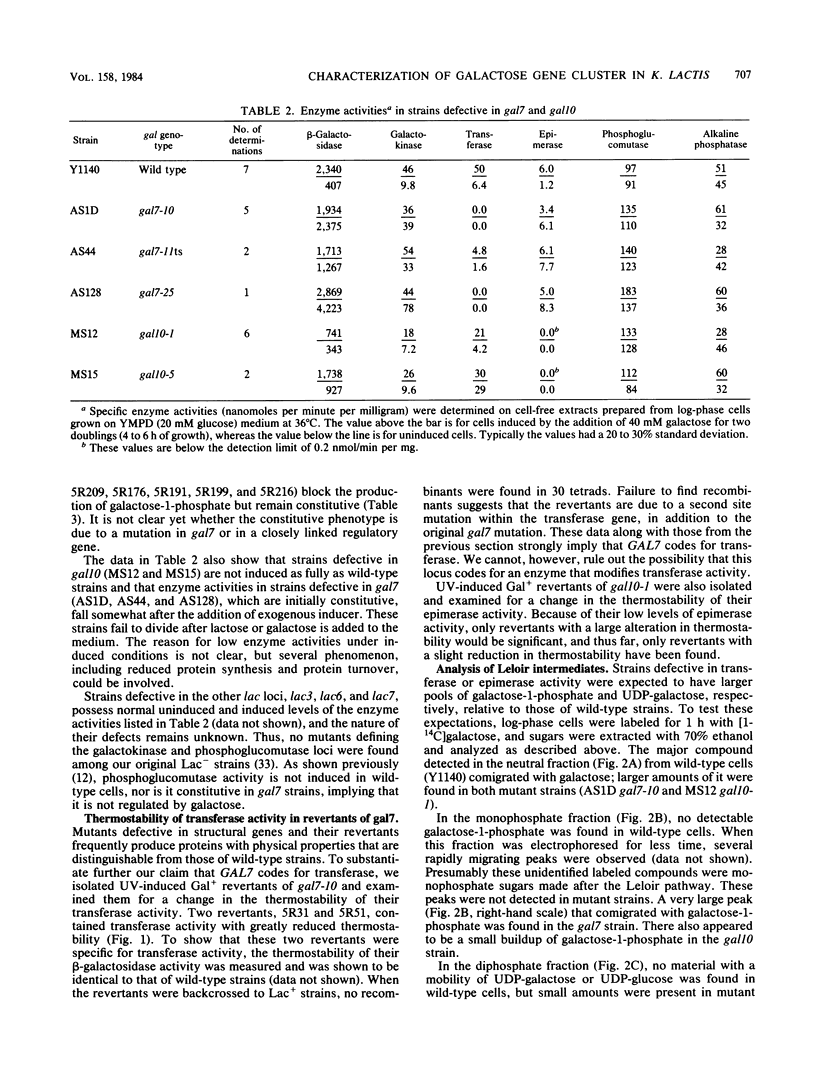
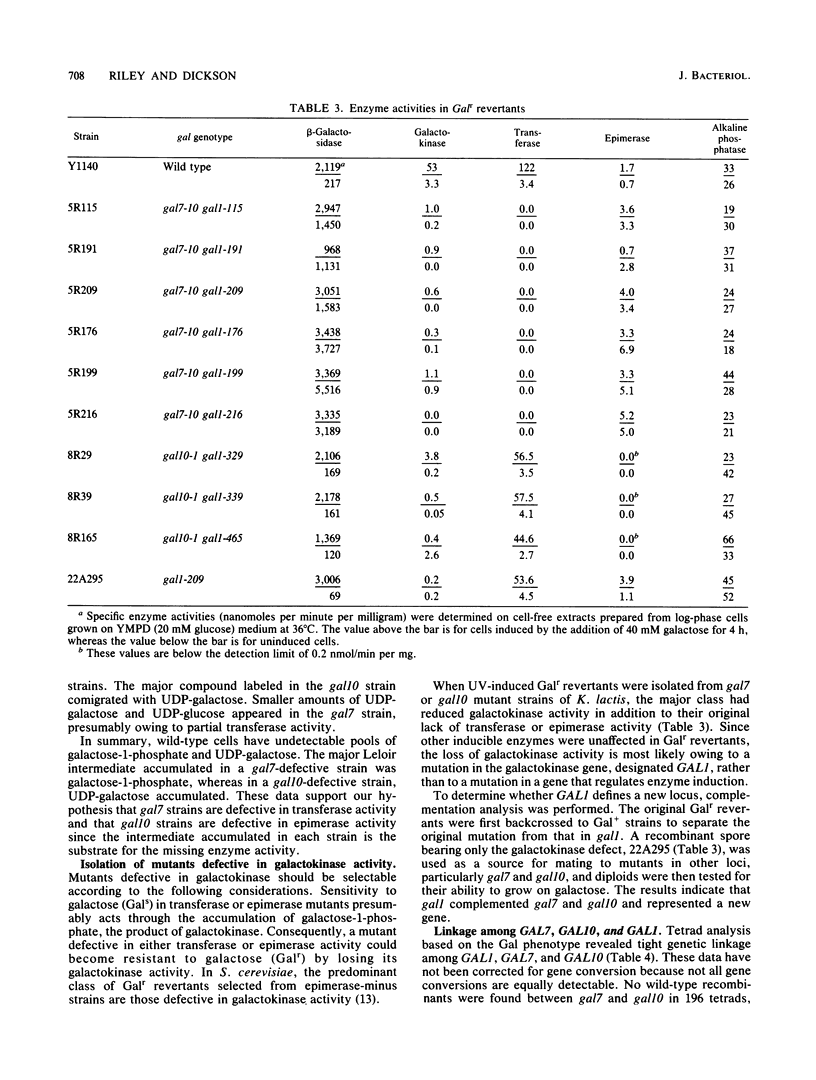
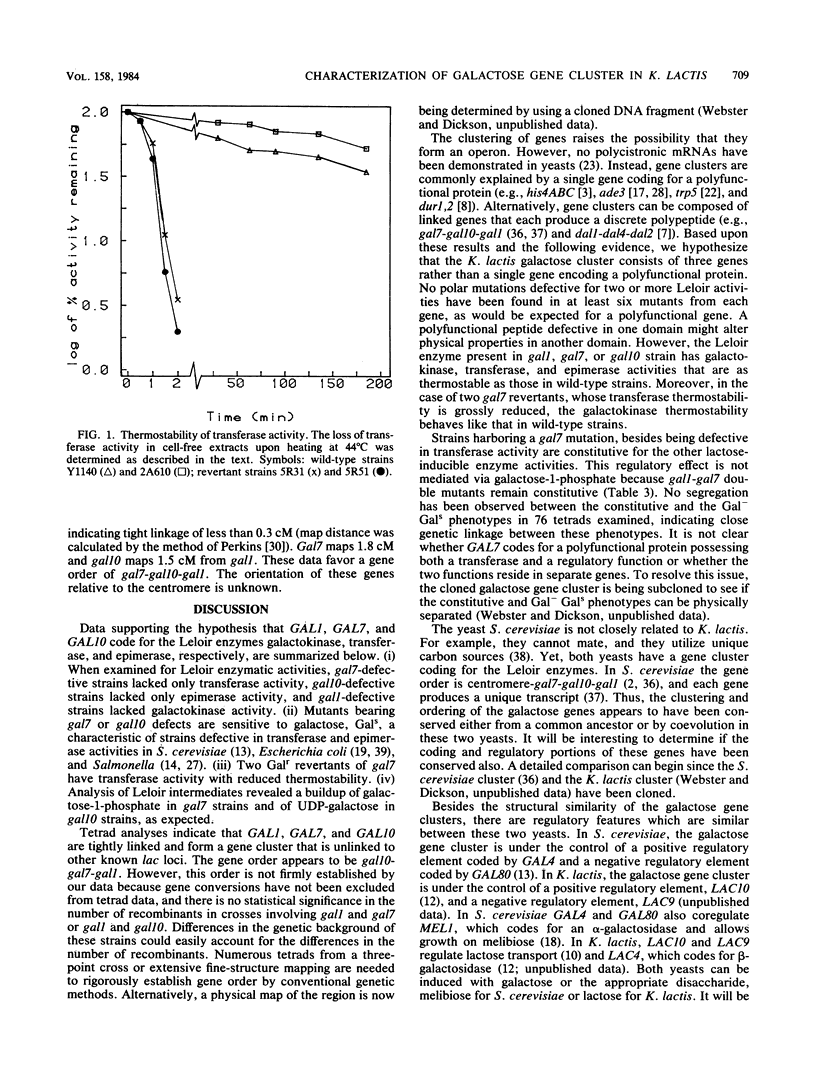
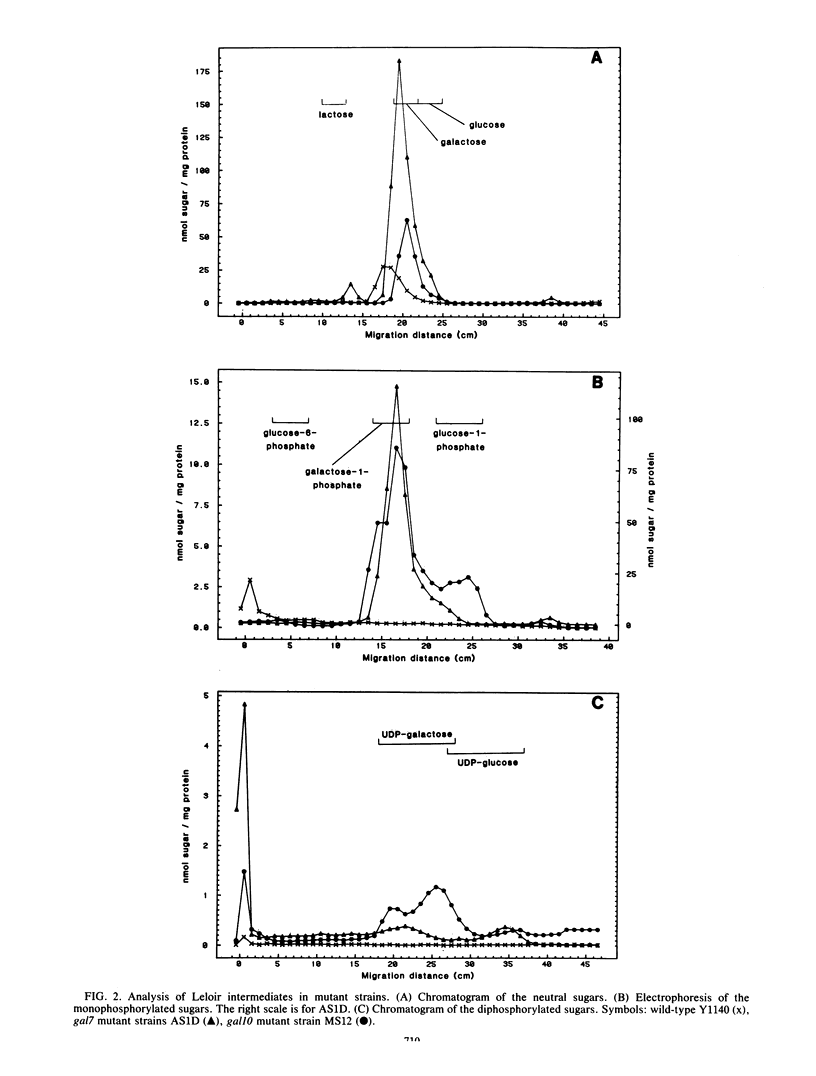
Abstract
We isolated and identified mutant strains of Kluyveromyces lactis that are defective for the Leloir pathway enzymes galactokinase, transferase, and epimerase, and we termed these loci GAL1 , GAL7 , and GAL10 , respectively. Genetic data indicate that these three genes are tightly linked, having an apparent order of GAL7 - GAL10 - GAL1 . This same gene order has been observed in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Strains harboring gal7 mutations have elevated levels of beta-galactosidase, coded by an unlinked gene, galactokinase, and epimerase activities under uninduced conditions. We investigated the genetic basis of this constitutive gene expression and found no recombinants between the constitutive and Gal- phenotypes among 76 tetrads, suggesting that either GAL7 or a tightly linked gene codes for a regulatory function. This is the second gene that has been shown to specifically coregulate expression of the genes coding for beta-galactosidase and the Leloir pathway enzymes.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams B. G. Induction of galactokinase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: kinetics of induction and glucose effects. J Bacteriol. 1972 Aug;111(2):308–315. doi: 10.1128/jb.111.2.308-315.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bassel J., Mortimer R. Genetic order of the galactose structural genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1971 Oct;108(1):179–183. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.1.179-183.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bochner B. R., Maron D. M., Ames B. N. Detection of phosphate esters on chromatograms: an improved reagent. Anal Biochem. 1981 Oct;117(1):81–83. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90695-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broach J. R. Galactose regulation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The enzymes encoded by the GAL7, 10, 1 cluster are co-ordinately controlled and separately translated. J Mol Biol. 1979 Jun 15;131(1):41–53. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90300-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARMINATTI H., PASSERON S., DANKERT M., RECONDO E. SEPARATION OF SUGAR NUCLEOTIDES, PHOSPHORIC ESTERS AND FREE SUGARS BY PAPER CHROMATOGRAPHY WITH SOLVENTS CONTAINING BORATES OF ORGANIC BASES. J Chromatogr. 1965 May;18:342–348. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)80372-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper T. G., Gorski M., Turoscy V. A cluster of three genes responsible for allantoin degradation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1979 Jun;92(2):383–396. doi: 10.1093/genetics/92.2.383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper T. G., Lam C., Turoscy V. Structural analysis of the dur loci in S. cerevisiae: two domains of a single multifunctional gene. Genetics. 1980 Mar;94(3):555–580. doi: 10.1093/genetics/94.3.555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper T. G., Lawther R. P. Induction of the allantoin degradative enzymes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by the last intermediate of the pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Aug;70(8):2340–2344. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.8.2340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOUGLAS H. C., HAWTHORNE D. C. ENZYMATIC EXPRESSION AND GENETIC LINKAGE OF GENES CONTROLLING GALACTOSE UTILIZATION IN SACCHAROMYCES. Genetics. 1964 May;49:837–844. doi: 10.1093/genetics/49.5.837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson R. C., Barr K. Characterization of lactose transport in Kluyveromyces lactis. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jun;154(3):1245–1251. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.3.1245-1251.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson R. C., Markin J. S. Physiological studies of beta-galactosidase induction in Kluyveromyces lactis. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jun;142(3):777–785. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.3.777-785.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson R. C., Sheetz R. M., Lacy L. R. Genetic regulation: yeast mutants constitutive for beta-galactosidase activity have an increased level of beta-galactosidase messenger ribonucleic acid. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Nov;1(11):1048–1056. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.11.1048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FUKASAWA T., NIKAIDO H. Galactose-sensitive mutants of Salmonella. Nature. 1959 Oct 10;184(Suppl 15):1168–1169. doi: 10.1038/1841168a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jobe A., Bourgeois S. lac Repressor-operator interaction. VI. The natural inducer of the lac operon. J Mol Biol. 1972 Aug 28;69(3):397–408. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90253-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston S. A., Hopper J. E. Isolation of the yeast regulatory gene GAL4 and analysis of its dosage effects on the galactose/melibiose regulon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6971–6975. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones E. W. Bipartite structure of the ade3 locus of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1977 Feb;85(2):209–223. doi: 10.1093/genetics/85.2.209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KURAHASHI K., WAHBA A. J. Interference with growth of certain Escherichia coli mutants by galactose. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1958 Nov;30(2):298–302. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(58)90054-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kew O. M., Douglas H. C. Genetic co-regulation of galactose and melibiose utilization in Saccharomyces. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jan;125(1):33–41. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.1.33-41.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laughon A., Gesteland R. F. Isolation and preliminary characterization of the GAL4 gene, a positive regulator of transcription in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6827–6831. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manney T. R. Evidence for chain termination by super-suppressible mutants in yeast. Genetics. 1968 Dec;60(4):719–733. doi: 10.1093/genetics/60.4.719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto K., Toh-e A., Oshima Y. Isolation and characterization of dominant mutations resistant to carbon catabolite repression of galactokinase synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Feb;1(2):83–93. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.2.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto K., Yoshimatsu T., Oshima Y. Recessive mutations conferring resistance to carbon catabolite repression of galactokinase synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1983 Mar;153(3):1405–1414. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.3.1405-1414.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paukert J. L., Williams G. R., Rabinowitz J. C. Formyl-methenyl-methylenetetrahydrofolate synthetase (combined); correlation of enzymic activities with limited proteolytic degradation of the protein from yeast. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jul 11;77(1):147–154. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(77)80176-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins D. D. Biochemical Mutants in the Smut Fungus Ustilago Maydis. Genetics. 1949 Sep;34(5):607–626. doi: 10.1093/genetics/34.5.607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwimmer S., Bevenue A. Reagent for Differentiation of 1,4- and 1,6-Linked Glucosaccharides. Science. 1956 Mar 30;123(3196):543–544. doi: 10.1126/science.123.3196.543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segawa T., Fukasawa T. The enzymes of the galactose cluster in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Purification and characterization of galactose-1-phosphate uridylyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 10;254(21):10707–10709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheetz R. M., Dickson R. C. Lac4 is the structural gene for beta-galactosidase in Kluyveromyces lactis. Genetics. 1981 Aug;98(4):729–745. doi: 10.1093/genetics/98.4.729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheetz R. M., Dickson R. C. Mutations affecting synthesis of beta-galactosidase activity in the yeast Kluyveromyces lactis. Genetics. 1980 Aug;95(4):877–890. doi: 10.1093/genetics/95.4.877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St John T. P., Davis R. W. The organization and transcription of the galactose gene cluster of Saccharomyces. J Mol Biol. 1981 Oct 25;152(2):285–315. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90244-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St John T. P., Scherer S., McDonell M. W., Davis R. W. Deletion analysis of the Saccharomyces GAL gene cluster. Transcription from three promoters. J Mol Biol. 1981 Oct 25;152(2):317–334. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90245-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart P. R. Analytical methods for yeasts. Methods Cell Biol. 1975;12:111–147. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60955-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarmolinsky M. B., Wiesmeyer H., Kalckar H. M., Jordan E. HEREDITARY DEFECTS IN GALACTOSE METABOLISM IN ESCHERICHIA COLI MUTANTS, II. GALACTOSE-INDUCED SENSITIVITY. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1959 Dec;45(12):1786–1791. doi: 10.1073/pnas.45.12.1786. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



