Abstract
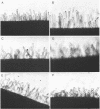
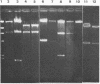
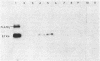
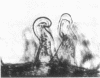
A first visible step in the nodulation of legumes by Rhizobium spp. is the deformation and curling of root hairs. We have identified and cloned DNA sequences encoding this function from two strains of Rhizobium japonicum (USDA 122 and USDA 110) with a weakly homologous probe from Rhizobium meliloti. Root hair curling encoded by the cloned DNA fragments was examined on soybeans (Glycine soja ) after conjugative transfer of these sequences in broad-host-range vectors to various bacterial genera. Pseudomonas putida gave unambiguous expression of the root hair curling genes. This enabled us to identify the 8.7-kilobase EcoRI fragments encoding root hair curling from each strain. The phenotypes encoded by the plasmids pBS1 (derived from strain USDA 122) and pBS2 (derived from strain USDA 110) are distinct and represent a phenotype characteristic of their parent R. japonicum strains. Subclones of pBS1 and pBS2 were generated in single and multicopy vectors, and their expression was analyzed in P. putida. We established that a 4.2-kilobase internal Sa/I fragment of pBS1 and a 3.5-kilobase SstI -EcoRI fragment of pBS2 are sufficient to confer root hair curling on soybeans.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bagdasarian M., Lurz R., Rückert B., Franklin F. C., Bagdasarian M. M., Frey J., Timmis K. N. Specific-purpose plasmid cloning vectors. II. Broad host range, high copy number, RSF1010-derived vectors, and a host-vector system for gene cloning in Pseudomonas. Gene. 1981 Dec;16(1-3):237–247. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90080-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beringer J. E. R factor transfer in Rhizobium leguminosarum. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Sep;84(1):188–198. doi: 10.1099/00221287-84-1-188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bánfalvi Z., Sakanyan V., Koncz C., Kiss A., Dusha I., Kondorosi A. Location of nodulation and nitrogen fixation genes on a high molecular weight plasmid of R. meliloti. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;184(2):318–325. doi: 10.1007/BF00272925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantrell M. A., Haugland R. A., Evans H. J. Construction of a Rhizobium japonicum gene bank and use in isolation of a hydrogen uptake gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):181–185. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAHRAEUS G. The infection of clover root hairs by nodule bacteria studied by a simple glass slide technique. J Gen Microbiol. 1957 Apr;16(2):374–381. doi: 10.1099/00221287-16-2-374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman A. M., Long S. R., Brown S. E., Buikema W. J., Ausubel F. M. Construction of a broad host range cosmid cloning vector and its use in the genetic analysis of Rhizobium mutants. Gene. 1982 Jun;18(3):289–296. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90167-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Hogness D. S. Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3961–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haugland R., Verma D. P. Interspecific plasmid and genomic DNA sequence homologies and localization of nif genes in effective and ineffective strains of Rhizobium japonicum. J Mol Appl Genet. 1981;1(3):205–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heberlein G. T., De Ley J., Tijtgat R. Deoxyribonucleic acid homology and taxonomy of Agrobacterium, Rhizobium, and Chromobacterium. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jul;94(1):116–124. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.1.116-124.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn B. In vitro packaging of lambda and cosmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:299–309. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68021-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holloway B. W., Krishnapillai V., Morgan A. F. Chromosomal genetics of Pseudomonas. Microbiol Rev. 1979 Mar;43(1):73–102. doi: 10.1128/mr.43.1.73-102.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ish-Horowicz D., Burke J. F. Rapid and efficient cosmid cloning. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):2989–2998. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.2989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keyser H. H., Bohlool B. B., Hu T. S., Weber D. F. Fast-growing rhizobia isolated from root nodules of soybean. Science. 1982 Mar 26;215(4540):1631–1632. doi: 10.1126/science.215.4540.1631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khmel'nitskii M. I., Zlotnikov K. M., Baev A. A. Geneticheskii analiz u Rizobium japonicum. Dokl Akad Nauk SSSR. 1981;256(1):191–195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knauf V. C., Nester E. W. Wide host range cloning vectors: a cosmid clone bank of an Agrobacterium Ti plasmid. Plasmid. 1982 Jul;8(1):45–54. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(82)90040-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosslak R. M., Bohlool B. B., Dowdle S., Sadowsky M. J. Competition of Rhizobium japonicum Strains in Early Stages of Soybean Nodulation. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Oct;46(4):870–873. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.4.870-873.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuykendall L. D. Transfer of R factors to and between genetically marked sublines of Rhizobium japonicum. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 May;37(5):862–866. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.5.862-866.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu C. P., Tucker P. W., Mushinski J. F., Blattner F. R. Mapping of heavy chain genes for mouse immunoglobulins M and D. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1348–1353. doi: 10.1126/science.6774414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maier R. J., Brill W. J. Ineffective and non-nodulating mutant strains of Rhizobium japonicum. J Bacteriol. 1976 Aug;127(2):763–769. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.2.763-769.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel M., Higa A. Calcium-dependent bacteriophage DNA infection. J Mol Biol. 1970 Oct 14;53(1):159–162. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90051-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilacinski W. P., Schmidt E. L. Plasmid transfer within and between serologically distinct strains of Rhizobium japonicum, using antibiotic resistance mutants and auxotrophs. J Bacteriol. 1981 Feb;145(2):1025–1030. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.2.1025-1030.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg C., Boistard P., Dénarié J., Casse-Delbart F. Genes controlling early and late functions in symbiosis are located on a megaplasmid in Rhizobium meliloti. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;184(2):326–333. doi: 10.1007/BF00272926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWINGHAMER E. A. Studies on induced variation in the rhizobia. I. Defined media and nodulation test techniques. Appl Microbiol. 1960 Nov;8:349–352. doi: 10.1128/am.8.6.349-352.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verma D. P., Nash D. T., Schulman H. M. Isolation and in vitro translation of soybean leghaemoglobin mRNA. Nature. 1974 Sep 6;251(5470):74–77. doi: 10.1038/251074a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woo S. L. A sensitive and rapid method for recombinant phage screening. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:389–395. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68028-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]