Abstract
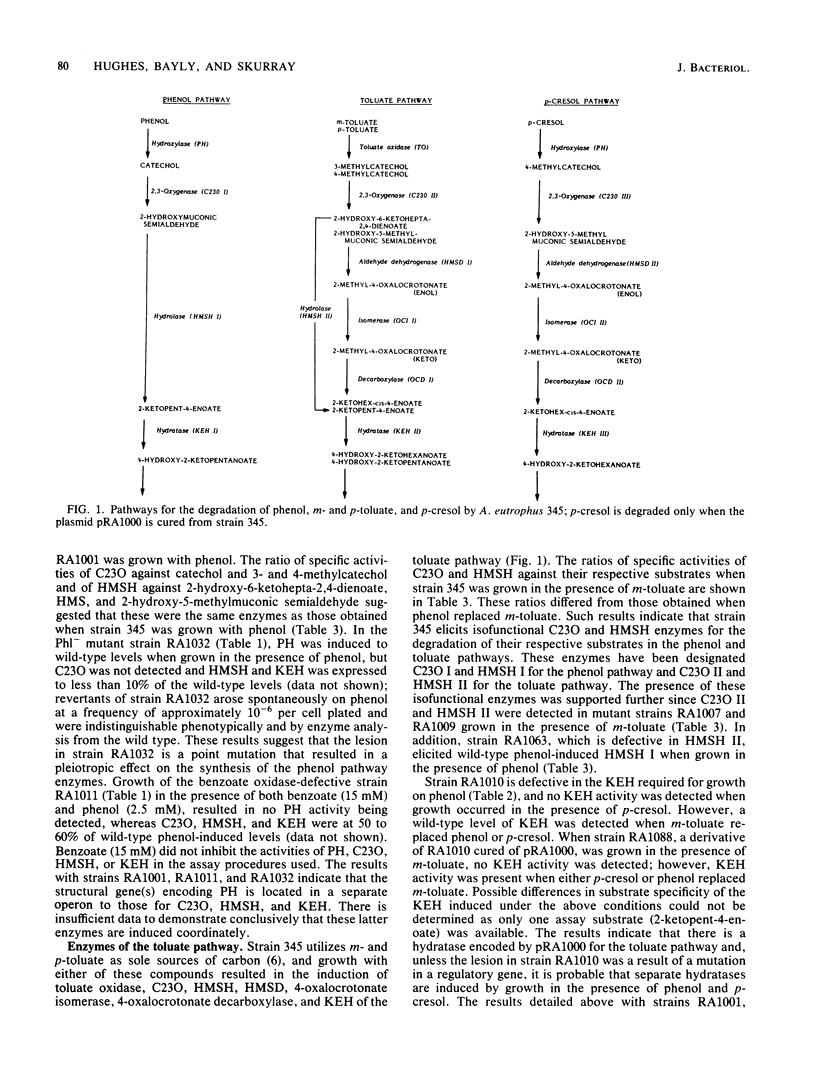
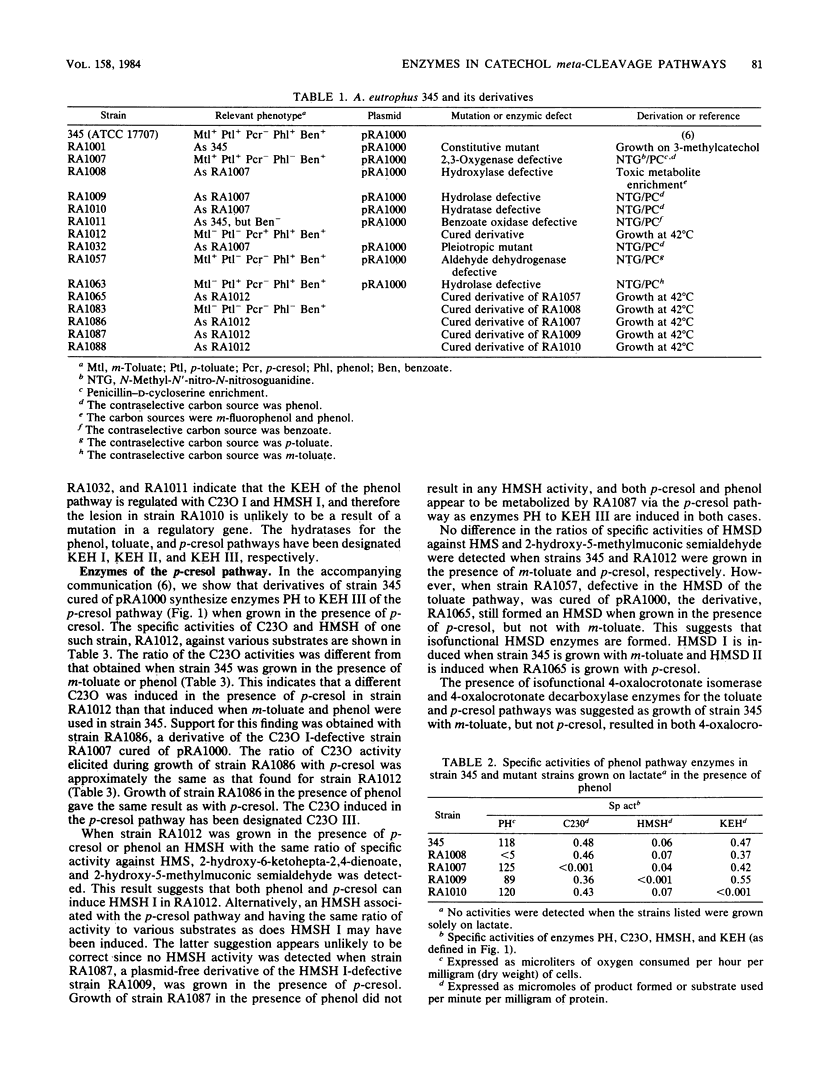
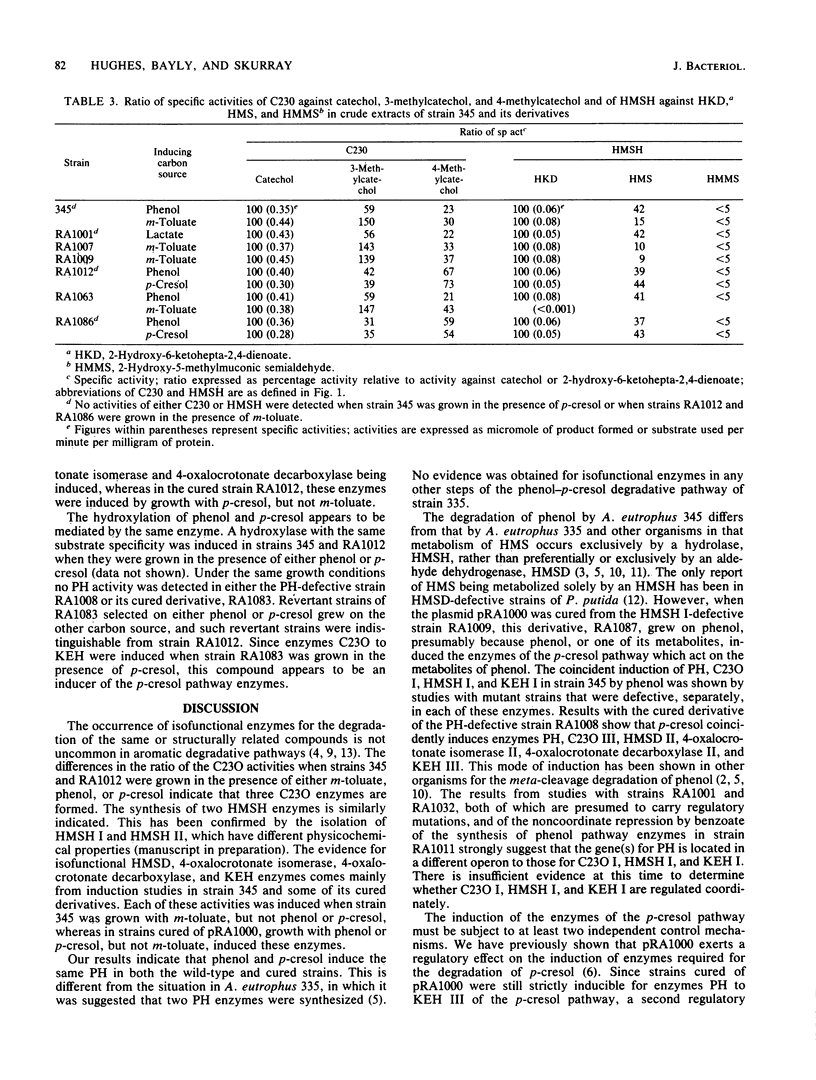
A study of the degradation of phenol, p-cresol, and m- and p-toluate by Alcaligenes eutrophus 345 has provided evidence that these compounds are metabolized via separate catechol meta-cleavage pathways. Analysis of the enzymes synthesized by wild-type and mutant strains and by strains cured of the plasmid pRA1000, which encodes m- and p-toluate degradation, indicated that two or more isofunctional enzymes mediated several steps in the pathway. The formation of three catechol 2,3-oxygenases and two 2-hydroxymuconic semialdehyde hydrolases was indicated from an examination of the ratio of the specific activities of these enzymes against various substrates. Evidence for two 2-hydroxymuconic semialdehyde dehydrogenases, two 4-oxalocrotonate isomerases and decarboxylases, and three 2-ketopent-4-enoate hydratases was derived from the induction of these enzymes under different growth conditions. Each activity was detected when the wild type was grown in the presence of m-toluate, but not when grown with phenol (except for a hydratase) or p-cresol, whereas in strains cured of pRA1000, growth with phenol or p-cresol, but not with m-toluate, induced these enzymes. Hydroxylation of phenol and p-cresol appears to be mediated by the same enzyme.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bayly R. C., Wigmore G. J. Metabolism of phenol and cresols by mutants of Pseudomonas putida. J Bacteriol. 1973 Mar;113(3):1112–1120. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.3.1112-1120.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall F. A., Sala-Trepat J. M., Williams P. A. The coexistence of two pathways for the metabolism of 2-hydroxymuconic semialdehyde in a naphthalene-grown pseudomonad. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 May 7;43(3):463–469. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90636-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes E. J., Bayly R. C. Control of catechol meta-cleavage pathway in Alcaligenes eutrophus. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jun;154(3):1363–1370. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.3.1363-1370.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes E. J., Bayly R. C., Skurray R. A. Characterization of a TOL-like plasmid from Alcaligenes eutrophus that controls expression of a chromosomally encoded p-cresol pathway. J Bacteriol. 1984 Apr;158(1):73–78. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.1.73-78.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson B. F., Stanier R. Y. Dissimilation of aromatic compounds by Alcaligenes eutrophus. J Bacteriol. 1971 Aug;107(2):468–475. doi: 10.1128/jb.107.2.468-475.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poh C. L., Bayly R. C. Evidence for isofunctional enzymes used in m-cresol and 2,5-xylenol degradation via the gentisate pathway in Pseudomonas alcaligenes. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jul;143(1):59–69. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.1.59-69.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sala-Trepat J. M., Evans W. C. The meta cleavage of catechol by Azotobacter species. 4-Oxalocrotonate pathway. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Jun 11;20(3):400–413. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01406.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigmore G. J., Bayly R. C., Di Berardino D. Pseudomonas putida mutants defective in the metabolism of the products of meta fission of catechol and its methyl analogues. J Bacteriol. 1974 Oct;120(1):31–37. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.1.31-37.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams P. A., Murray K. Metabolism of benzoate and the methylbenzoates by Pseudomonas putida (arvilla) mt-2: evidence for the existence of a TOL plasmid. J Bacteriol. 1974 Oct;120(1):416–423. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.1.416-423.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



