Abstract
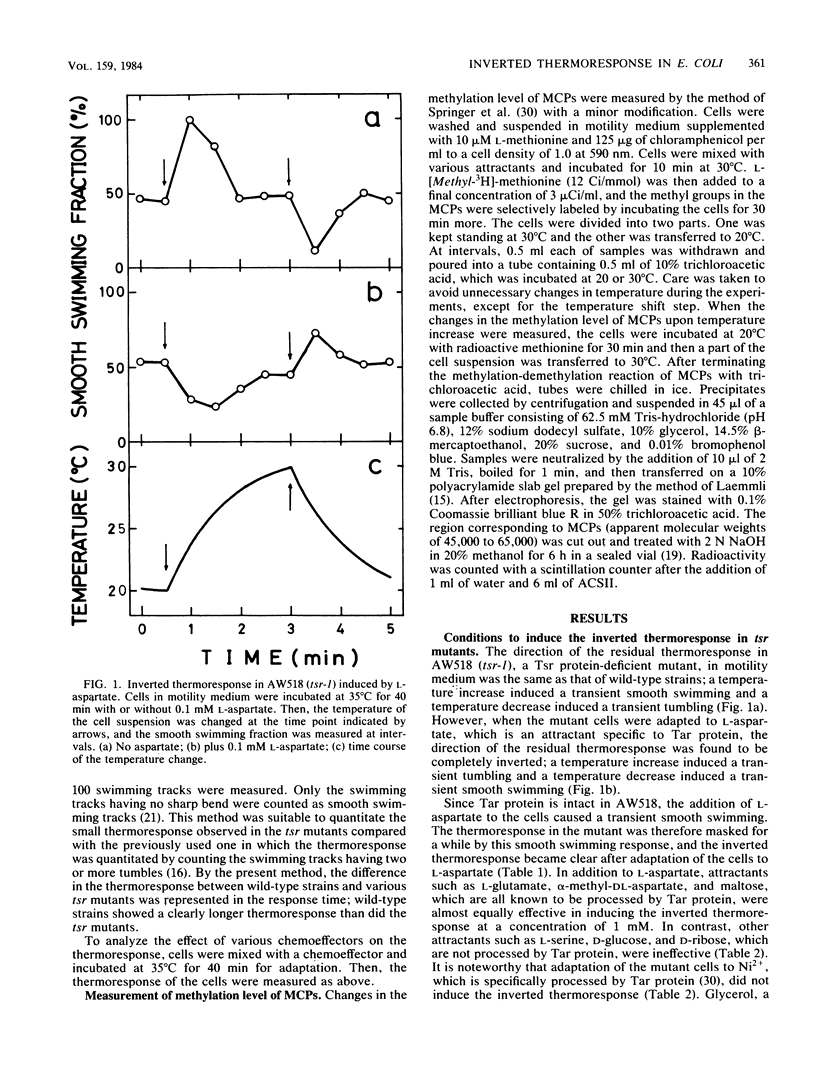
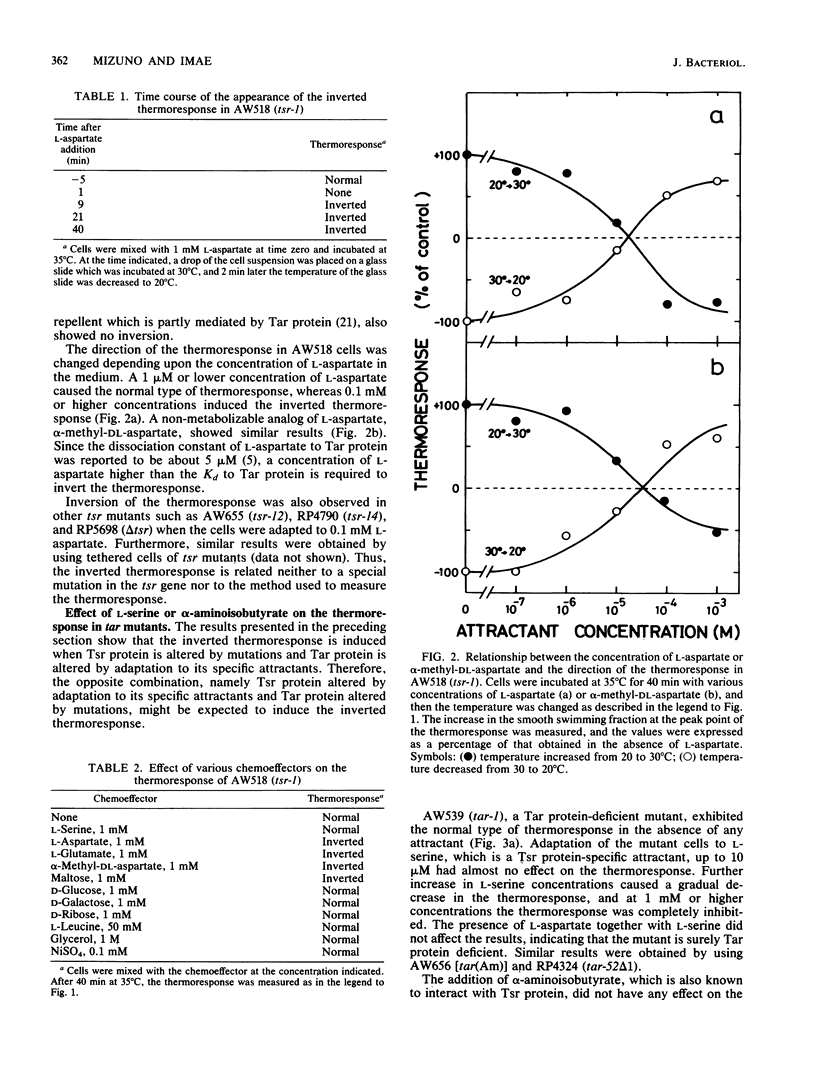
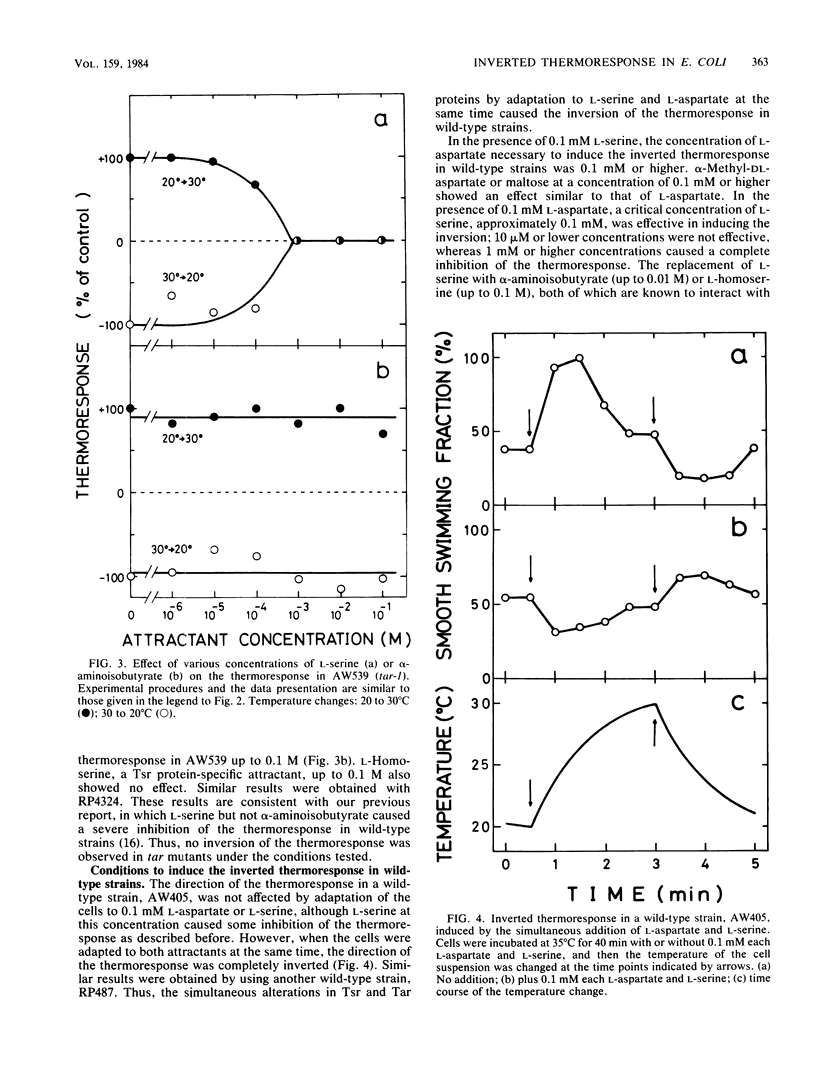
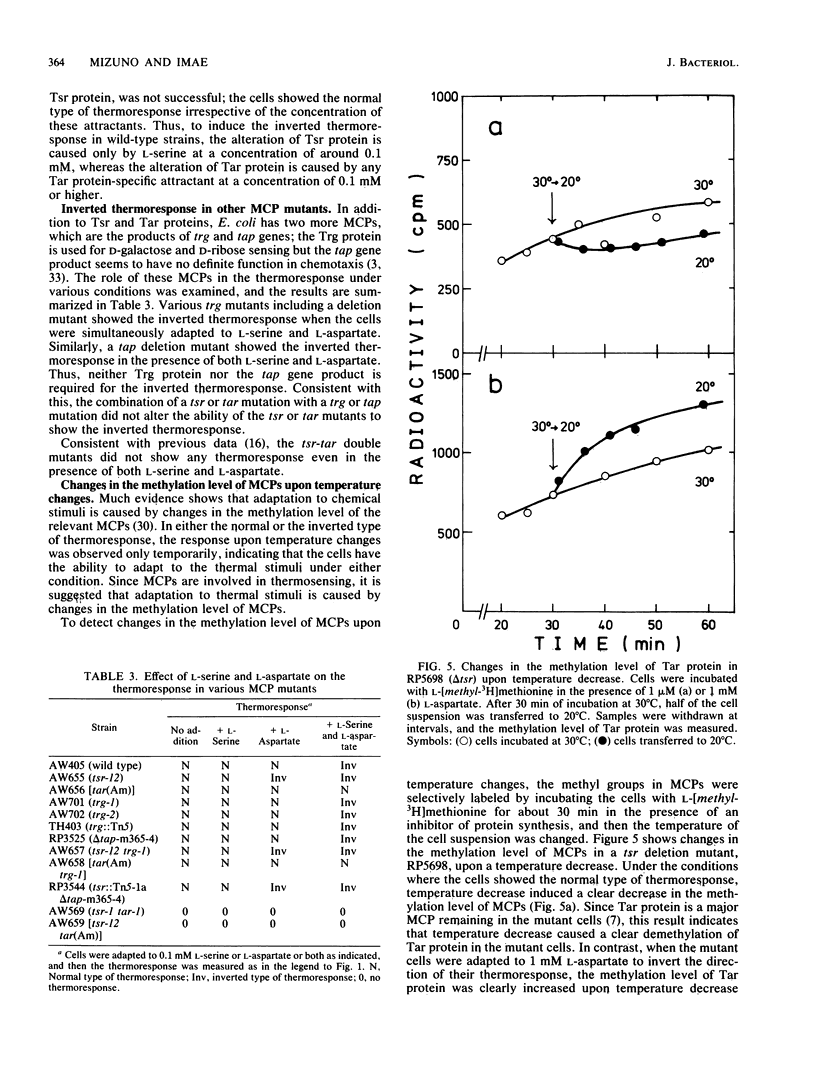
Mutants in Escherichia coli having defects in one of the methyl-accepting chemotaxis proteins, Tsr protein, which is the chemoreceptor and transducer for L-serine, showed a reduced but similar type of thermoresponse compared with wild-type strains; the cells showed smooth swimming upon temperature increase and tumbling upon temperature decrease. However, when the mutant cells were adapted to attractants such as L-aspartate and maltose, which are specific to another methyl-accepting chemotaxis protein, Tar protein, the direction of the thermoresponse was found to be inverted; a temperature increase induced tumbling and a temperature decrease induced smooth swimming. Consistent with this, the mutant cells showed inverted changes in the methylation level of Tar protein upon temperature changes. Wild-type strains but not Tar protein-deficient mutants exhibited the inverted thermoresponse when the cells were simultaneously adapted to L-aspartate and L-serine, indicating that Tar protein has a key role in the inversion of the thermoresponse. Thus, besides Tsr protein, Tar protein has a certain role in thermoreception. A simple model for thermoreception and inversion of the thermoresponse is also discussed.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler J. The sensing of chemicals by bacteria. Sci Am. 1976 Apr;234(4):40–47. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican0476-40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd A., Kendall K., Simon M. I. Structure of the serine chemoreceptor in Escherichia coli. Nature. 1983 Feb 17;301(5901):623–626. doi: 10.1038/301623a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd A., Krikos A., Simon M. Sensory transducers of E. coli are encoded by homologous genes. Cell. 1981 Nov;26(3 Pt 1):333–343. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90202-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chelsky D., Dahlquist F. W. Chemotaxis in Escherichia coli: associations of protein components. Biochemistry. 1980 Sep 30;19(20):4633–4639. doi: 10.1021/bi00561a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke S., Koshland D. E., Jr Membrane receptors for aspartate and serine in bacterial chemotaxis. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 10;254(19):9695–9702. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENSEL H., IGGO A., WITT I. A quantitative study of sensitive cutaneous thermoreceptors with C afferent fibres. J Physiol. 1960 Aug;153:113–126. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harayama S., Palva E. T., Hazelbauer G. L. Transposon-insertion mutants of Escherichia coli K12 defective in a component common to galactose and ribose chemotaxis. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Mar 20;171(2):193–203. doi: 10.1007/BF00270005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazelbauer G. L., Engström P., Harayama S. Methyl-accepting chemotaxis protein III and transducer gene trg. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jan;145(1):43–49. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.1.43-49.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedblom M. L., Adler J. Chemotactic response of Escherichia coli to chemically synthesized amino acids. J Bacteriol. 1983 Sep;155(3):1463–1466. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.3.1463-1466.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedblom M. L., Adler J. Genetic and biochemical properties of Escherichia coli mutants with defects in serine chemotaxis. J Bacteriol. 1980 Dec;144(3):1048–1060. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.3.1048-1060.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan S., Macnab R. M., DeFranco A. L., Koshland D. E., Jr Inversion of a behavioral response in bacterial chemotaxis: explanation at the molecular level. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4150–4154. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kihara M., Macnab R. M. Cytoplasmic pH mediates pH taxis and weak-acid repellent taxis of bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1209–1221. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1209-1221.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondoh H., Ball C. B., Adler J. Identification of a methyl-accepting chemotaxis protein for the ribose and galactose chemoreceptors of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):260–264. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krikos A., Mutoh N., Boyd A., Simon M. I. Sensory transducers of E. coli are composed of discrete structural and functional domains. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):615–622. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90442-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda K., Imae Y., Shioi J. I., Oosawa F. Effect of temperature on motility and chemotaxis of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1039–1046. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1039-1046.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda K., Imae Y. Thermosensory transduction in Escherichia coli: inhibition of the thermoresponse by L-serine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):91–95. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuura S., Shioi J. I., Imae Y., Iida S. Characterization of the Bacillus subtilis motile system driven by an artificially created proton motive force. J Bacteriol. 1979 Oct;140(1):28–36. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.1.28-36.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minoshima S., Hayashi H. Studies on bacterial chemotaxis. VI. Effect of cheX mutation on the methylation of methyl-accepting chemotaxis protein of Escherichia coli. J Biochem. 1980 May;87(5):1371–1377. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muskavitch M. A., Kort E. N., Springer M. S., Goy M. F., Adler J. Attraction by repellents: an error in sensory information processing by bacterial mutants. Science. 1978 Jul 7;201(4350):63–65. doi: 10.1126/science.351803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oosawa K., Imae Y. Glycerol and ethylene glycol: members of a new class of repellents of Escherichia coli chemotaxis. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):104–112. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.104-112.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson J. S. Complementation analysis and deletion mapping of Escherichia coli mutants defective in chemotaxis. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jul;135(1):45–53. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.1.45-53.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson J. S., Houts S. E. Isolation and behavior of Escherichia coli deletion mutants lacking chemotaxis functions. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jul;151(1):106–113. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.1.106-113.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson J. S. Novel mutations affecting a signaling component for chemotaxis of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jun;142(3):953–961. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.3.953-961.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson J. S., Revello P. T. Sensory adaptation mutants of E. coli. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1221–1230. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90048-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Repaske D. R., Adler J. Change in intracellular pH of Escherichia coli mediates the chemotactic response to certain attractants and repellents. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1196–1208. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1196-1208.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rollins C., Dahlquist F. W. The methyl-accepting chemotaxis proteins of E. coli: a repellent-stimulated, covalent modification, distinct from methylation. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):333–340. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90051-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubik B. A., Koshland D. E., Jr Potentiation, desensitization, and inversion of response in bacterial sensing of chemical stimuli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2820–2824. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherris D., Parkinson J. S. Posttranslational processing of methyl-accepting chemotaxis proteins in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6051–6055. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer M. S., Goy M. F., Adler J. Protein methylation in behavioural control mechanisms and in signal transduction. Nature. 1979 Jul 26;280(5720):279–284. doi: 10.1038/280279a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer M. S., Goy M. F., Adler J. Sensory transduction in Escherichia coli: two complementary pathways of information processing that involve methylated proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3312–3316. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang E. A., Koshland D. E., Jr Receptor structure in the bacterial sensing system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7157–7161. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang E. A., Mowry K. L., Clegg D. O., Koshland D. E., Jr Tandem duplication and multiple functions of a receptor gene in bacterial chemotaxis. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 10;257(9):4673–4676. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


