Abstract
We have studied the regulation of the lambda cII gene in vivo using cloned lambda fragments. Lambda N protein stimulated cII expression. Surprisingly, although very high cII protein levels were detected by gel electrophoresis, little cII protein activity, measured as stimulation of the lambda pI and pE promoters, was observed. The half-life of cII protein depended critically on its initial level. At low concentrations its half-life was as short as 1.5 min, whereas at high cII protein levels, it could be as long as 22 min. The Escherichia coli mutant ER437 directs lambda towards lysogeny; cII protein was more stable in this strain than in the wild type. On the other hand, although cyclic AMP is required for efficient lysogeny, it did not appear to influence the synthesis, stability, or activity of cII protein.
Full text
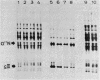
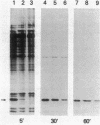
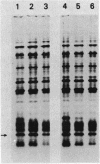
PDF

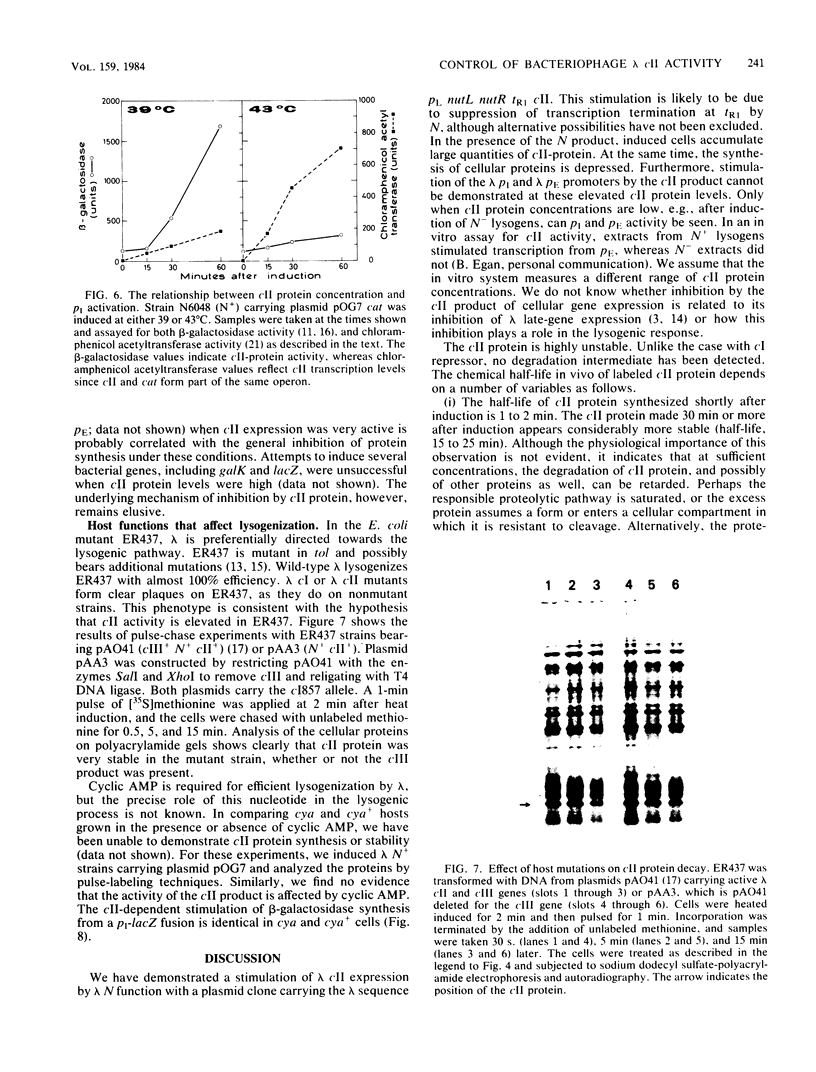
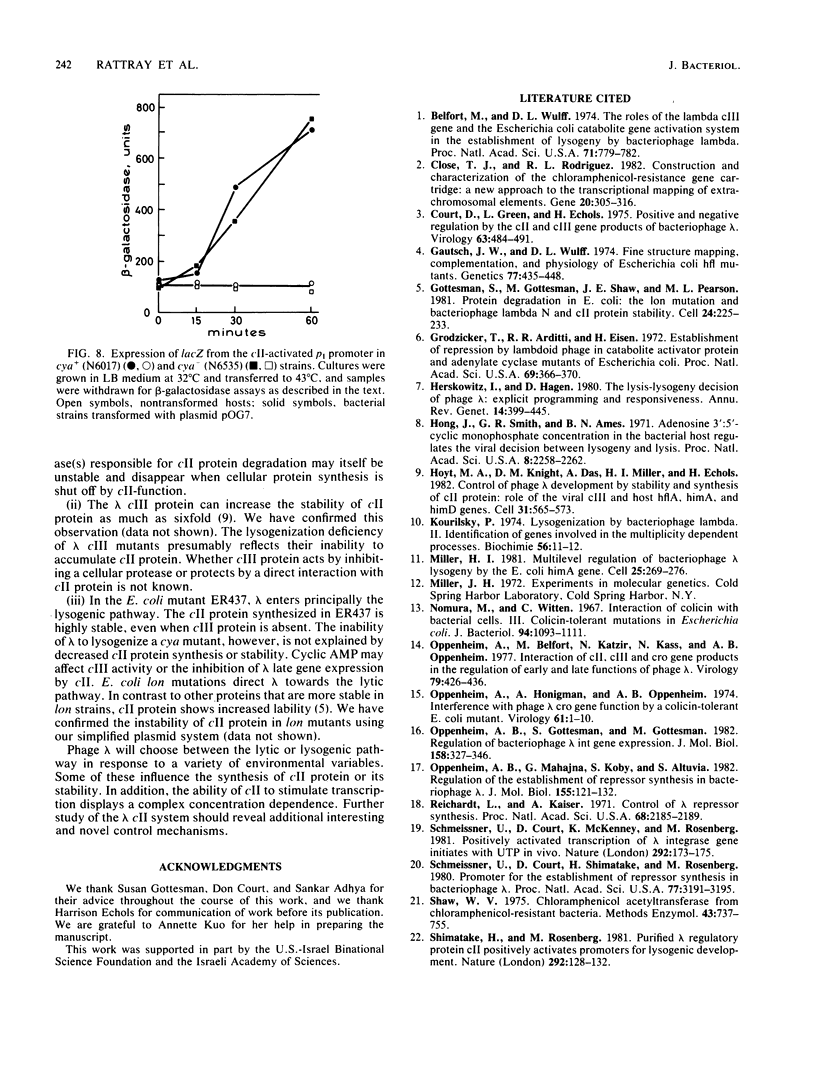
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Belfort M., Wulff D. The roles of the lambda c3 gene and the Escherichia coli catabolite gene activation system in the establishment of lysogeny by bacteriophage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Mar;71(3):779–782. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.3.779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Close T. J., Rodriguez R. L. Construction and characterization of the chloramphenicol-resistance gene cartridge: a new approach to the transcriptional mapping of extrachromosomal elements. Gene. 1982 Dec;20(2):305–316. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90048-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Court D., Green L., Echols H. Positive and negative regulation by the cII and cIII gene products of bacteriophage lambda. Virology. 1975 Feb;63(2):484–491. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90321-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautsch J. W., Wulff D. L. Fine structure mapping, complementation, and physiology of Escherichia coli hfl mutants. Genetics. 1974 Jul;77(3):435–448. doi: 10.1093/genetics/77.3.435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesman S., Gottesman M., Shaw J. E., Pearson M. L. Protein degradation in E. coli: the lon mutation and bacteriophage lambda N and cII protein stability. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):225–233. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90518-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grodzicker T., Arditti R. R., Eisen H. Establishment of repression by lambdoid phage in catabolite activator protein and adenylate cyclase mutants of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Feb;69(2):366–370. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.2.366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herskowitz I., Hagen D. The lysis-lysogeny decision of phage lambda: explicit programming and responsiveness. Annu Rev Genet. 1980;14:399–445. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.14.120180.002151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong J. S., Smith G. R., Ames B. N. Adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate concentration in the bacterial host regulates the viral decision between lysogeny and lysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Sep;68(9):2258–2262. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.9.2258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyt M. A., Knight D. M., Das A., Miller H. I., Echols H. Control of phage lambda development by stability and synthesis of cII protein: role of the viral cIII and host hflA, himA and himD genes. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(3 Pt 2):565–573. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90312-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller H. I. Multilevel regulation of bacteriophage lambda lysogeny by the E. coli himA gene. Cell. 1981 Jul;25(1):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90252-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura M., Witten C. Interaction of colicins with bacterial cells. 3. Colicin-tolerant mutations in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1967 Oct;94(4):1093–1111. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.4.1093-1111.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheim A. B., Gottesman S., Gottesman M. Regulation of bacteriophage lambda int gene expression. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jul 5;158(3):327–346. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90201-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheim A. B., Mahajna G., Koby S., Altuvia S. Regulation of the establishment of repressor synthesis in bacteriophage lambda. J Mol Biol. 1982 Feb 25;155(2):121–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90440-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheim A., Belfort M., Katzir N., Kass N., Oppenheim A. B. Interaction of cII, cIII, and cro gene products in the regulation of early and late functions of phage lambda. Virology. 1977 Jun 15;79(2):426–436. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90368-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheim A., Honigman A., Oppenheim A. B. Interference with phage lambda cro gene function by a colicin-tolerant Escherichia coli mutant. Virology. 1974 Sep;61(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90236-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichardt L., Kaiser A. D. Control of lambda repressor synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Sep;68(9):2185–2189. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.9.2185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmeissner U., Court D., McKenney K., Rosenberg M. Positively activated transcription of lambda integrase gene initiates with UTP in vivo. Nature. 1981 Jul 9;292(5819):173–175. doi: 10.1038/292173a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmeissner U., Court D., Shimatake H., Rosenberg M. Promoter for the establishment of repressor synthesis in bacteriophage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3191–3195. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw W. V. Chloramphenicol acetyltransferase from chloramphenicol-resistant bacteria. Methods Enzymol. 1975;43:737–755. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(75)43141-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simatake H., Rosenberg M. Purified lambda regulatory protein cII positively activates promoters for lysogenic development. Nature. 1981 Jul 9;292(5819):128–132. doi: 10.1038/292128a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]