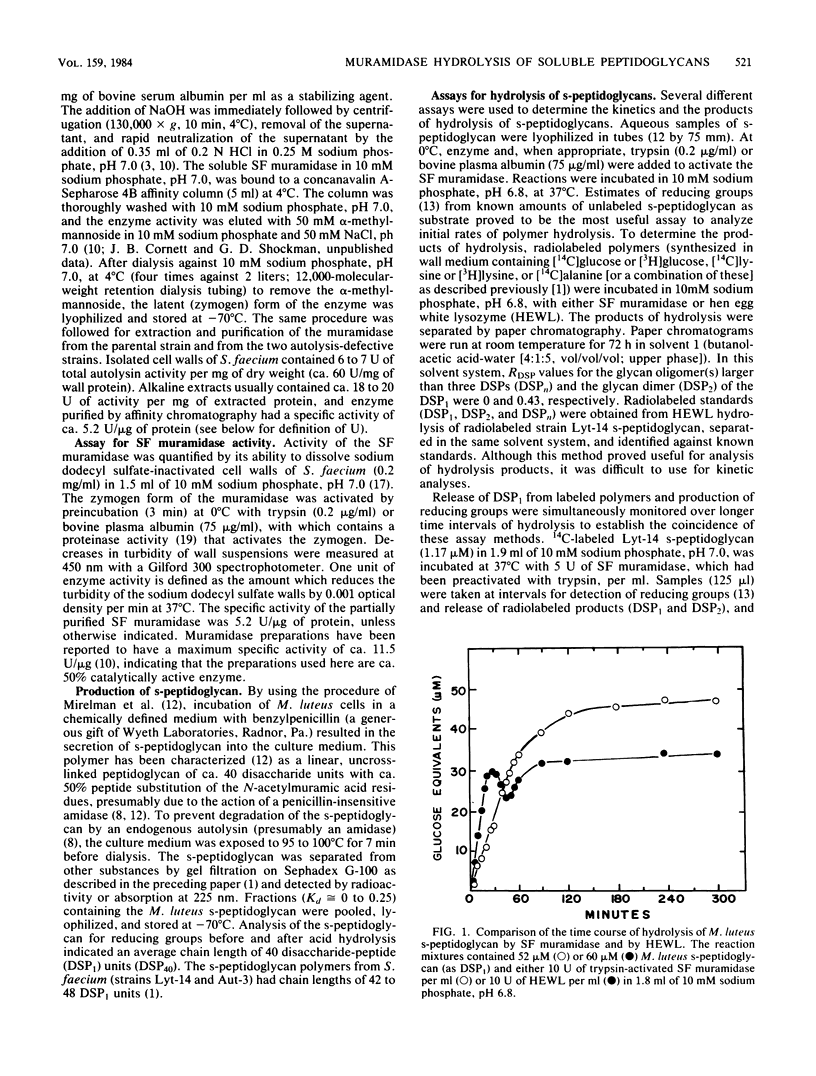
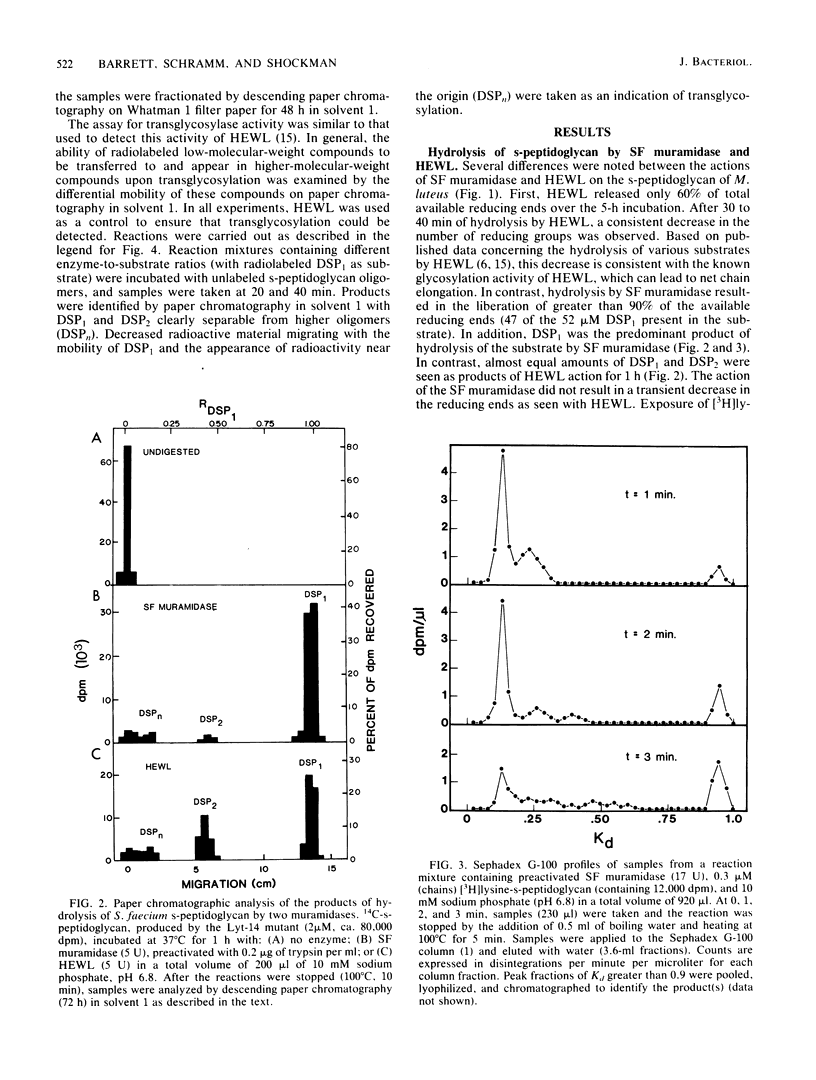
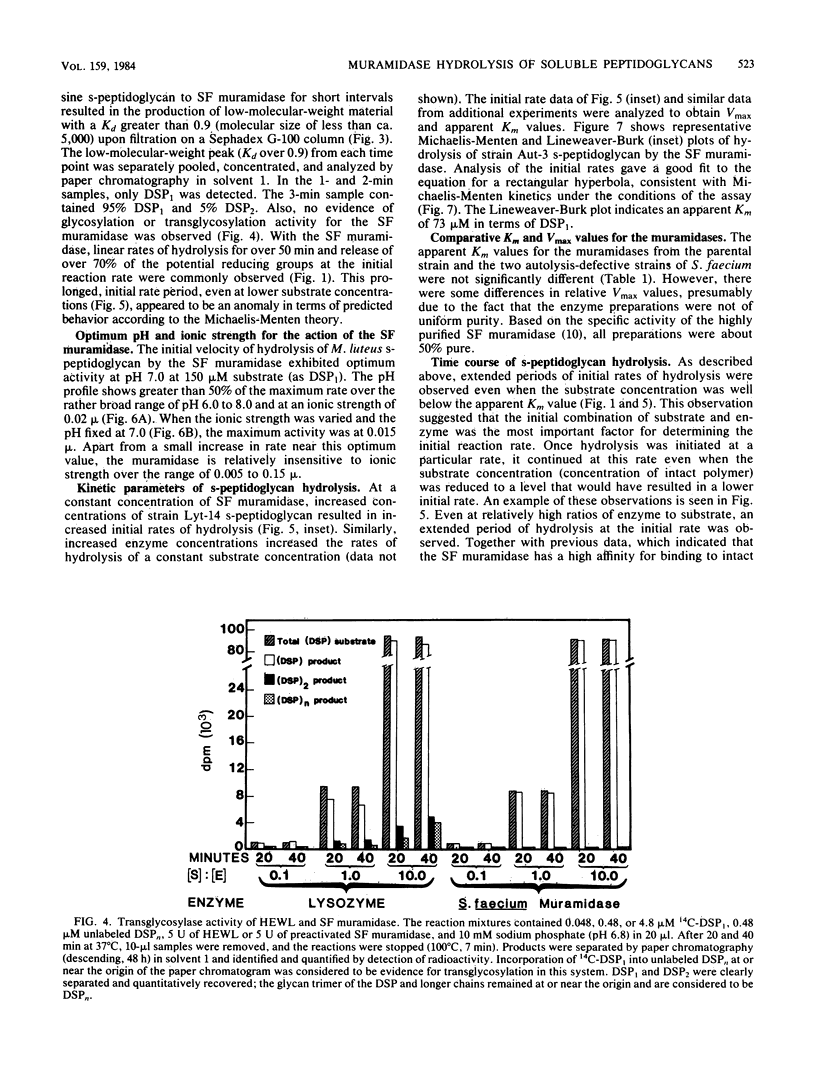
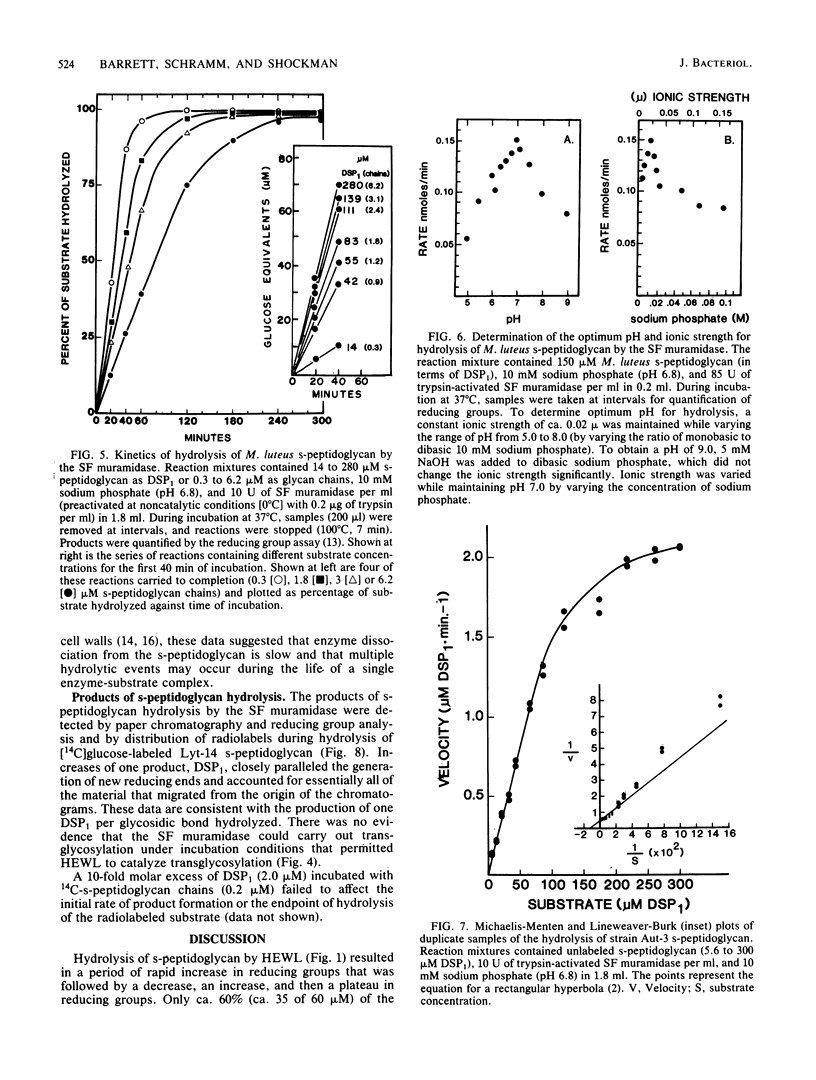
Abstract
Soluble, linear, uncross-linked peptidoglycans, prepared from two autolysis-defective mutants of Streptococcus faecium ATCC 9790 and from Micrococcus leuteus, were used as substrates for studies of hydrolysis by an N-acetylmuramoylhydrolase (muramidase). The kinetics of hydrolysis of these substrates and the ability of the muramidases isolated from S. faecium ATCC 9790 and from two autolysis-defective mutants, Lyt-14 and Aut-3, to carry out transglycosylation reactions were compared with the action of hen egg white lysozyme (EC 3.2.1.17). Hydrolysis of these substrates by the endogenous streptococcal muramidases resulted in the production of disaccharide-peptide monomers with the structure (formula; see text) as nearly the sole product. As estimated from increases in reducing groups, hydrolysis proceeded at a linear rate for extended intervals, with consumption of up to 75% of the substrate, even at substrate concentrations well below the Km value. Apparent Km and relative Vmax values for the three streptococcal enzymes were indistinguishable from each other or from those for hen egg white lysozyme. These results indicate that the autolysis-defective phenotype of these mutants cannot be attributed to differences in their muramidases. In contrast to the action of hen egg white lysozyme, the streptococcal muramidase failed to catalyze transglycosylations. The extended periods of hydrolysis at constant rates are consistent with the occurrence of multiple catalytic events after the formation of the enzyme-substrate complex.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barrett J. F., Shockman G. D. Isolation and characterization of soluble peptidoglycan from several strains of Streptococcus faecium. J Bacteriol. 1984 Aug;159(2):511–519. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.2.511-519.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleland W. W. The statistical analysis of enzyme kinetic data. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1967;29:1–32. doi: 10.1002/9780470122747.ch1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornett J. B., Johnson C. A., Shockman G. D. Release of autolytic enzyme from Streptococcus, faecium cell walls by treatment with dilute alkali. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jun;138(3):699–704. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.3.699-704.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornett J. B., Redman B. E., Shockman G. D. Autolytic defective mutant of Streptococcus faecalis. J Bacteriol. 1978 Feb;133(2):631–640. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.2.631-640.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies R. C., Neuberger A., Wilson B. M. The dependence of lysozyme activity on pH and ionic strength. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Apr 22;178(2):294–305. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(69)90397-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDELMAN J. The formation of oligosaccharides by enzymic transglycosylation. Adv Enzymol Relat Subj Biochem. 1956;17:189–232. doi: 10.1002/9780470122624.ch5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghuysen J. M., Bricas E., Leyh-Bouille M., Lache M., Shockman G. D. The peptide N alpha-(L-alanyl-D-isoglutaminyl)-N epsilon-(D-isoasparaginyl)-L-lysyl-D-alanine and the disaccharide N-acetylglucosaminyl-beta-1,4-N-acetylmuramic acid in cell wall peptidoglycan of Streptococcus faecalis strain ATCC 9790. Biochemistry. 1967 Aug;6(8):2607–2619. doi: 10.1021/bi00860a044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen S. E., Campbell J. N. Amidase activity involved in peptidoglycan biosynthesis in membranes of Micrococcus luteus (sodonensis). J Bacteriol. 1976 Jul;127(1):319–326. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.1.319-326.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawamura T., Shockman G. D. Purification and some properties of the endogenous, autolytic N-acetylmuramoylhydrolase of Streptococcus faecium, a bacterial glycoenzyme. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 10;258(15):9514–9521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirelman D., Bracha R., Sharon N. Inhibition by penicillin of the incorporation and cross-linking of L-lysine in intact cells of Micrococcus luteus. FEBS Lett. 1974 Feb 1;39(1):105–110. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80028-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirelman D., Bracha R., Sharon N. Penicillin-induced secretion of soluble, uncross-linked peptidoglycan by Micrococcus luteus cells. Biochemistry. 1974 Nov 19;13(24):5045–5053. doi: 10.1021/bi00721a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARK J. T., JOHNSON M. J. A submicrodetermination of glucose. J Biol Chem. 1949 Nov;181(1):149–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pooley H. M., Shockman G. D. Relationship between the latent form and the active form of the autolytic enzyme of Streptococcus faecalis. J Bacteriol. 1969 Nov;100(2):617–624. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.2.617-624.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHARON N., SEIFTER S. A TRANSGLYCOSYLATION REACTION CATALYZED BY LYSOZYME. J Biol Chem. 1964 Jul;239:PC2398–PC2399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shockman G. D., Cheney M. C. Autolytic enzyme system of Streptococcus faecalis. V. Nature of the autolysin-cell wall complex and its relationship to properties of the autolytic enzyme of Streptococcus faecalis. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jun;98(3):1199–1207. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.3.1199-1207.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shockman G. D., Thompson J. S., Conover M. J. The autolytic enzyme system of Streptococcus faecalis. II. Partial characterization of the autolysin and its substrate. Biochemistry. 1967 Apr;6(4):1054–1065. doi: 10.1021/bi00856a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shungu D. L., Cornett J. B., Shockman G. D. Morphological and physiological study of autolytic-defective Streptococcus faecium strains. J Bacteriol. 1979 May;138(2):598–608. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.2.598-608.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson W. D., Foster J. F. Conformation-dependent limited proteolysis of bovine plasma albumin by an enzyme present in commercial albumin preparations. Biochemistry. 1971 May 11;10(10):1772–1780. doi: 10.1021/bi00786a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


