Abstract
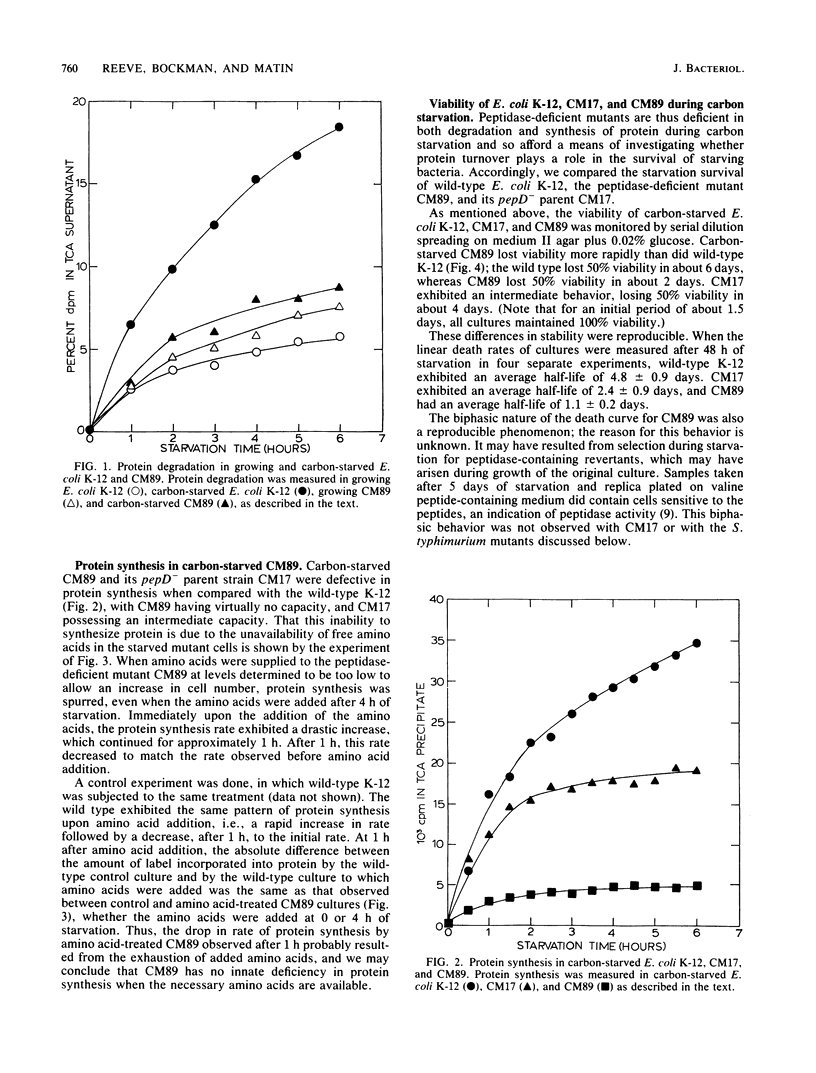
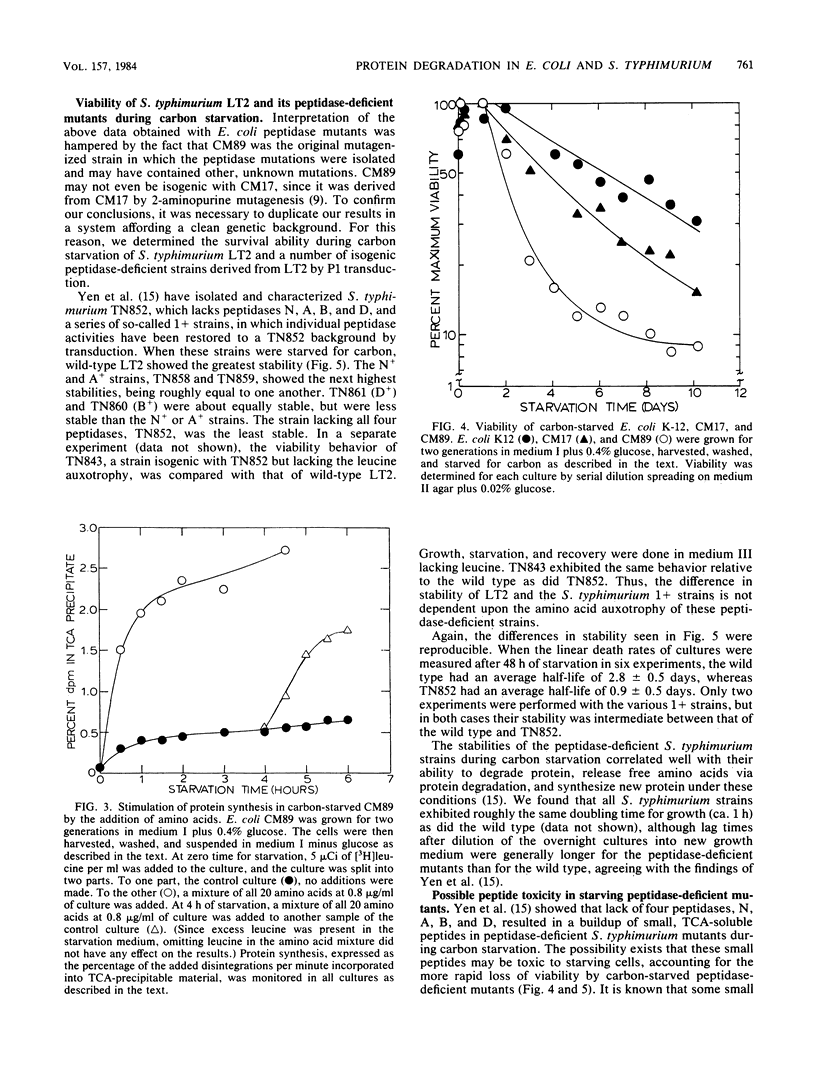
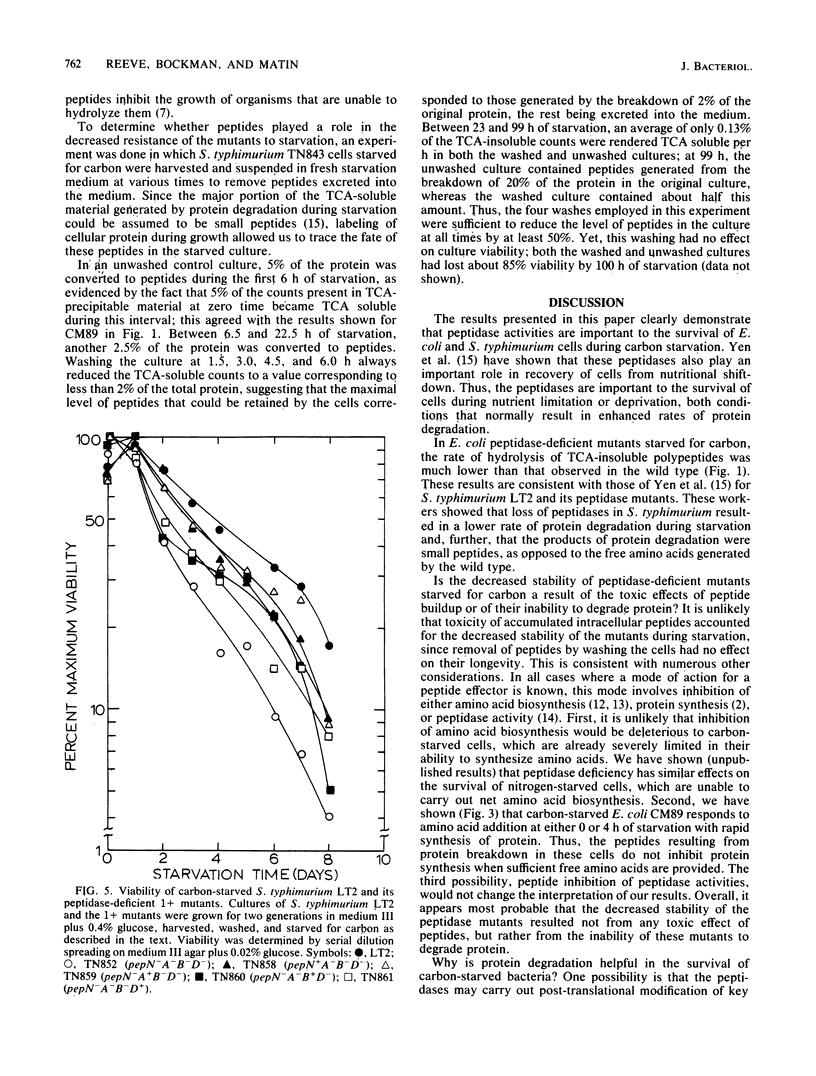
When an Escherichia coli K-12 culture was starved for glucose, 50% of the cells lost viability in about 6 days. When a K-12 mutant lacking five distinct peptidase activities, CM89, was starved in the same manner, viability was lost much more rapidly; 50% of the cells lost viability in about 2 days, whereas a parent strain lacking only one peptidase activity lost 50% viability in about 4 days. Compared with the wild-type strain and with its parent strain CM17, CM89 was defective in both protein degradation and protein synthesis during carbon starvation. Similar results were obtained with glucose-starved Salmonella typhimurium LT2 and LT2-derived mutants lacking various peptidase activities. An S. typhimurium mutant lacking four peptidases, TN852, which was deficient in both protein degradation and synthesis during carbon starvation (Yen et al., J. Mol. Biol. 143:21-33, 1980), was roughly one-third as stable as the isogenic wild type. Isogenic S. typhimurium strains that lacked various combinations of three of four peptidases and that displayed protein degradation and synthesis rates intermediate between those of LT2 and TN852 (Yen et al., J. Mol. Biol. 143:21-33, 1980) displayed corresponding stabilities during carbon starvation. These results point to a role for protein degradation in the survival of bacteria during starvation for carbon.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Calcott P. H., Postgate J. R. On substrate-accelerated death in Klebsiella aerogenes. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 Apr;70(1):115–122. doi: 10.1099/00221287-70-1-115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilvarg C., Levin Y. Response of Escherichia coli to ornithyl peptides. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jan 25;247(2):543–549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg A. L., St John A. C. Intracellular protein degradation in mammalian and bacterial cells: Part 2. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:747–803. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.003531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANDELSTAM J. The intracellular turnover of protein and nucleic acids and its role in biochemical differentiation. Bacteriol Rev. 1960 Sep;24(3):289–308. doi: 10.1128/br.24.3.289-308.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANDELSTAM J. Turnover of protein in growing and non-growing populations of Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1958 May;69(1):110–119. doi: 10.1042/bj0690110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matin A., Veldhuis C., Stegeman V., Veenhuis M. Selective advantage of a Spirillum sp. in a carbon-limited environment. Accumulation of poly-beta-hydroxybutyric acid and its role in starvation. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Jun;112(2):349–355. doi: 10.1099/00221287-112-2-349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C. G., Mackinnon K. Peptidase mutants of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1974 Oct;120(1):355–363. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.1.355-363.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C. G. Peptidases and proteases of Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1975;29:485–504. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.29.100175.002413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C. G., Schwartz G. Peptidase-deficient mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1978 Aug;135(2):603–611. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.2.603-611.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St John A. C., Conklin K., Rosenthal E., Goldberg A. L. Further evidence for the involvement of charged tRNA and guanosine tetraphosphate in the control of protein degradation in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jun 10;253(11):3945–3951. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Switzer R. L. The inactivation of microbial enzymes in vivo. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1977;31:135–157. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.31.100177.001031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vonder Haar R. A., Umbarger H. E. Isoleucine and valine metabolism in Escherichia coli. XIX. Inhibition of isoleucine biosynthesis by glycyl-leucine. J Bacteriol. 1972 Oct;112(1):142–147. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.1.142-147.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasmuth J. J., Umbarger H. E. Role for free isoleucine of glycyl-leucine in the repression of threonine deaminase in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jan;117(1):29–39. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.1.29-39.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen C., Green L., Miller C. G. Degradation of intracellular protein in Salmonella typhimurium peptidase mutants. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 15;143(1):21–33. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90122-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen C., Green L., Miller C. G. Peptide accumulation during growth of peptidase deficient mutants. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 15;143(1):35–48. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90123-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zychlinsky E., Matin A. Effect of starvation on cytoplasmic pH, proton motive force, and viability of an acidophilic bacterium, Thiobacillus acidophilus. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):371–374. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.371-374.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



