Abstract
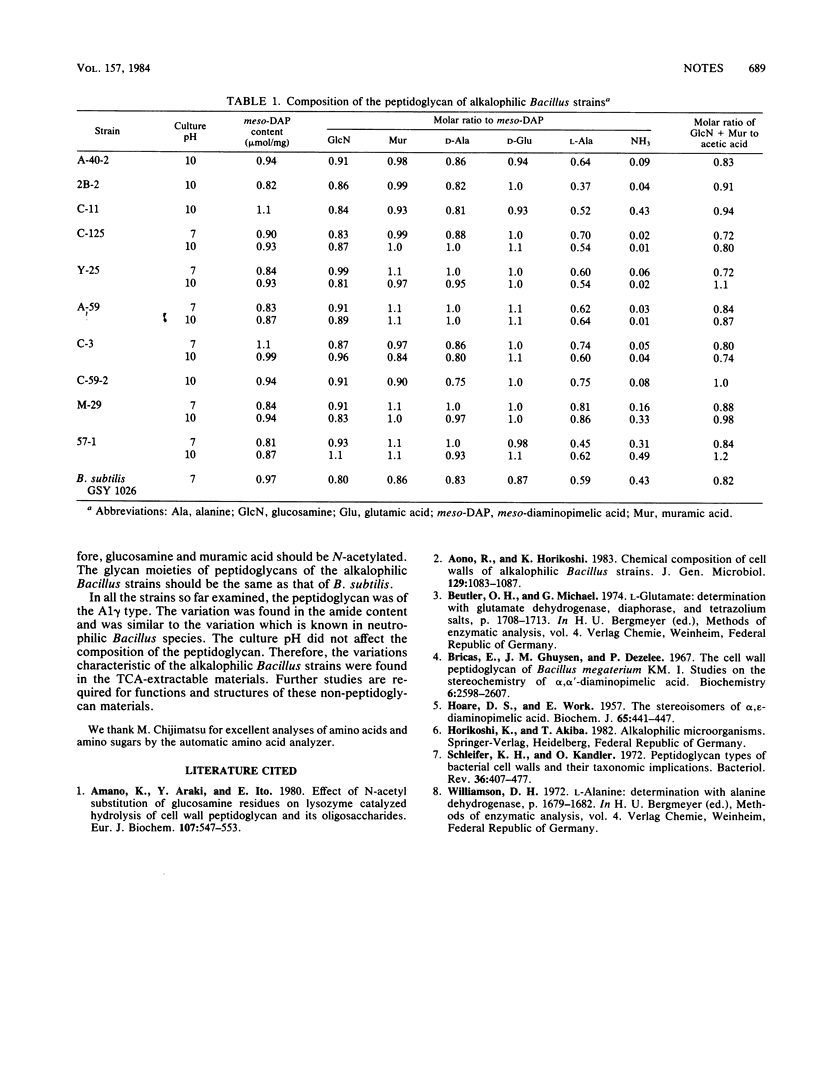
Peptidoglycans of 10 alkalophilic Bacillus strains were isolated as trichloroacetic acid-insoluble materials from cell walls prepared by treatment with sodium dodecyl sulfate, disruption with a sonic oscillator, and trypsin digestion. Major constituents detected commonly in hydrolysates of the peptidoglycans were glucosamine, muramic acid, D- and L-alanine, D-glutamic acid, meso-diaminopimelic acid, and acetic acid. Ammonia derived from amide was found in a portion of the hydrolysates. The composition of peptidoglycan was not changed whether the strain was cultured at pH 7 or 10. All the peptidoglycan examined was of the A1 gamma type of peptidoglycan found in most strains of the genus Bacillus.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amano K., Araki Y., Ito E. Effect of N-acyl substitution at glucosamine residues on lysozyme-catalyzed hydrolysis of cell-wall peptidoglycan and its oligosaccharides. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jun;107(2):547–553. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06062.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bricas E., Ghuysen J. M., Dezélée P. The cell wall peptidoglycan of Bacillus megaterium KM. I. Studies on the stereochemistry of alpha, alpha'-diaminopimelic acid. Biochemistry. 1967 Aug;6(8):2598–2607. doi: 10.1021/bi00860a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOARE D. S., WORK E. The stereoisomers of alpha epsilon-diaminopimelic acid. II. Their distribution in the bacterial order Actinomycetales and in certain Eubacteriales. Biochem J. 1957 Mar;65(3):441–447. doi: 10.1042/bj0650441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleifer K. H., Kandler O. Peptidoglycan types of bacterial cell walls and their taxonomic implications. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Dec;36(4):407–477. doi: 10.1128/br.36.4.407-477.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



