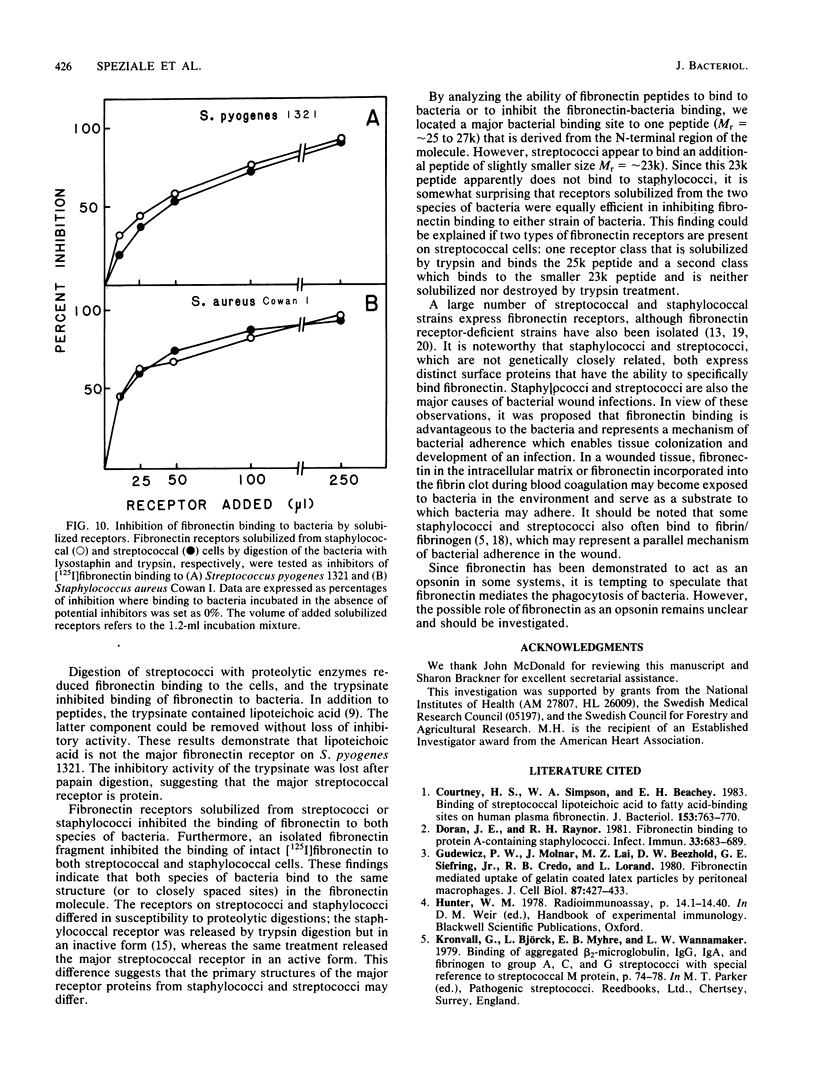
In previous studies, Staphylococcus aureus has been shown to bind fibronectin (P. Kuusela, Nature (London) 276:718-720, 1978), an interaction that may be important in bacterial attachment and opsonization. Recently some strains of streptococci of serological groups A, C, and G were also found to bind fibronectin. The binding to one selected strain of Streptococcus pyogenes has been characterized here. The binding of [125I]fibronectin to streptococcal cells resembles that to staphylococcal cells and was found to be time dependent, functionally irreversible, and specific in the sense that unlabeled proteins other than fibronectin did not block binding. Bacteria incubated with proteases largely lost their ability to bind fibronectin, and material released from the streptococci by a brief trypsin digestion contained active fibronectin receptors. This material inhibited the binding of [125I]fibronectin to the streptococci. The inhibitory activity was adsorbed on a column of fibronectin-Sepharose but not on a column of unsubstituted Sepharose 4B or egg albumin Sepharose. The receptor appeared to be a protein nature since the inhibitory activity of the trypsinate was destroyed by papain and was not absorbed on a column containing monoclonal antibodies directed against lipoteichoic acid bound to protein A-Sepharose. Binding sites in fibronectin for streptococci and staphylococci, respectively, were localized by analyzing the ability of isolated fragments to inhibit [125I]fibronectin binding to bacteria and by adsorbing 125I-labeled tryptic fragments with staphylococcal and streptococcal cells. Both species of bacteria appeared to preferentially bind a fragment (Mr = approximately 25,000) originating from the N-terminal region of the protein. In addition, streptococci also bound a slightly smaller fragment (Mr = approximately 23,000). Fibronectin receptors solubilized from either streptococci or staphylococci inhibited the binding of fibronectin to both species of bacteria.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Courtney H. S., Simpson W. A., Beachey E. H. Binding of streptococcal lipoteichoic acid to fatty acid-binding sites on human plasma fibronectin. J Bacteriol. 1983 Feb;153(2):763–770. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.2.763-770.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doran J. E., Raynor R. H. Fibronectin binding to protein A-containing staphylococci. Infect Immun. 1981 Sep;33(3):683–689. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.3.683-689.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gudewicz P. W., Molnar J., Lai M. Z., Beezhold D. W., Siefring G. E., Jr, Credo R. B., Lorand L. Fibronectin-mediated uptake of gelatin-coated latex particles by peritoneal macrophages. J Cell Biol. 1980 Nov;87(2 Pt 1):427–433. doi: 10.1083/jcb.87.2.427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronvall G., Simmons A., Myhre E. B., Jonsson S. Specific absorption of human serum albumin, immunoglobulin A, and immunoglobulin G with selected strains of group A and G streptococci. Infect Immun. 1979 Jul;25(1):1–10. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.1.1-10.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuusela P. Fibronectin binds to Staphylococcus aureus. Nature. 1978 Dec 14;276(5689):718–720. doi: 10.1038/276718a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald J. A., Kelley D. G. Degradation of fibronectin by human leukocyte elastase. Release of biologically active fragments. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 25;255(18):8848–8858. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miörner H., Johansson G., Kronvall G. Lipoteichoic acid is the major cell wall component responsible for surface hydrophobicity of group A streptococci. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):336–343. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.336-343.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosesson M. W., Umfleet R. A. The cold-insoluble globulin of human plasma. I. Purification, primary characterization, and relationship to fibrinogen and other cold-insoluble fraction components. J Biol Chem. 1970 Nov 10;245(21):5728–5736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosher D. F. Fibronectin. Prog Hemost Thromb. 1980;5:111–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosher D. F., Proctor R. A. Binding and factor XIIIa-mediated cross-linking of a 27-kilodalton fragment of fibronectin to Staphylococcus aureus. Science. 1980 Aug 22;209(4459):927–929. doi: 10.1126/science.7403857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myhre E. B., Kuusela P. Binding of human fibronectin to group A, C, and G streptococci. Infect Immun. 1983 Apr;40(1):29–34. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.1.29-34.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E., Engvall E., Hayman E. G. Fibronectin: current concepts of its structure and functions. Coll Relat Res. 1981;1(1):95–128. doi: 10.1016/s0174-173x(80)80011-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rydén C., Rubin K., Speziale P., Hök M., Lindberg M., Wadström T. Fibronectin receptors from Staphylococcus aureus. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 10;258(5):3396–3401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson W. A., Beachey E. H. Adherence of group A streptococci to fibronectin on oral epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):275–279. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.275-279.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W. Analysis of bacteriophage T7 early RNAs and proteins on slab gels. J Mol Biol. 1973 Sep 15;79(2):237–248. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Switalski L. M., Ljungh A., Rydén C., Rubin K., Hök M., Wadström T. Binding of fibronectin to the surface of group A, C, and G streptococci isolated from human infections. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Dec;1(6):381–387. doi: 10.1007/BF02019939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Switalski L. M., Rydén C., Rubin K., Ljungh A., Hök M., Wadström T. Binding of fibronectin to Staphylococcus strains. Infect Immun. 1983 Nov;42(2):628–633. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.2.628-633.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verbrugh H. A., Peterson P. K., Smith D. E., Nguyen B. Y., Hoidal J. R., Wilkinson B. J., Verhoef J., Furcht L. T. Human fibronectin binding to staphylococcal surface protein and its relative inefficiency in promoting phagocytosis by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes, monocytes, and alveolar macrophages. Infect Immun. 1981 Sep;33(3):811–819. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.3.811-819.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villiger B., Kelley D. G., Engleman W., Kuhn C., 3rd, McDonald J. A. Human alveolar macrophage fibronectin: synthesis, secretion, and ultrastructural localization during gelatin-coated latex particle binding. J Cell Biol. 1981 Sep;90(3):711–720. doi: 10.1083/jcb.90.3.711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vuento M., Vaheri A. Purification of fibronectin from human plasma by affinity chromatography under non-denaturing conditions. Biochem J. 1979 Nov 1;183(2):331–337. doi: 10.1042/bj1830331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Water L., 3rd, Schroeder S., Crenshaw E. B., 3rd, Hynes R. O. Phagocytosis of gelatin-latex particles by a murine macrophage line is dependent on fibronectin and heparin. J Cell Biol. 1981 Jul;90(1):32–39. doi: 10.1083/jcb.90.1.32. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]