Abstract
The production of hook protein and flagellin in 29 Fla- mutants of Escherichia coli K-12 was determined by the complement fixation assay. Six mutants produced hook protein, and four of them also produced flagellin. A flaE mutation was introduced into these fla mutants carrying the hook structure. All of these mutants made polyhooks and were used as hosts for a newly isolated host-range mutant of chi phage that has a high affinity for the hook structure. All except one mutant produced significant amounts of progeny phages. A flaD flaE double mutant was that exception which did not yield significant amounts of progeny by the phage propagation method. All of the flaE double mutants produced comparable amounts of polyhooks, and no qualitative difference was detected between chi-sensitive and chi-insensitive mutants by the complement fixation assay. Accordingly, it was thought that the polyhook of the flaD flaE mutant had a mechanical defect for chi phage infection. This assumption was confirmed by tethered-cell experiments; the flaD flaE mutant did not rotate. These results are well explained by a proposed regulation pathway of flagellar genes. flaE mutants can express other genes which govern the final step of the flagellar morphogenesis, whereas flaD mutants cannot rotate, possibly because the mocha operon is not expressed. The results obtained in E. coli were also found to be applicable to Salmonella typhimurium.
Full text
PDF

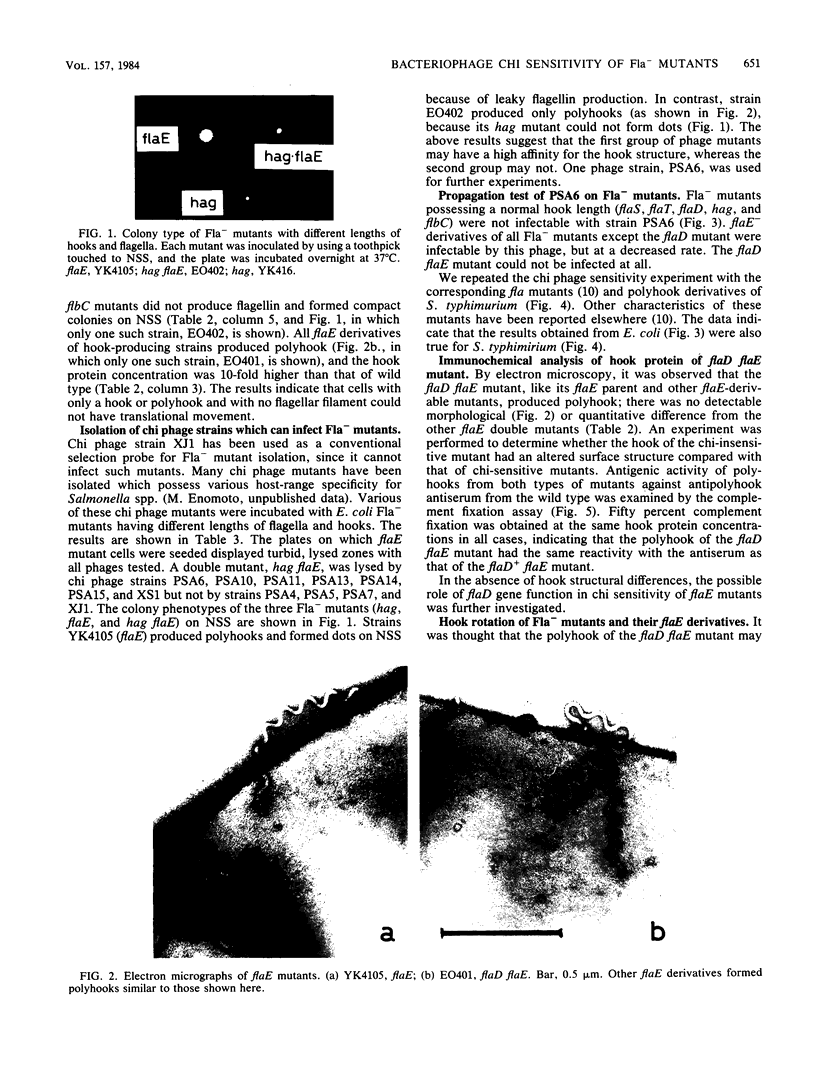

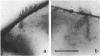
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abram D., Mitchen J. R., Koffler H., Vatter A. E. Differentiation within the bacterial flagellum and isolation of the proximal hook. J Bacteriol. 1970 Jan;101(1):250–261. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.1.250-261.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aizawa S. I., Kato S., Asakura S., Kagawa H., Yamaguchi S. In vitro polymerization of polyhook protein from Salmonella SJW880. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Oct 21;625(2):291–303. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(80)90293-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asakura S. Polymerization of flagellin and polymorphism of flagella. Adv Biophys. 1970;1:99–155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePamphilis M. L., Adler J. Fine structure and isolation of the hook-basal body complex of flagella from Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jan;105(1):384–395. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.1.384-395.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Icho T., Iino T. Isolation and characterization of motile Escherichia coli mutants resistant to bacteriophage chi. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):854–860. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.854-860.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iino T. Genetics of structure and function of bacterial flagella. Annu Rev Genet. 1977;11:161–182. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.11.120177.001113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagawa H., Asakura S., Iino T. Serological study of bacterial flagellar hooks. J Bacteriol. 1973 Mar;113(3):1474–1481. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.3.1474-1481.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagawa H., Morishita H., Enomoto M. Reconstitution in vitro of flagellar filaments onto hook structures attached to bacterial cells. J Mol Biol. 1981 Dec 5;153(2):465–470. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90291-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagawa H., Nishiyama T., Yamaguchi S. Motility development of Salmonella typhimurium cells with flaV mutations after addition of exogenous flagellin. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jul;155(1):435–437. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.1.435-437.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagawa H., Owaribe K., Asakura S., Takahashi N. Flagellar hook protein from Salmonella SJ25. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jan;125(1):68–73. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.1.68-73.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato S., Aizawa S., Asakura S. Reconstruction in vitro of the flagellar polyhook from Salmonella. J Mol Biol. 1982 Nov 15;161(4):551–560. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90407-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleckner N., Chan R. K., Tye B. K., Botstein D. Mutagenesis by insertion of a drug-resistance element carrying an inverted repetition. J Mol Biol. 1975 Oct 5;97(4):561–575. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80059-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komeda Y. Fusions of flagellar operons to lactose genes on a mu lac bacteriophage. J Bacteriol. 1982 Apr;150(1):16–26. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.1.16-26.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komeda Y., Iino T. Regulation of expression of the flagellin gene (hag) in Escherichia coli K-12: analysis of hag-lac gene fusions. J Bacteriol. 1979 Sep;139(3):721–729. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.3.721-729.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komeda Y., Kutsukake K., Iino T. Definition of additional flagellar genes in Escherichia coli K12. Genetics. 1980 Feb;94(2):277–290. doi: 10.1093/genetics/94.2.277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komeda Y., Silverman M., Simon M. Identification of the structural gene for the hook subunit protein of Escherichia coli flagella. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jan;133(1):364–371. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.1.364-371.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kutsukake K., Iino T., Komeda Y., Yamaguchi S. Functional homology of fla genes between Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1980 Apr;178(1):59–67. doi: 10.1007/BF00267213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCDONOUGH M. W. AMINO ACID COMPOSITION OF ANTIGENICALLY DISTINCT SALMONELLA FLAGELLAR PROTEINS. J Mol Biol. 1965 Jun;12:342–355. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80258-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEYNELL E. W. A phage, phi chi, which attacks motile bacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1961 Jun;25:253–290. doi: 10.1099/00221287-25-2-253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macnab R., Koshland D. E., Jr Bacterial motility and chemotaxis: light-induced tumbling response and visualization of individual flagella. J Mol Biol. 1974 Apr 15;84(3):399–406. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90448-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravid S., Eisenbach M. Correlation between bacteriophage chi adsorption and mode of flagellar rotation of Escherichia coli chemotaxis mutants. J Bacteriol. 1983 May;154(2):604–611. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.2.604-611.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schade S. Z., Adler J., Ris H. How bacteriophage chi attacks motile bacteria. J Virol. 1967 Jun;1(3):599–609. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.3.599-609.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman M., Simon M. I. Bacterial flagella. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1977;31:397–419. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.31.100177.002145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman M., Simon M. Flagellar rotation and the mechanism of bacterial motility. Nature. 1974 May 3;249(452):73–74. doi: 10.1038/249073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki T., Iino T., Horiguchi T., Yamaguchi S. Incomplete flagellar structures in nonflagellate mutants of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1978 Feb;133(2):904–915. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.2.904-915.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki T., Komeda Y. Incomplete flagellar structures in Escherichia coli mutants. J Bacteriol. 1981 Feb;145(2):1036–1041. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.2.1036-1041.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WASSERMAN E., LEVINE L. Quantitative micro-complement fixation and its use in the study of antigenic structure by specific antigen-antibody inhibition. J Immunol. 1961 Sep;87:290–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]