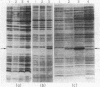
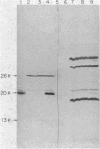
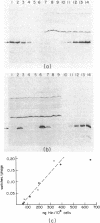
Abstract
The alternate expression of the Salmonella flagellin genes H1 and H2 is controlled by the orientation of a 995-base-pair invertible segment of DNA located at the 5' end of the H2 gene. The hin gene, which is encoded within the invertible region, is essential for the inversion of this DNA segment. We cloned the hin gene into Escherichia coli and placed it under the control of the PL promoter of bacteriophage lambda. These cells overproduced the Hin protein. In vivo inversion activity was measured by using a recombinant lambda phage which contains the H2 and lacZ genes under the control of the invertible region. Using this phage, we showed that the amount of inversion activity is proportional to the amount of Hin protein in the cell. An inactive form of the protein was purified by using the unusual solubility properties of the overproduced protein. The amino acid composition of the protein agreed with the DNA sequence of the hin gene. Antibodies were made to the isolated protein. These antibodies cross-reacted with two other unidentified E. coli proteins.
Full text
PDF

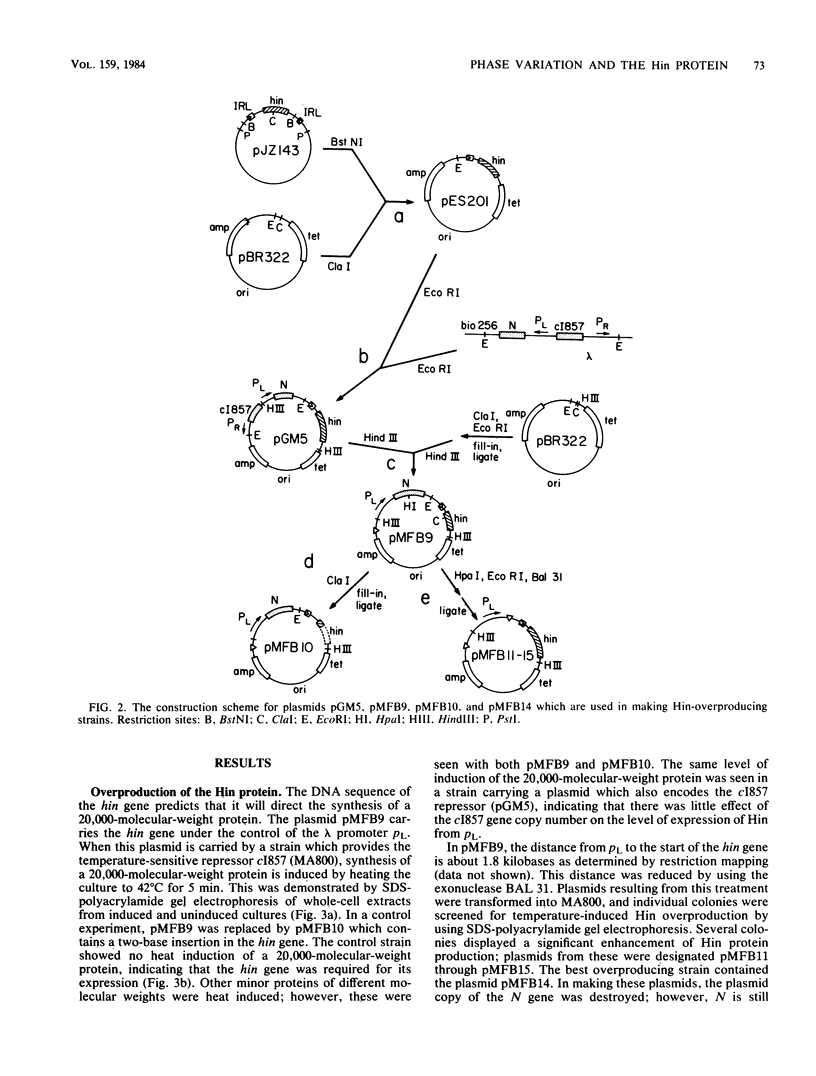
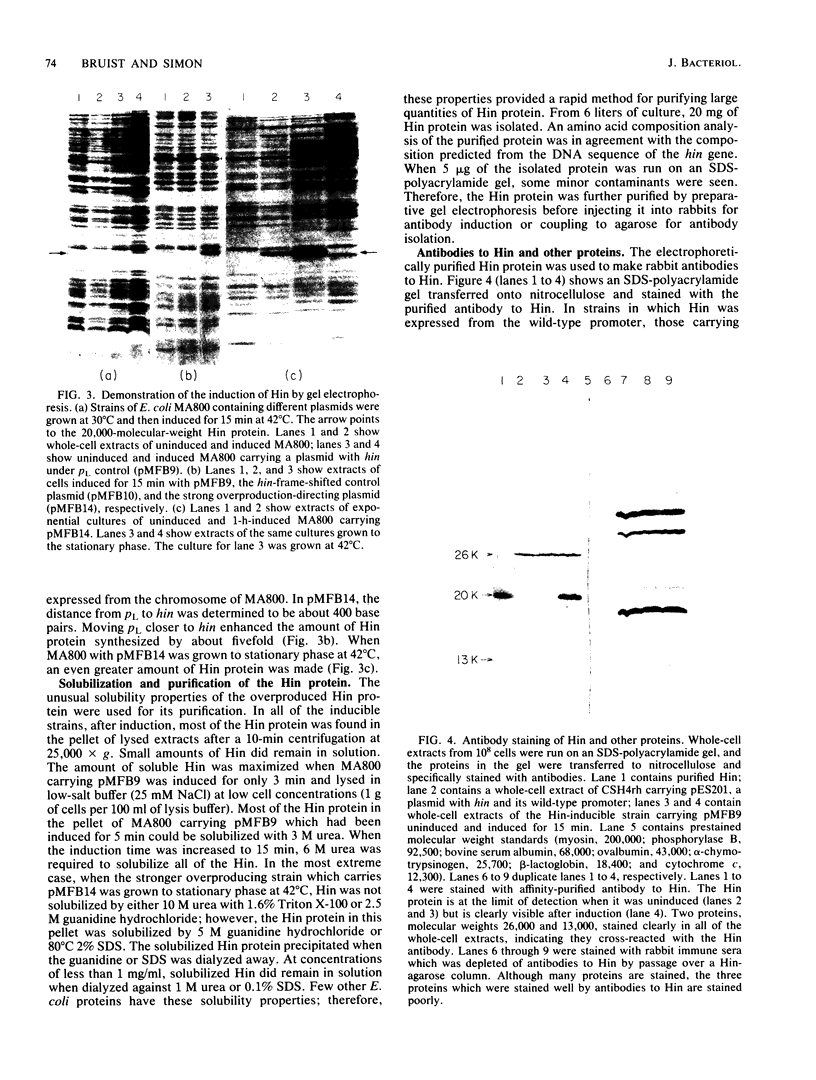

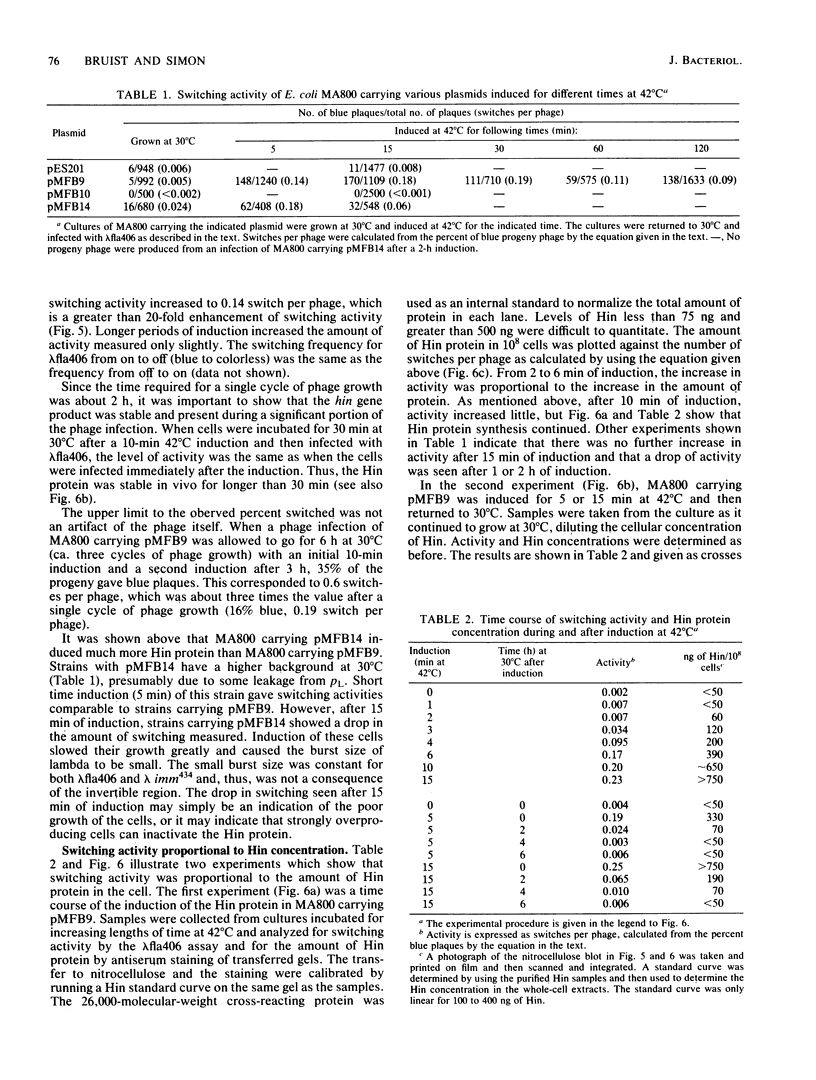
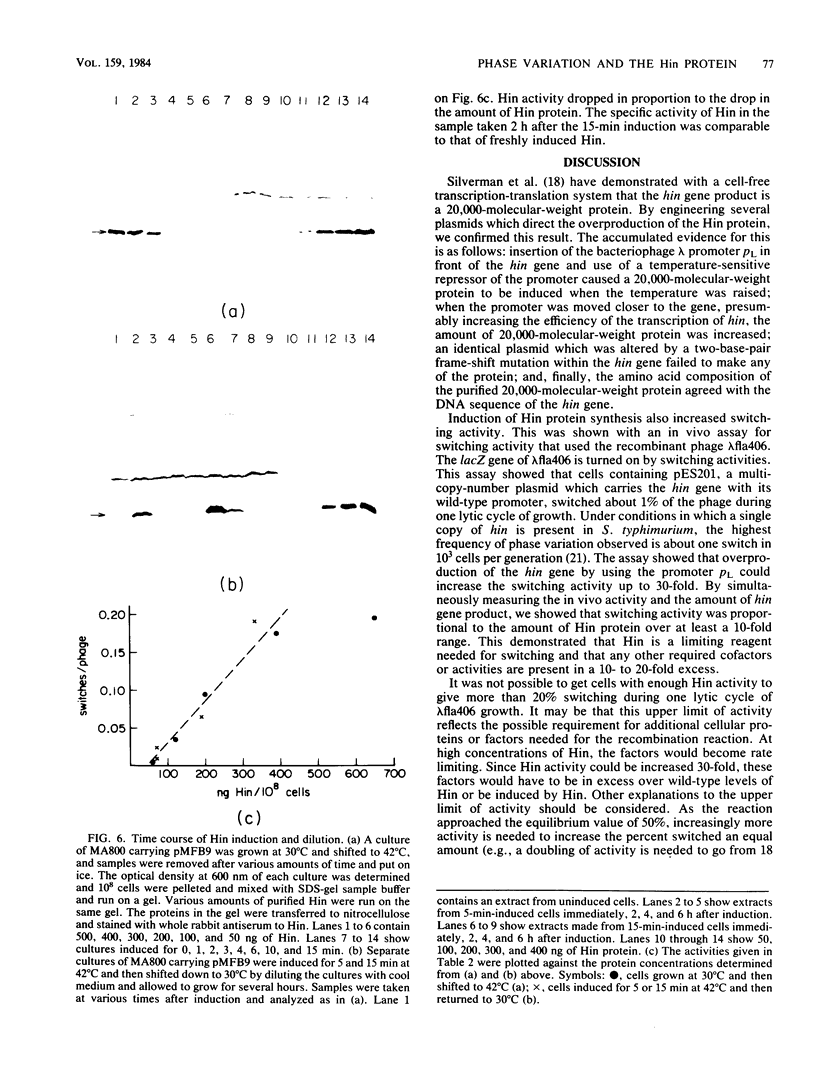


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blattner F. R., Williams B. G., Blechl A. E., Denniston-Thompson K., Faber H. E., Furlong L., Grunwald D. J., Kiefer D. O., Moore D. D., Schumm J. W. Charon phages: safer derivatives of bacteriophage lambda for DNA cloning. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):161–169. doi: 10.1126/science.847462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enomoto M., Oosawa K., Momota H. Mapping of the pin locus coding for a site-specific recombinase that causes flagellar-phase variation in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1983 Nov;156(2):663–668. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.2.663-668.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill R., Heffron F., Dougan G., Falkow S. Analysis of sequences transposed by complementation of two classes of transposition-deficient mutants of Tn3. J Bacteriol. 1978 Nov;136(2):742–756. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.2.742-756.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesman M. E., Adhya S., Das A. Transcription antitermination by bacteriophage lambda N gene product. J Mol Biol. 1980 Jun 15;140(1):57–75. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90356-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkes R., Niday E., Gordon J. A dot-immunobinding assay for monoclonal and other antibodies. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):142–147. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90677-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedgpeth J., Ballivet M., Eisen H. Lambda phage promoter used to enhance expression of a plasmid-cloned gene. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Jul 11;163(2):197–203. doi: 10.1007/BF00267410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunkapiller M. W., Lujan E., Ostrander F., Hood L. E. Isolation of microgram quantities of proteins from polyacrylamide gels for amino acid sequence analysis. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:227–236. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91019-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komeda Y., Silverman M., Simon M. Genetic analysis of Escherichia coli K-12 region I flagellar mutants. J Bacteriol. 1977 Sep;131(3):801–808. doi: 10.1128/jb.131.3.801-808.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- March S. C., Parikh I., Cuatrecasas P. A simplified method for cyanogen bromide activation of agarose for affinity chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1974 Jul;60(1):149–152. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90139-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plasterk R. H., Brinkman A., van de Putte P. DNA inversions in the chromosome of Escherichia coli and in bacteriophage Mu: relationship to other site-specific recombination systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(17):5355–5358. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.17.5355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed R. R. Transposon-mediated site-specific recombination: a defined in vitro system. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):713–719. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90178-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott T. N., Simon M. I. Genetic analysis of the mechanism of the Salmonella phase variation site specific recombination system. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;188(2):313–321. doi: 10.1007/BF00332694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman M., Simon M. Phase variation: genetic analysis of switching mutants. Cell. 1980 Apr;19(4):845–854. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90075-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman M., Zieg J., Hilmen M., Simon M. Phase variation in Salmonella: genetic analysis of a recombinational switch. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):391–395. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman M., Zieg J., Mandel G., Simon M. Analysis of the functional components of the phase variation system. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981;45(Pt 1):17–26. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1981.045.01.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman M., Zieg J., Simon M. Flagellar-phase variation: isolation of the rh1 gene. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):517–523. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.517-523.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M., Zieg J., Silverman M., Mandel G., Doolittle R. Phase variation: evolution of a controlling element. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1370–1374. doi: 10.1126/science.6251543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zieg J., Hilmen M., Simon M. Regulation of gene expression by site-specific inversion. Cell. 1978 Sep;15(1):237–244. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90098-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zieg J., Silverman M., Hilmen M., Simon M. Recombinational switch for gene expression. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):170–172. doi: 10.1126/science.322276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zieg J., Simon M. Analysis of the nucleotide sequence of an invertible controlling element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4196–4200. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]