Abstract
The putrescine biosynthetic enzyme agmatine ureohydrolase (AUH) (agmatinase; EC 3.5.3.11) catalyzes the conversion of agmatine to putrescine in Escherichia coli. The specific activity of AUH was determined in crude extracts prepared from wild-type strains and from strains with mutations in the adenylate cyclase gene (cya) or the cAMP receptor protein gene (crp) or both. In glucose minimal medium, a delta cya strain exhibited 70 to 90% higher AUH activity than a cya+ strain. Addition of 1 to 10 mM cAMP to cya+ and delta cya strains cultured in glucose repressed AUH activity in a dose-dependent manner. Addition of 1 to 10 mM cAMP to a delta crp strain failed to repress AUH activity. Addition of agmatine resulted in a three- to fourfold induction of AUH in delta cya and delta crp strains. This induction could be blocked by the addition of chloramphenicol. Simultaneous additions of various proportions of cAMP and agmatine resulted in reduced levels of induction and repression of AUH activity. This antagonistic regulation was shown to be exerted by independent mechanisms since AUH activity could be induced by agmatine in a delta crp strain supplemented with cAMP. These results suggest that both agmatine and cAMP antagonistically regulate AUH activity at the level of transcription. In minimal medium supplemented with 1 mM putrescine, the strains did not exhibit repression of AUH activity. In contrast, in minimal medium supplemented with 1 mM ornithine or arginine, cya+ or delta cya strains exhibited induced AUH activity as a result of conversion of these substrates to agmatine. Further experiments in vitro demonstrated that the effects observed with cAMP, agmatine, and arginine were not post-translationally mediated.
Full text
PDF

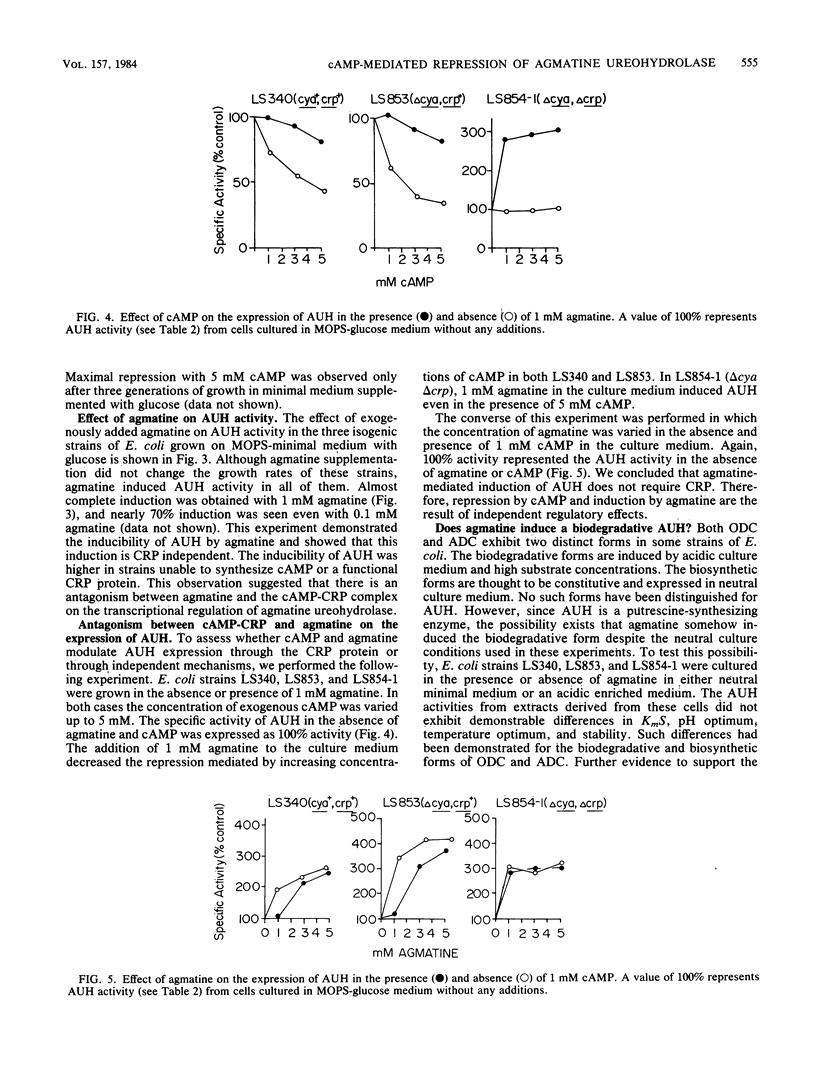




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aiba H. Autoregulation of the Escherichia coli crp gene: CRP is a transcriptional repressor for its own gene. Cell. 1983 Jan;32(1):141–149. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90504-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botsford J. L. Cyclic nucleotides in procaryotes. Microbiol Rev. 1981 Dec;45(4):620–642. doi: 10.1128/mr.45.4.620-642.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle S. M., MacIntyre M. F., Sells B. H. Polyamine levels in Escherichia coli during nutritional shiftup and exponential growth. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Aug 2;477(3):221–227. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(77)90047-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buettner M. J., Spitz E., Rickenberg H. V. Cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jun;114(3):1068–1073. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.3.1068-1073.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dagert M., Ehrlich S. D. Prolonged incubation in calcium chloride improves the competence of Escherichia coli cells. Gene. 1979 May;6(1):23–28. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90082-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedrich B., Magasanik B. Utilization of arginine by Klebsiella aerogenes. J Bacteriol. 1978 Feb;133(2):680–685. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.2.680-685.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hafner E. W., Tabor C. W., Tabor H. Mutants of Escherichia coli that do not contain 1,4-diaminobutane (putrescine) or spermidine. J Biol Chem. 1979 Dec 25;254(24):12419–12426. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyriakidis D. A., Heller J. S., Canellakis E. S. Modulation of ornithine decarboxylase activity in Escherichia coli by positive and negative effectors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4699–4703. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAAS W. K., MAAS R., WIAME J. M., GLANSDORFF N. STUDIES ON THE MECHANISM OF REPRESSION OF ARGININE BIOSYNTHESIS IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. I. DOMINANCE OF REPRESSIBILITY IN ZYGOTES. J Mol Biol. 1964 Mar;8:359–364. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80199-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maas W. K. Mapping of genes involved in the synthesis of spermidine in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;119(1):1–9. doi: 10.1007/BF00270439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magasanik B., Stadtman E. Regulation of glutamine synthetase. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1980;40:337–343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercenier A., Simon J. P., Haas D., Stalon V. Catabolism of L-arginine by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Gen Microbiol. 1980 Feb;116(2):381–389. doi: 10.1099/00221287-116-2-381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris D. R., Fillingame R. H. Regulation of amino acid decarboxylation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1974;43(0):303–325. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.43.070174.001511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris D. R., Koffron K. L. Putrescine biosynthesis in Escherichia coli. Regulation through pathway selection. J Biol Chem. 1969 Nov 25;244(22):6094–6099. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris D. R., Pardee A. B. Multiple pathways of putrescine biosynthesis in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1966 Jul 10;241(13):3129–3135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastan I., Adhya S. Cyclic adenosine 5'-monophosphate in Escherichia coli. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Sep;40(3):527–551. doi: 10.1128/br.40.3.527-551.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner S., Miller R. E., Valentine R. C. Adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate control of the enzymes of glutamine metabolism in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Oct;69(10):2922–2926. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.10.2922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roon R. J., Barker H. A. Fermentation of agmatine in Streptococcus faecalis: occurrence of putrescine transcarbamoylase. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jan;109(1):44–50. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.1.44-50.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SERCARZ E. E., GORINI L. DIFFERENT CONTRIBUTION OF EXOGENOUS AND ENDOGENOUS ARGININE TO REPRESSOR FORMATION. J Mol Biol. 1964 Feb;8:254–262. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80135-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor C. W., Tabor H. 1,4-Diaminobutane (putrescine), spermidine, and spermine. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:285–306. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.001441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor H., Tabor C. W. Formation of 1,4-diaminobutane and of spermidine by an ornithine auxotroph of Escherichia coli grown on limiting ornithine or arginine. J Biol Chem. 1969 May 10;244(9):2286–2292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright J. M., Boyle S. M. Negative control of ornithine decarboxylase and arginine decarboxylase by adenosine-3':5'-cyclic monophosphate in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;186(4):482–487. doi: 10.1007/BF00337952. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



