Abstract
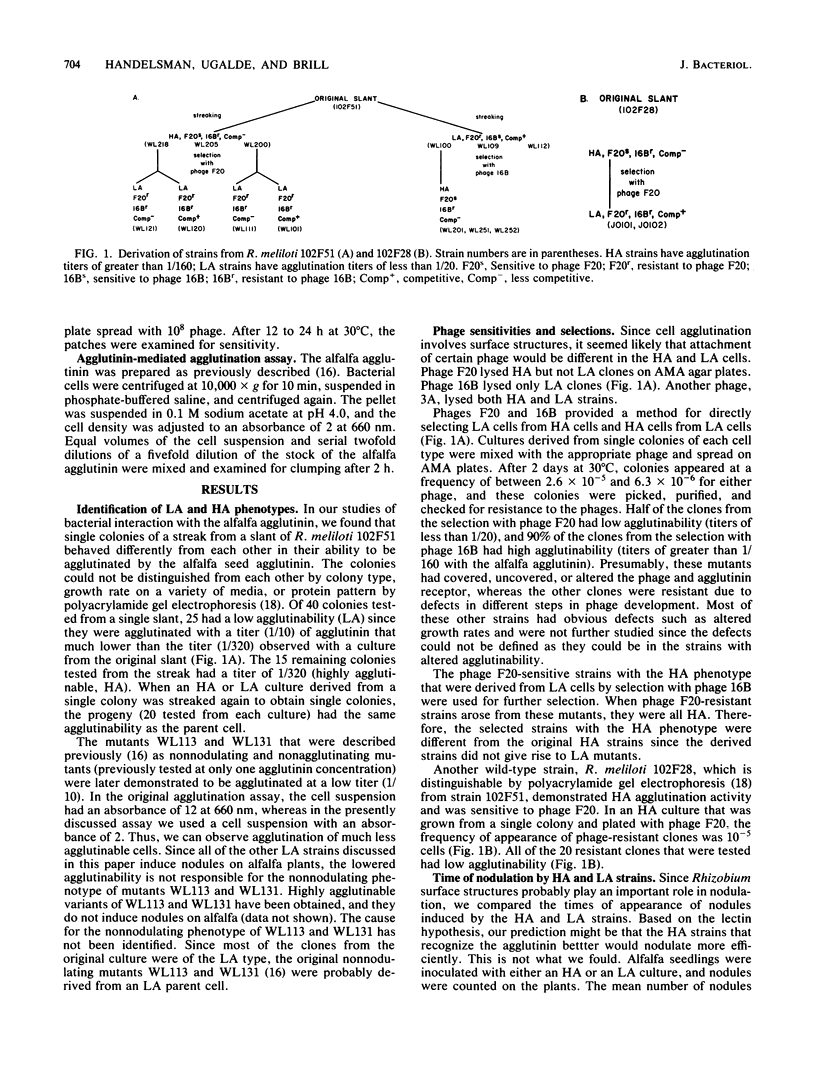
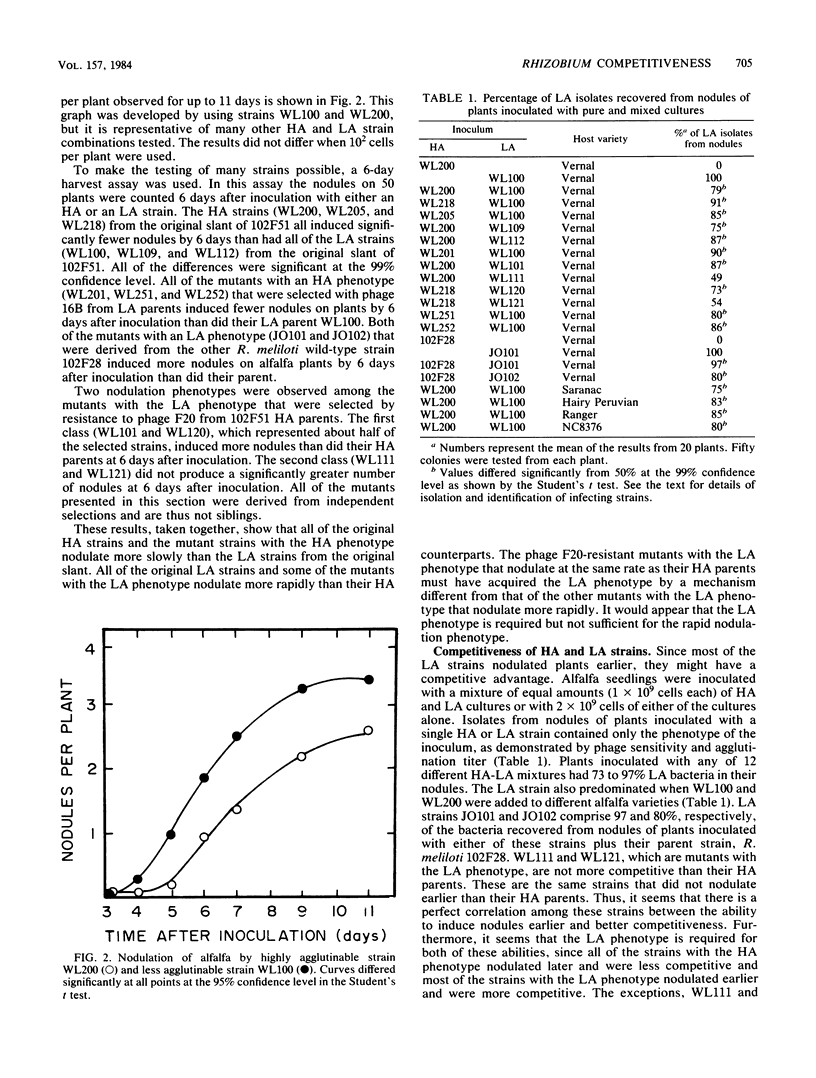
We have isolated two types of isolates having identical colony morphologies from stock cultures of two different Rhizobium meliloti strains. One isolate was agglutinated at a high-dilution titer (HA, highly agglutinable) of the alfalfa agglutinin and was sensitive to phage F20, and the other was agglutinated at a lower agglutinin titer (LA) and was sensitive to phage 16B. All LA isolates from the original slant produced nodules on alfalfa earlier than did HA strains from the original slant. When these HA and LA strains were mixed and used as the inoculum in both vermiculite and field soil in the laboratory, LA strains were always the predominant strains recovered from the nodules. LA strains were obtained from HA cells by selection for resistance to phage F20, and HA strains were obtained from LA cells by selection for resistance to phage 16B. All of the strains with the HA phenotype that were derived from LA strains by phage selection had the nodulation properties of the HA strains from the original slant. Two classes of strains with the LA phenotype were obtained from HA cells by phage selection. One was identical to the original LA strains from the slant, and the other had the nodulation properties of the HA strains. Thus, we have shown that some cell surface properties change the nodulation abilities of R. meliloti strains and, furthermore, that specific phages can be used to enrich for more competitive rhizobia.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bohlool B. B., Schmidt E. L. Lectins: a possible basis for specificity in the Rhizobium--legume root nodule symbiosis. Science. 1974 Jul 19;185(4147):269–271. doi: 10.1126/science.185.4147.269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradshaw-Rouse J. J., Whatley M. H., Coplin D. L., Woods A., Sequeira L., Kelman A. Agglutination of Erwinia stewartii Strains with a Corn Agglutinin: Correlation with Extracellular Polysaccharide Production and Pathogenicity. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Aug;42(2):344–350. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.2.344-350.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dazzo F. B., Hubbell D. H. Antigenic differences between infective and noninfective strains of Rhizobium trifolii. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Aug;30(2):172–177. doi: 10.1128/am.30.2.172-177.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dazzo F. B., Yanke W. E., Brill W. J. Trifolin: a Rhizobium recognition protein from white clover. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Mar 20;539(3):276–286. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90032-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maier R. J., Brill W. J. Mutant Strains of Rhizobium japonicum with Increased Ability to Fix Nitrogen for Soybean. Science. 1978 Aug 4;201(4354):448–450. doi: 10.1126/science.201.4354.448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noel K. D., Brill W. J. Diversity and Dynamics of Indigenous Rhizobium japonicum Populations. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Nov;40(5):931–938. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.5.931-938.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paau A. S., Bloch C. B., Brill W. J. Developmental fate of Rhizobium meliloti bacteroids in alfalfa nodules. J Bacteriol. 1980 Sep;143(3):1480–1490. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.3.1480-1490.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paau A. S., Leps W. T., Brill W. J. Agglutinin from Alfalfa Necessary for Binding and Nodulation by Rhizobium meliloti. Science. 1981 Sep 25;213(4515):1513–1515. doi: 10.1126/science.213.4515.1513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pull S. P., Pueppke S. G., Hymowitz T., Orf J. H. Soybean lines lacking the 120,000-dalton seed lectin. Science. 1978 Jun 16;200(4347):1277–1279. doi: 10.1126/science.200.4347.1277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts G. P., Leps W. T., Silver L. E., Brill W. J. Use of two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis to identify and classify Rhizobium strains. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Feb;39(2):414–422. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.2.414-422.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semu E., Hume D. J., Corke C. T. Influence of soybean inoculation and nitrogen levels on populations and serogroups of Rhizobium japonicum in Ontario. Can J Microbiol. 1979 Jun;25(6):739–745. doi: 10.1139/m79-107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



