Abstract
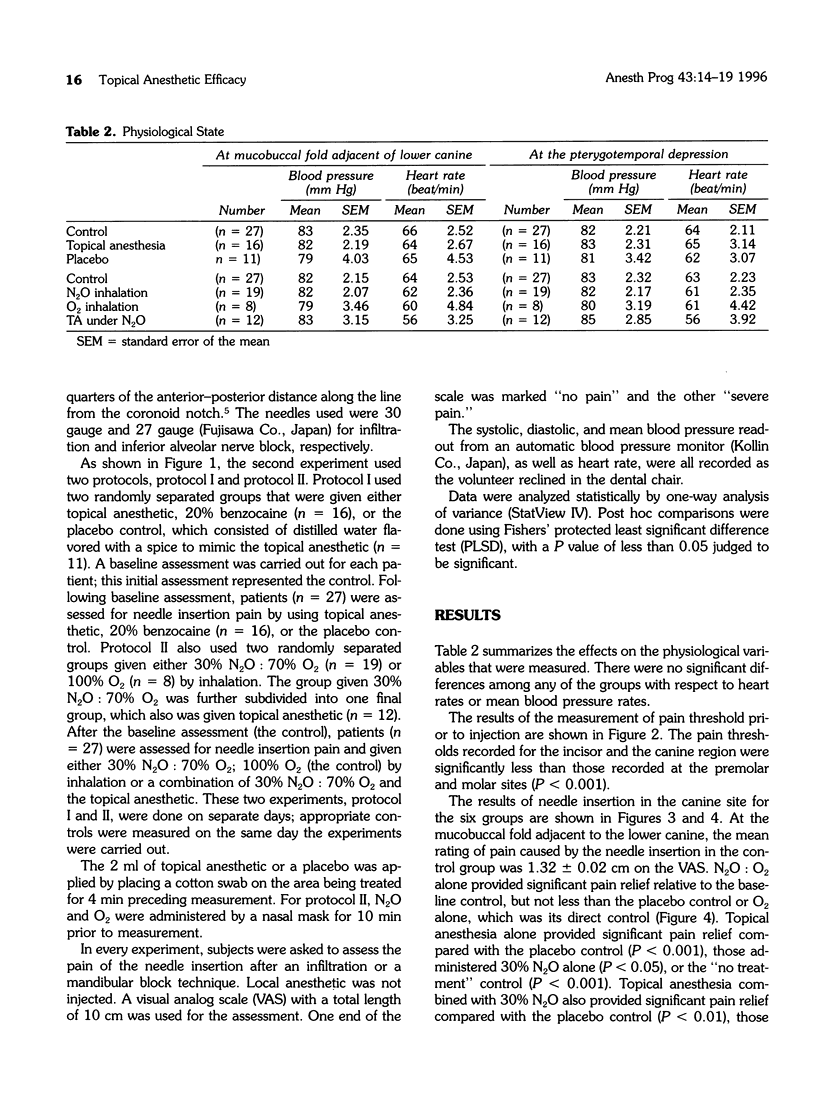
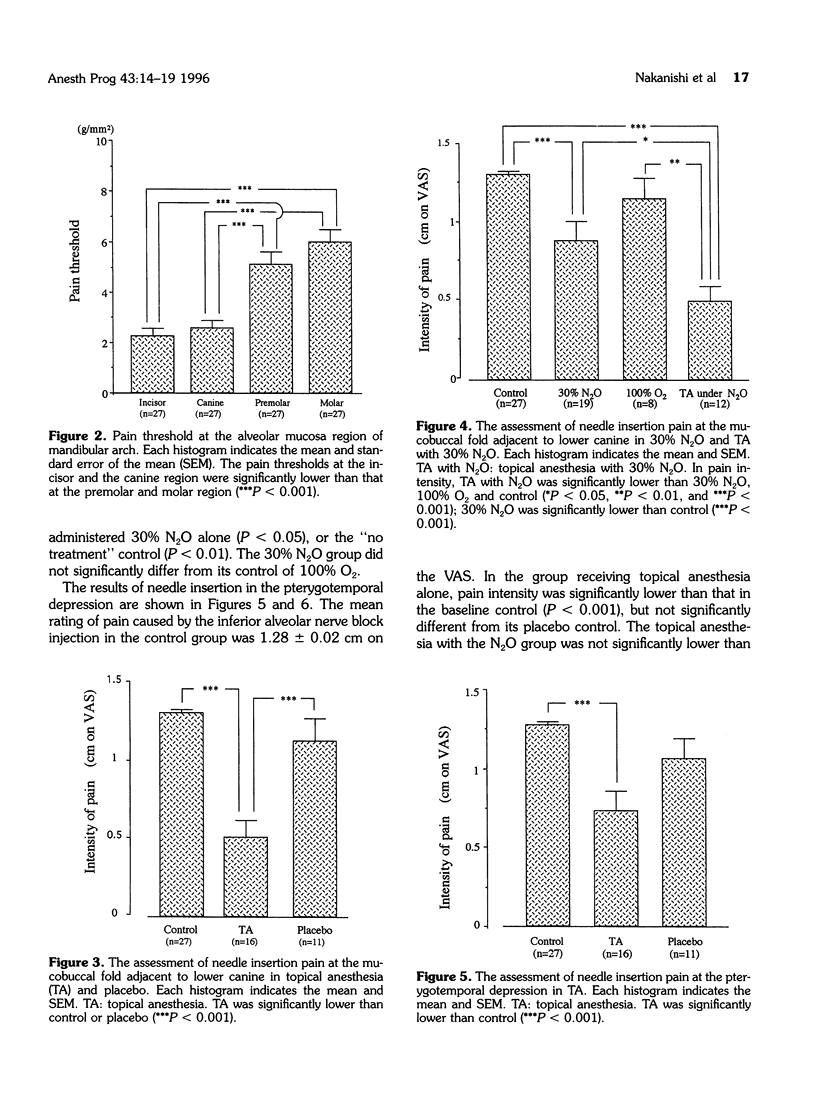
This study compared the threshold of pain sensitivity in the anterior mandibular mucobuccal fold with the posterior. This was followed by a comparison of the reduction of needle insertion pain in the anterior mucobuccal fold and the pterygo-temporal depression by either topical anesthesia or nitrous oxide inhalation. The pain threshold was determined by an analgometer, a pain-measuring device that depends on pressure readings; additionally, pain caused by a needle inserted by a normal technique was assessed using a visual analog scale (VAS). The threshold of pain was significantly lower in the incisor and canine regions than in the premolar and the molar regions (P < 0.001). Compared to a placebo, topical anesthesia significantly reduced the pain from needle insertion in the mucobuccal fold adjacent to the mandibular canine (P < 0.001), but did not significantly reduce pain in the pterygotemporal depression. The addition of 30% nitrous oxide did not significantly alter pain reduction compared to a control of 100% oxygen. These results suggest that topical anesthesia application may be effective in reducing the pain of needle insertion in the anterior mandibular mucobuccal fold, but may not be as effective for a standard inferior alveolar nerve block. The addition of 30% nitrous oxide did not lead to a significant improvement.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brownbill J. W., Walker P. O., Bourcy B. D., Keenan K. M. Comparison of inferior dental nerve block injections in child patients using 30-gauge and 25-gauge short needles. Anesth Prog. 1987 Nov-Dec;34(6):215–219. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman W. P., Arrowood J. G., Beecher H. K. THE ANALGETIC EFFECTS OF LOW CONCENTRATIONS OF NITROUS OXIDE COMPARED IN MAN WITH MORPHINE SULPHATE. J Clin Invest. 1943 Nov;22(6):871–875. doi: 10.1172/JCI101461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUNDEE J. W., MOORE J. Alterations in response to somatic pain associated with anaesthesia. IV. The effect of subanaesthetic concentrations of inhalation agents. Br J Anaesth. 1960 Oct;32:453–459. doi: 10.1093/bja/32.10.453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiset L., Milgrom P., Weinstein P., Getz T., Glassman P. Psychophysiological responses to dental injections. J Am Dent Assoc. 1985 Oct;111(4):578–583. doi: 10.14219/jada.archive.1985.0160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller N. P., Menke R. A., Meyers W. J. Perception of pain to three different intraoral penetrations of needles. J Am Dent Assoc. 1979 Nov;99(5):822–824. doi: 10.14219/jada.archive.1979.0384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill C. J., Orr D. L., 2nd A double-blind crossover comparison of topical anesthetics. J Am Dent Assoc. 1979 Feb;98(2):213–214. doi: 10.14219/jada.archive.1979.0476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kincheloe J. E., Mealiea W. L., Jr, Mattison G. D., Seib K. Psychophysical measurement on pain perception after administration of a topical anesthetic. Quintessence Int. 1991 Apr;22(4):311–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinknecht R. A., Klepac R. K., Alexander L. D. Origins and characteristics of fear of dentistry. J Am Dent Assoc. 1973 Apr;86(4):842–848. doi: 10.14219/jada.archive.1973.0165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARBROOK G. D., REES G. A., ROBERTSON G. S. RELIEF OF POST-OPERATIVE PAIN: COMPARISON OF A 25 PER CENT NITROUS-OXIDE AND OXYGEN MIXTURE WITH MORPHINE. Br Med J. 1964 Aug 22;2(5407):480–482. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5407.480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosivack R. G., Koenigsberg S. R., Maxwell K. C. An analysis of the effectiveness of two topical anesthetics. Anesth Prog. 1990 Nov-Dec;37(6):290–292. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svensson P., Petersen J. K. Anesthetic effect of EMLA occluded with Orahesive oral bandages on oral mucosa. A placebo-controlled study. Anesth Prog. 1992;39(3):79–82. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YAMADA M., MARUHASHI J., MIYAKE N. The distribution of sensory spots on the oral mucous membrane. Jpn J Physiol. 1952 Jul;2(4):328–332. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.2.328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



