Abstract
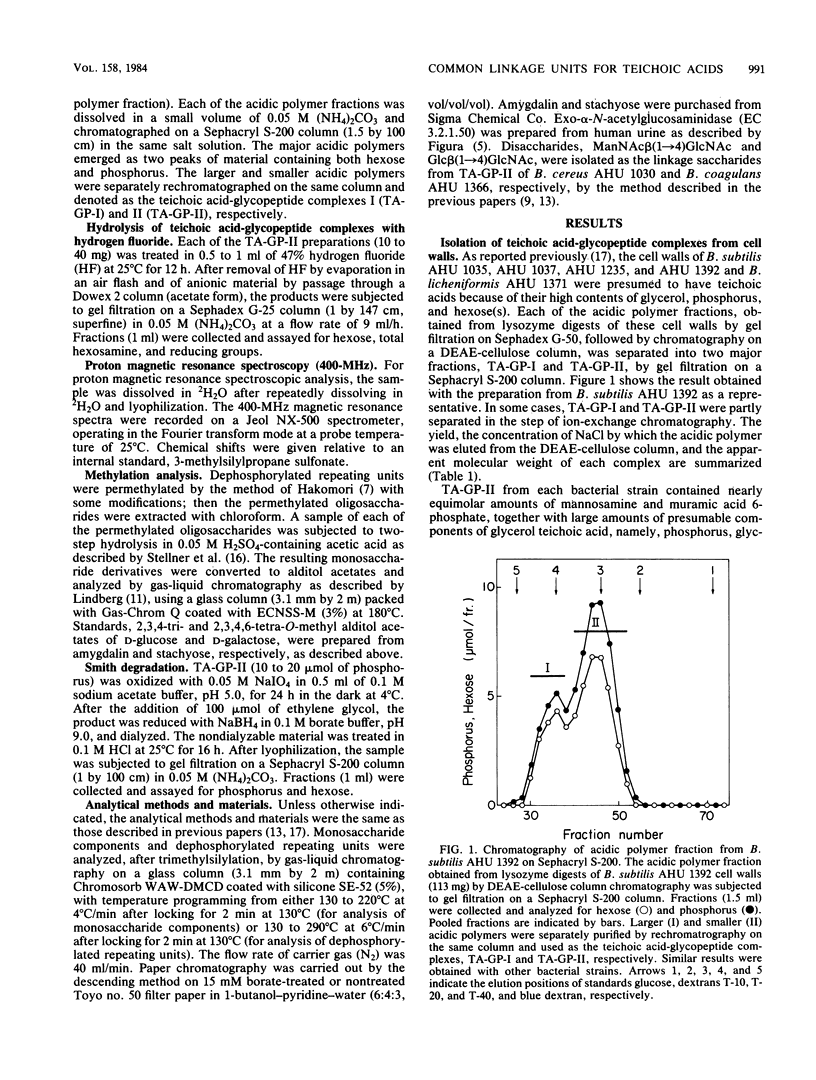
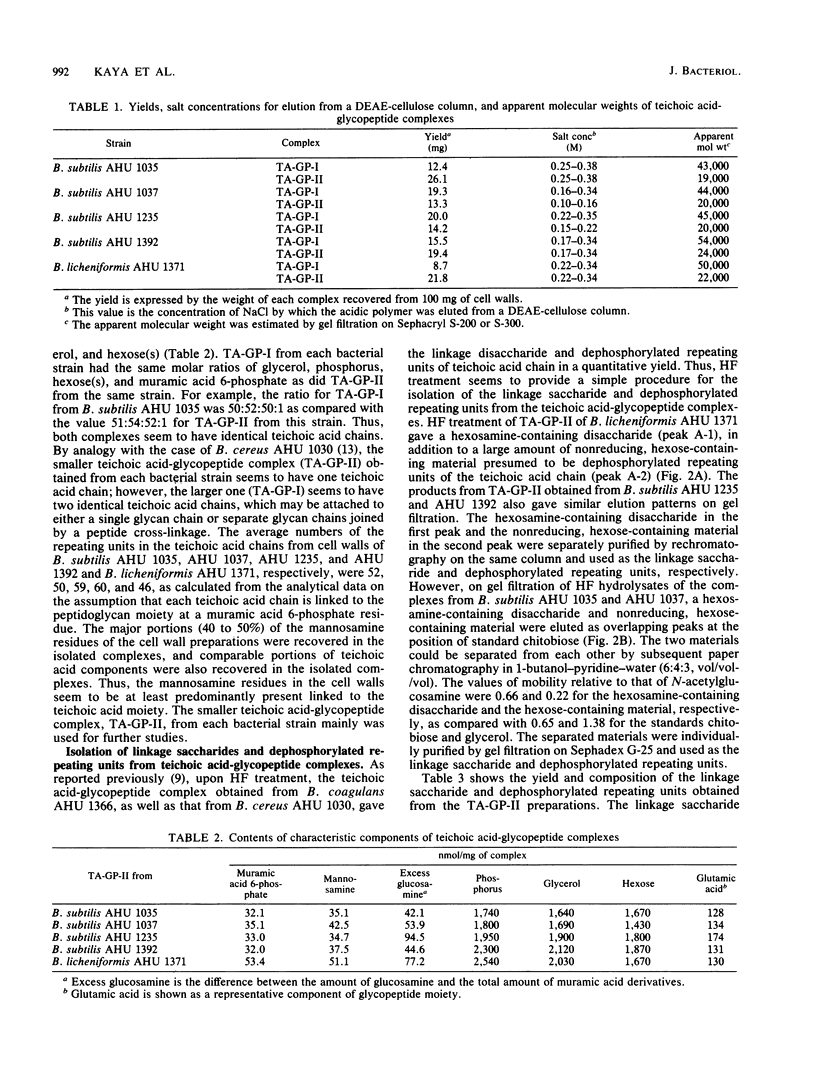
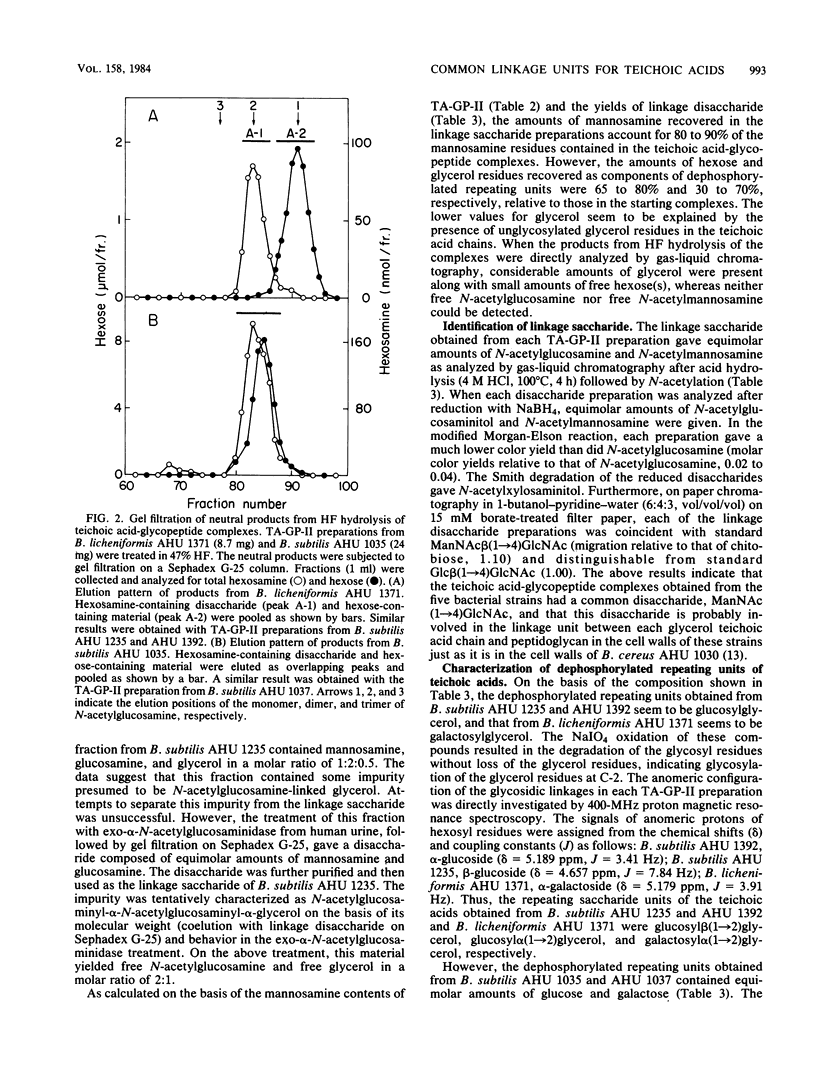
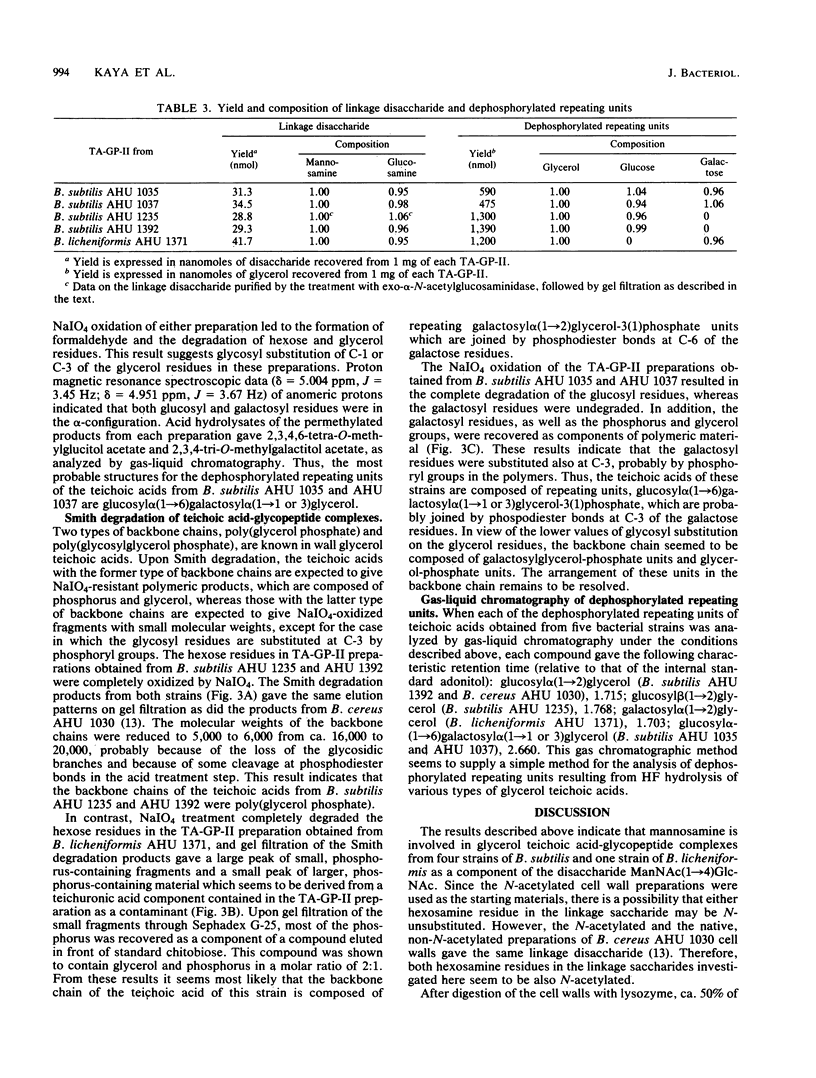
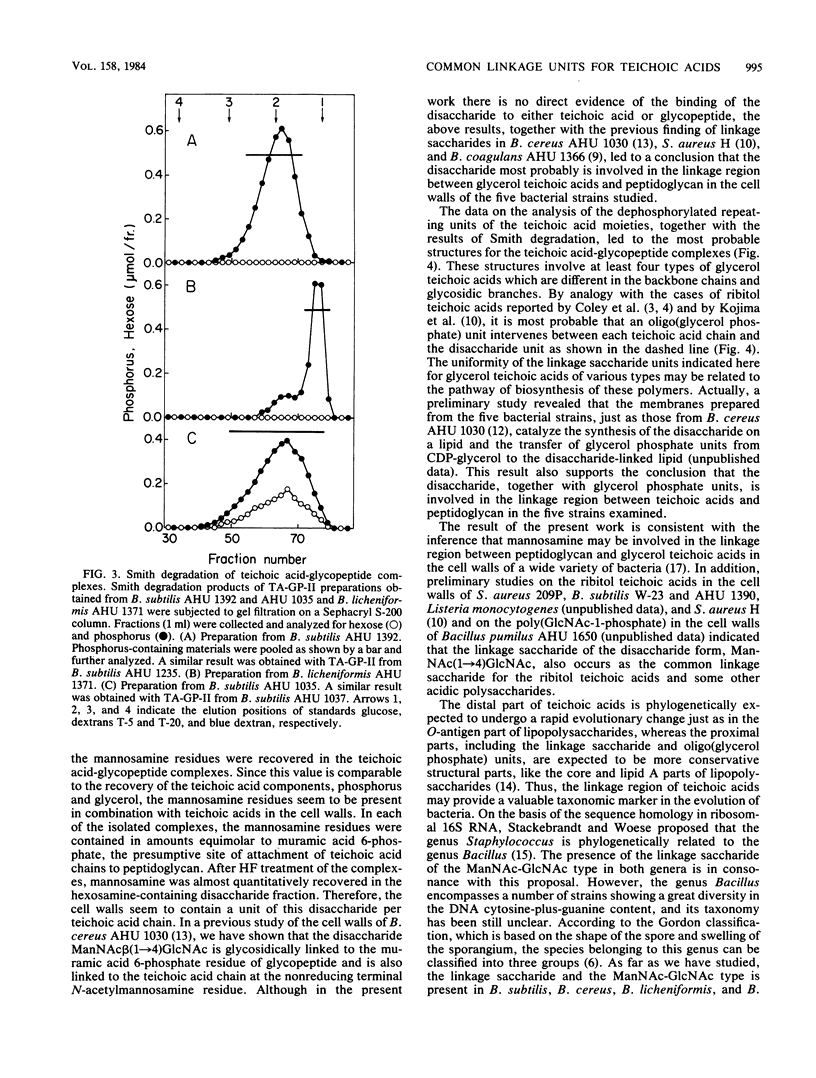
The structure of teichoic acid-glycopeptide complexes isolated from lysozyme digests of cell walls of Bacillus subtilis (four strains) and Bacillus licheniformis (one strain) was studied to obtain information on the structural relationship between glycerol teichoic acids and their linkage saccharides. Each preparation of the complexes contained equimolar amounts of muramic acid 6-phosphate and mannosamine in addition to glycopeptide components and glycerol teichoic acid components characteristic of the strain. Upon treatment with 47% hydrogen fluoride, these preparations gave, in common, a hexosamine-containing disaccharide, which was identified as N- acetylmannosaminyl (1----4) N-acetylglucosamine, along with large amounts of glycosylglycerols presumed to be the dephosphorylated repeating units of teichoic acid chains. The glycosylglycerol obtained from each bacterial strain was identified as follows: B. subtilis AHU 1392, glucosyl alpha (1----2)glycerol; B. subtilis AHU 1235, glucosyl beta(1----2) glycerol; B. subtilis AHU 1035 and AHU 1037, glucosyl alpha (1----6)galactosyl alpha (1----1 or 3)glycerol; B. licheniformis AHU 1371, galactosyl alpha (1----2)glycerol. By means of Smith degradation, the galactose residues in the teichoic acid-glycopeptide complexes from B. subtilis AHU 1035 and AHU 1037 and B. licheniformis AHU 1371 were shown to be involved in the backbone chains of the teichoic acid moieties. Thus, the glycerol teichoic acids in the cell walls of five bacterial strains seem to be joined to peptidoglycan through a common linkage disaccharide, N- acetylmannosaminyl (1----4)N-acetylglucosamine, irrespective of the structural diversity in the glycosidic branches and backbone chains.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amano K., Hazama S., Araki Y., Ito E. Isolation and characterization of structural components of Bacillus cereus AHU 1356 cell walls. Eur J Biochem. 1977 May 16;75(2):513–522. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11552.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Araki Y., Nakatani T., Nakayama K., Ito E. Occurrence of N-nonsubstituted glucosamine residues in peptidoglycan of lysozyme-resistant cell walls from Bacillus cereus. J Biol Chem. 1972 Oct 10;247(19):6312–6322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coley J., Archibald A. R., Baddiley J. A linkage unit joining peptidoglycan to teichoic acid in Staphylococcus aureus H. FEBS Lett. 1976 Jan 15;61(2):240–242. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)81047-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coley J., Tarelli E., Archibald A. R., Baddiley J. The linkage between teichoic acid and peptidoglycan in bacterial cell walls. FEBS Lett. 1978 Apr 1;88(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80594-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAKOMORI S. A RAPID PERMETHYLATION OF GLYCOLIPID, AND POLYSACCHARIDE CATALYZED BY METHYLSULFINYL CARBANION IN DIMETHYL SULFOXIDE. J Biochem. 1964 Feb;55:205–208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heptinstall J., Coley J., Ward P. J., Archibald A. R., Baddiley J. The linkage of sugar phosphate polymer to peptidoglycan in walls of Micrococcus sp. 2102. Biochem J. 1978 Feb 1;169(2):329–336. doi: 10.1042/bj1690329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaya S., Yokoyama K., Araki Y., Ito E. Structural and biosynthetic studies on linkage region between poly(galactosylglycerol phosphate) and peptidoglycan in Bacillus coagulans. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Feb 28;111(1):312–318. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(83)80153-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kojima N., Araki Y., Ito E. Structure of linkage region between ribitol teichoic acid and peptidoglycan in cell walls of Staphylococcus aureus H. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 10;258(15):9043–9045. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murazumi N., Sasaki Y., Okada J., Araki Y., Ito E. Biosynthesis of glycerol teichoic acid in Bacillus cereus: formation of linkage unit disaccharide on a lipid intermediate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Mar 31;99(2):504–510. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91773-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki Y., Araki Y., Ito E. Structure of teichoic-acid--glycopeptide complexes from cell walls of Bacillus cereus AHU 1030. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Apr 15;132(1):207–213. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07349.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleifer K. H., Stackebrandt E. Molecular systematics of prokaryotes. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1983;37:143–187. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.37.100183.001043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stellner K., Saito H., Hakomori S. I. Determination of aminosugar linkages in glycolipids by methylation. Aminosugar linkages of ceramide pentasaccharides of rabbit erythrocytes and of Forssman antigen. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Apr;155(2):464–472. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(73)90138-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoneyama T., Koike Y., Arakawa H., Yokoyama K., Sasaki Y., Kawamura T., Araki Y., Ito E., Takao S. Distribution of mannosamine and mannosaminuronic acid among cell walls of Bacillus species. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jan;149(1):15–21. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.1.15-21.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Figura K. Human alpha-N-acetylglucosaminidase. 1. Purification and properties. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Nov 1;80(2):523–533. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



