Abstract
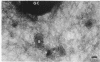
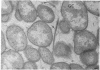
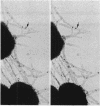
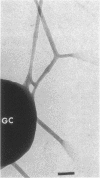
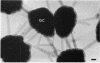
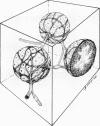
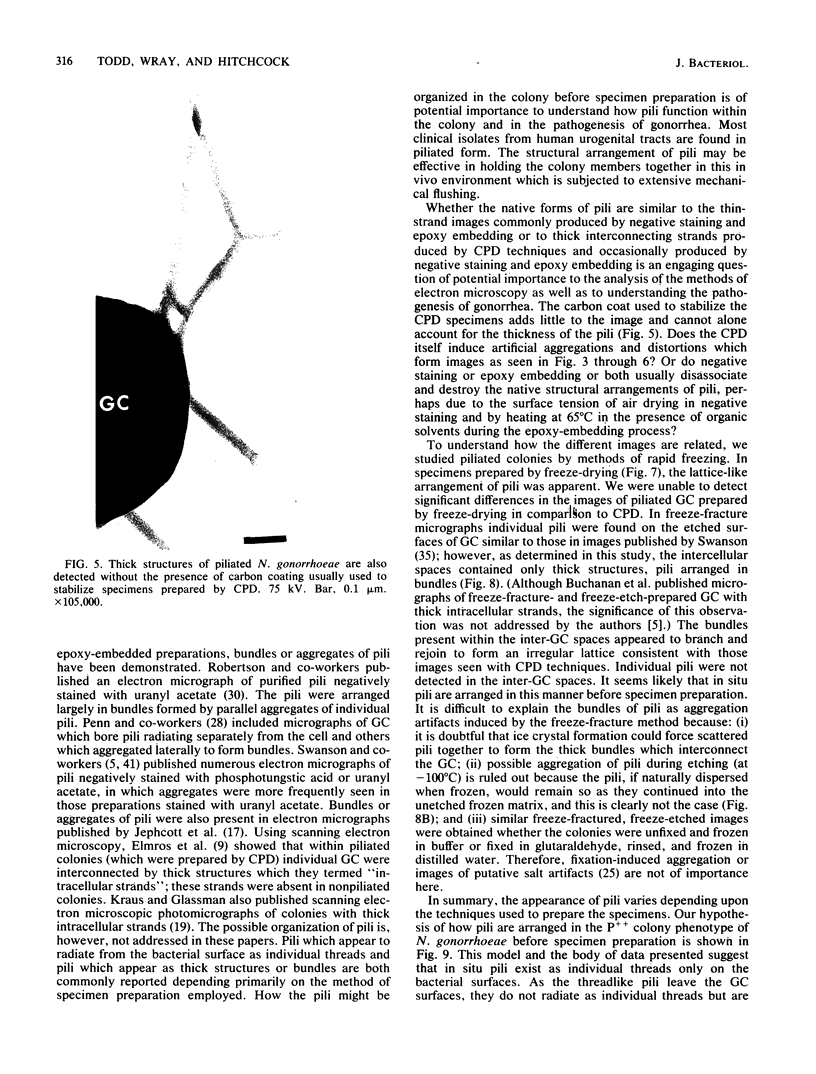
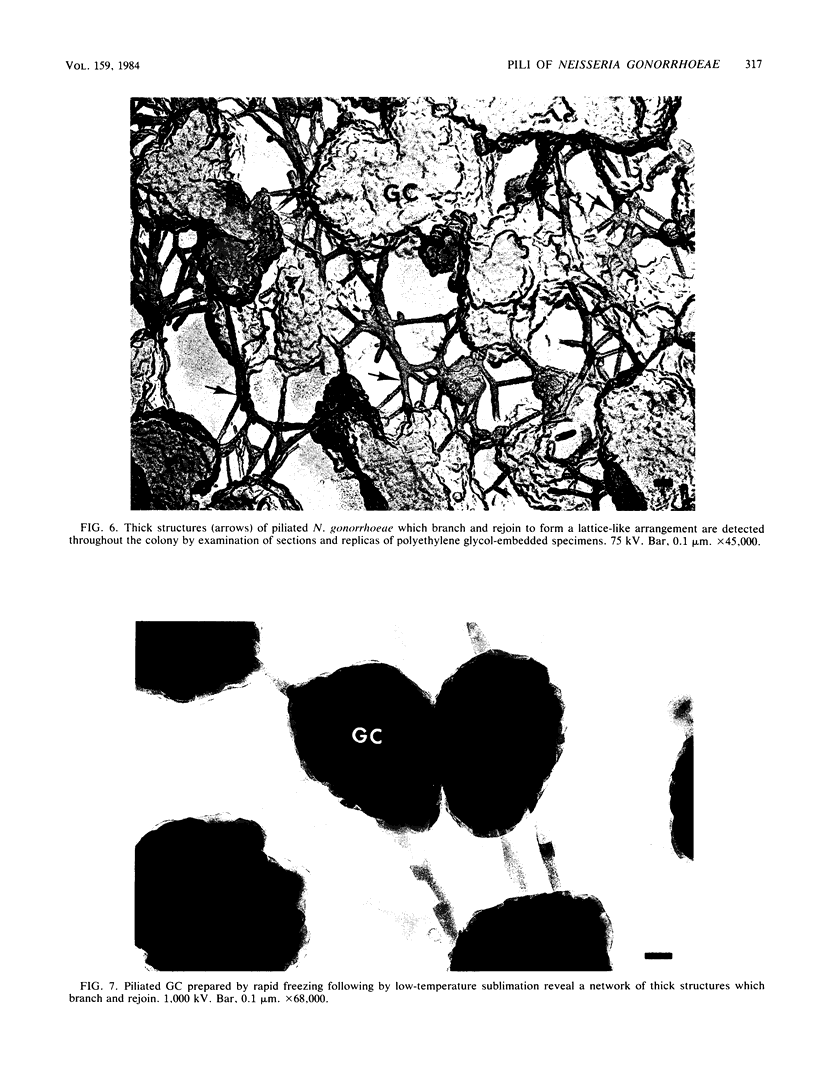
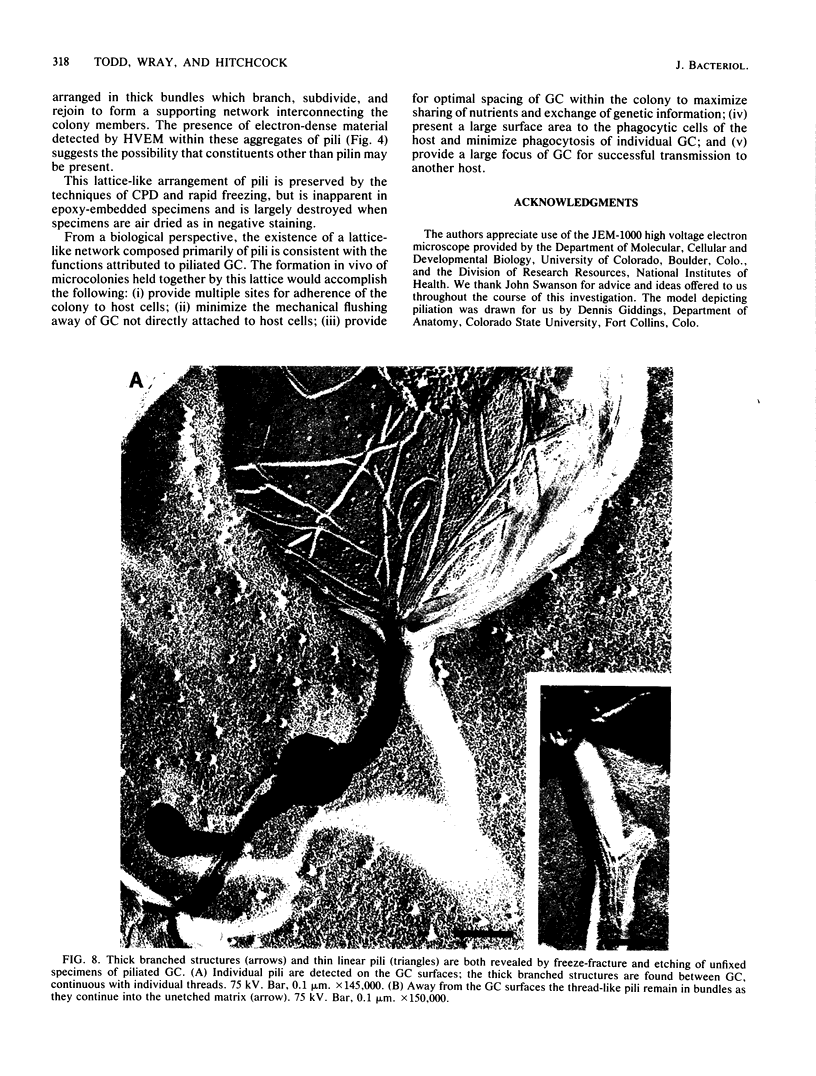
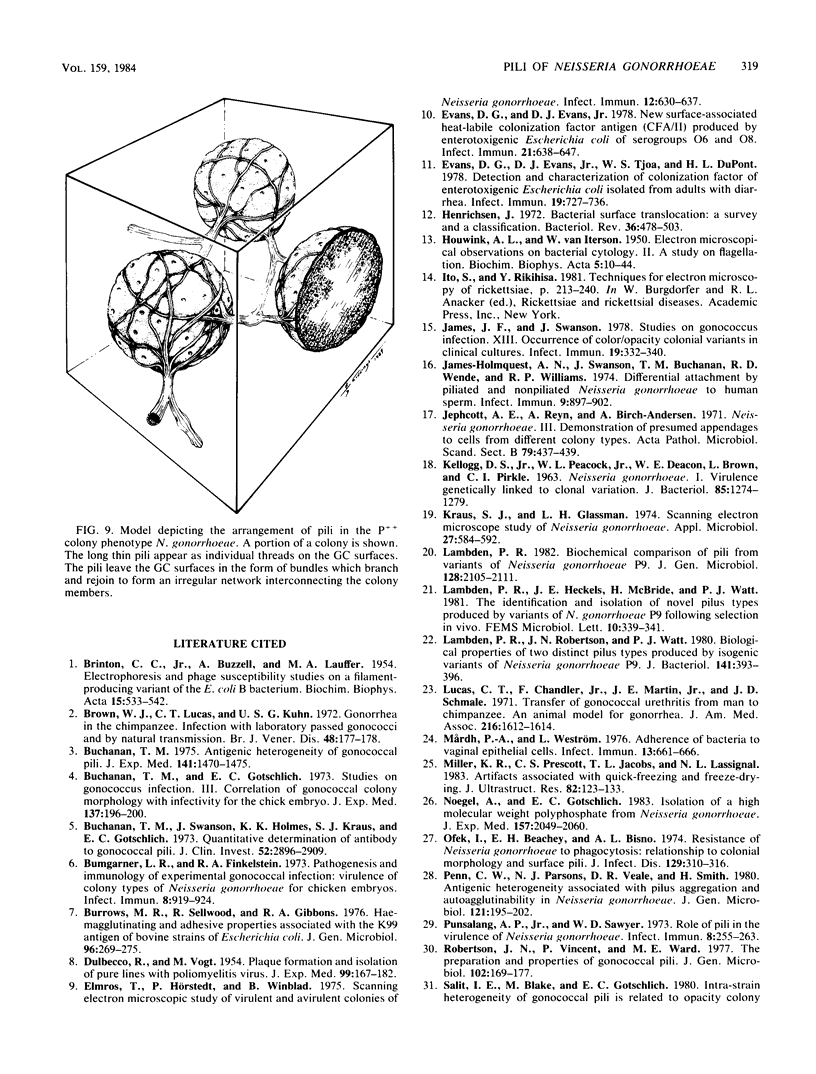
The morphology and arrangement of pili in the P++ colony phenotype of Neisseria gonorrhoeae were examined by a variety of electron microscopic techniques. The apparent structure and organization of gonococcal pili varied depending upon the method of specimen preparation. Pili as thin, individual, unbranched structures were demonstrated by negative staining and in sections of epoxy-embedded specimens. Pili forming thick structures which branch, subdivide, and rejoin to form an irregular lattice were demonstrated in specimens processed by the critical-point drying method and by rapid freezing and low temperature sublimination. We propose that in gonococcal colonies of the P++ phenotype, pili exist as individual threadlike structures only on the bacterial surfaces; as the pili leave the bacterial surfaces, they form thick bundles which branch, subdivide, and rejoin to form a supporting framework interconnecting the colony members. This arrangement of pili is usually disrupted by the commonly used method of negative staining and cannot be clearly detected within epoxy-embedded specimens. These data are summarized in a model depicting the organization of pili in the P++ colony phenotype of N. gonorrhoeae.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRINTON C. C., Jr, BUZZELL A., LAUFFER M. A. Electrophoresis and phage susceptibility studies on a filament-producing variant of the E. coli B bacterium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1954 Dec;15(4):533–542. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(54)90011-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. J., Lucas C. T., Kuhn U. S. Gonorrhoea in the chimpanzee. Infection with laboratory-passed gonococci and by natural transmission. Br J Vener Dis. 1972 Jun;48(3):177–178. doi: 10.1136/sti.48.3.177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan T. M. Antigenic heterogeneity of gonococcal pili. J Exp Med. 1975 Jun 1;141(6):1470–1475. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.6.1470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan T. M., Gotschlich E. C. Studies on gonococcus infection. 3. Correlation of gonococcal colony morphology with infectivity for the chick embryo. J Exp Med. 1973 Jan 1;137(1):196–200. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.1.196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan T. M., Swanson J., Holmes K. K., Kraus S. J., Gotschlich E. C. Quantitative determination of antibody to gonococcal pili. Changes in antibody levels with gonococcal infection. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2896–2909. doi: 10.1172/JCI107486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bumgarner L. R., Finkelstein R. A. Pathogenesis and immunology of experimental gonococcal infection: virulence of colony types of Neisseria gonorrhoeae for chicken embryos. Infect Immun. 1973 Dec;8(6):919–924. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.6.919-924.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burrows M. R., Sellwood R., Gibbons R. A. Haemagglutinating and adhesive properties associated with the K99 antigen of bovine strains of Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 Oct;96(2):269–275. doi: 10.1099/00221287-96-2-269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DULBECCO R., VOGT M. Plaque formation and isolation of pure lines with poliomyelitis viruses. J Exp Med. 1954 Feb;99(2):167–182. doi: 10.1084/jem.99.2.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edén C. S., Hansson H. A. Escherichia coli pili as possible mediators of attachment to human urinary tract epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1978 Jul;21(1):229–237. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.1.229-237.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elmros T., Hörstedt P., Winblad B. Scanning electron microscopic study of virulent and avirulent colonies of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1975 Sep;12(3):630–637. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.3.630-637.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. G., Evans D. J., Jr New surface-associated heat-labile colonization factor antigen (CFA/II) produced by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli of serogroups O6 and O8. Infect Immun. 1978 Aug;21(2):638–647. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.2.638-647.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. G., Evans D. J., Jr, Tjoa W. S., DuPont H. L. Detection and characterization of colonization factor of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli isolated from adults with diarrhea. Infect Immun. 1978 Feb;19(2):727–736. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.2.727-736.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOUWINK A. L., van ITERSON W. Electron microscopical observations on bacterial cytology; a study on flagellation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1950 Mar;5(1):10–44. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(50)90144-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henrichsen J. Bacterial surface translocation: a survey and a classification. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Dec;36(4):478–503. doi: 10.1128/br.36.4.478-503.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James-Holmquest A. N., Swanson J., Buchanan T. M., Wende R. D., Williams R. P. Differential attachment by piliated and nonpiliated Neisseria gonorrhoeae to human sperm. Infect Immun. 1974 May;9(5):897–902. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.5.897-902.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James J. F., Swanson J. Studies on gonococcus infection. XIII. Occurrence of color/opacity colonial variants in clinical cultures. Infect Immun. 1978 Jan;19(1):332–340. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.1.332-340.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jephcott A. E., Reyn A., Birch-Andersen A. Neisseria gonorrhoeae 3. Demonstration of presumed appendages to cells from different colony types. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1971;79(3):437–439. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1971.tb00086.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLOGG D. S., Jr, PEACOCK W. L., Jr, DEACON W. E., BROWN L., PIRKLE D. I. NEISSERIA GONORRHOEAE. I. VIRULENCE GENETICALLY LINKED TO CLONAL VARIATION. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jun;85:1274–1279. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.6.1274-1279.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraus S. J., Glassman L. H. Scanning electron microscope study of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Mar;27(3):584–592. doi: 10.1128/am.27.3.584-592.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambden P. R. Biochemical comparison of pili from variants of Neisseria gonorrhoeae P9. J Gen Microbiol. 1982 Sep;128(9):2105–2111. doi: 10.1099/00221287-128-9-2105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambden P. R., Robertson J. N., Watt P. J. Biological properties of two distinct pilus types produced by isogenic variants of Neisseria gonorrhoeae P9. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jan;141(1):393–396. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.1.393-396.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas C. T., Chandler F., Jr, Martin J. E., Jr, Schmale J. D. Transfer of gonococcal urethritis from man to chimpanzee. An animal model for gonorrhea. JAMA. 1971 Jun 7;216(10):1612–1614. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller K. R., Prescott C. S., Jacobs T. L., Lassignal N. L. Artifacts associated with quick-freezing and freeze-drying. J Ultrastruct Res. 1983 Feb;82(2):123–133. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(83)90047-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mårdh P. A., Westtöm L. Adherence of bacterial to vaginal epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1976 Mar;13(3):661–666. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.3.661-666.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noegel A., Gotschlich E. C. Isolation of a high molecular weight polyphosphate from Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Exp Med. 1983 Jun 1;157(6):2049–2060. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.6.2049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofek I., Beachey E. H., Bisno A. L. Resistance of Neisseria gonorrhoeae to phagocytosis: relationship to colonial morphology and surface pili. J Infect Dis. 1974 Mar;129(3):310–316. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.3.310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penn C. W., Parsons N. J., Veale D. R., Smith H. Antigenic heterogeneity associated with pilus aggregation and autoagglutinability in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Gen Microbiol. 1980 Nov;121(1):195–202. doi: 10.1099/00221287-121-1-195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Punsalang A. P., Jr, Sawyer W. D. Role of pili in the virulence of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1973 Aug;8(2):255–263. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.2.255-263.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson J. N., Vincent P., Ward M. E. The preparation and properties of gonococcal pili. J Gen Microbiol. 1977 Sep;102(1):169–177. doi: 10.1099/00221287-102-1-169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparling P. F. Genetic transformation of Neisseria gonorrhoeae to streptomycin resistance. J Bacteriol. 1966 Nov;92(5):1364–1371. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.5.1364-1371.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stirm S., Orskov F., Orskov I., Mansa B. Episome-carried surface antigen K88 of Escherichia coli. II. Isolation and chemical analysis. J Bacteriol. 1967 Feb;93(2):731–739. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.2.731-739.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J., King G., Zeligs B. Studies on gonococcus infection. VII. In vitro killing of gonococci by human leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1975 Jan;11(1):65–68. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.1.65-68.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J., Kraus S. J., Gotschlich E. C. Studies on gonococcus infection. I. Pili and zones of adhesion: their relation to gonococcal growth patterns. J Exp Med. 1971 Oct 1;134(4):886–906. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.4.886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J. Studies on gonococcus infection. II. Freeze-fracture, freeze-etch studies on gonocci. J Exp Med. 1972 Nov 1;136(5):1258–1271. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.5.1258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J. Studies on gonococcus infection. IV. Pili: their role in attachment of gonococci to tissue culture cells. J Exp Med. 1973 Mar 1;137(3):571–589. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.3.571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J. Surface components affecting interactions between Neisserai gonorrhoeae and eucaryotic cells. J Infect Dis. 1977 Aug;136 (Suppl):S138–S143. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.supplement.s138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J. Surface-exposed protein antigens of the gonococcal outer membrane. Infect Immun. 1981 Dec;34(3):804–816. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.3.804-816.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J., Zeligs B. Studies on gonococcus infection. VI. Electron microscopic study on in vitro phagocytosis of gonococci by human leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1974 Sep;10(3):645–656. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.3.645-656.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thongthai C., Sawyer W. D. Studies on the virulence of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. I. Relation of colonial morphology and resistance to phagocytosis by polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1973 Mar;7(3):373–379. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.3.373-379.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward M. E., Watt P. J., Robertson J. N. The human fallopian tube: a laboratory model for gonococcal infection. J Infect Dis. 1974 Jun;129(6):650–659. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.6.650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolosewick J. J. The application of polyethylene glycol (PEG) to electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1980 Aug;86(2):675–661. doi: 10.1083/jcb.86.2.675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]