Abstract
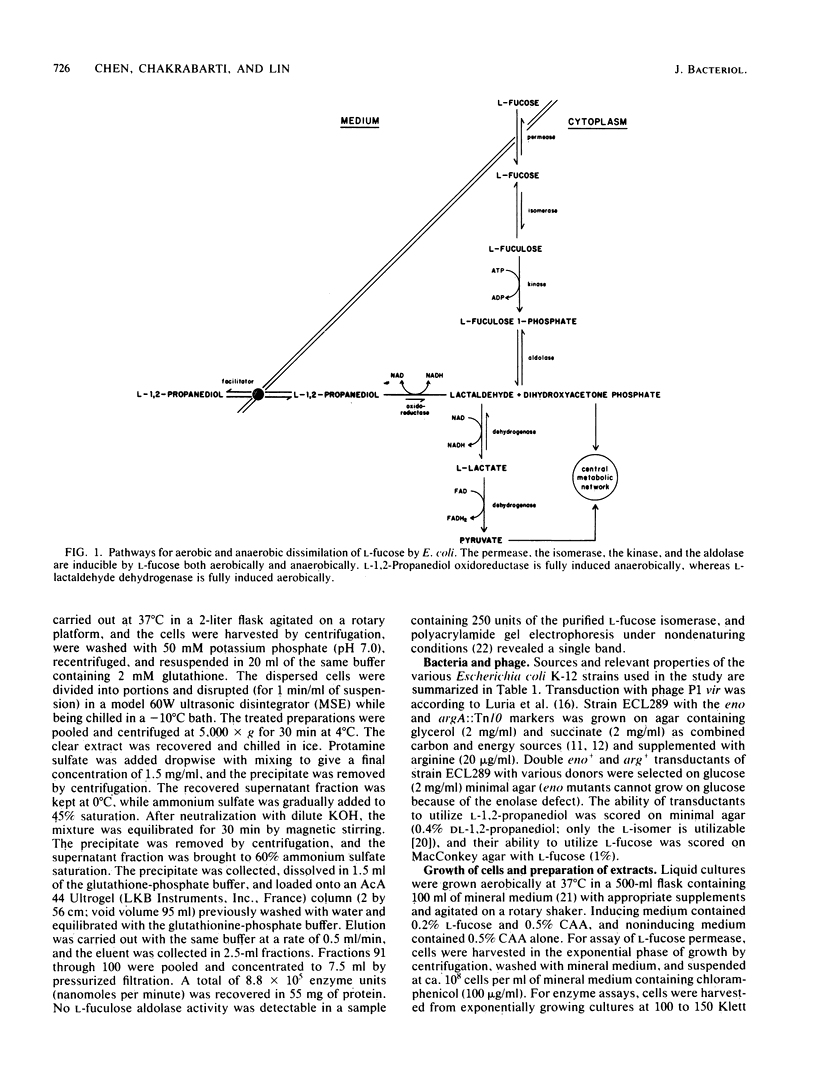
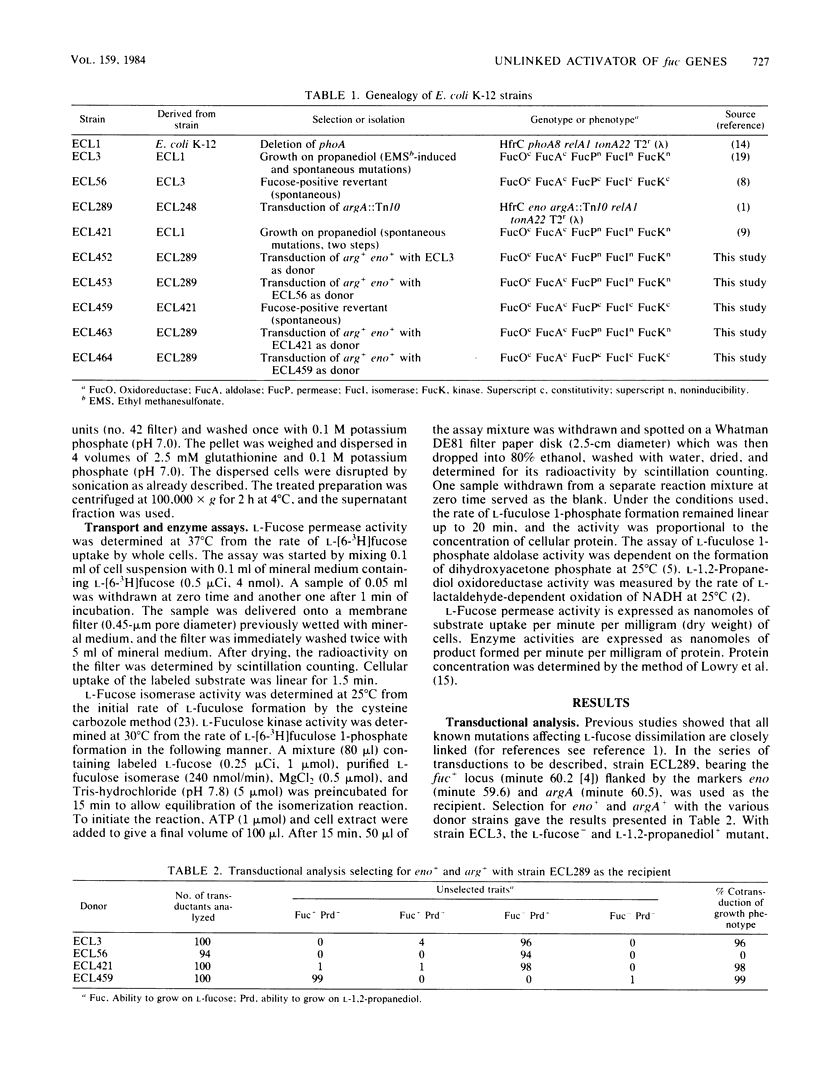
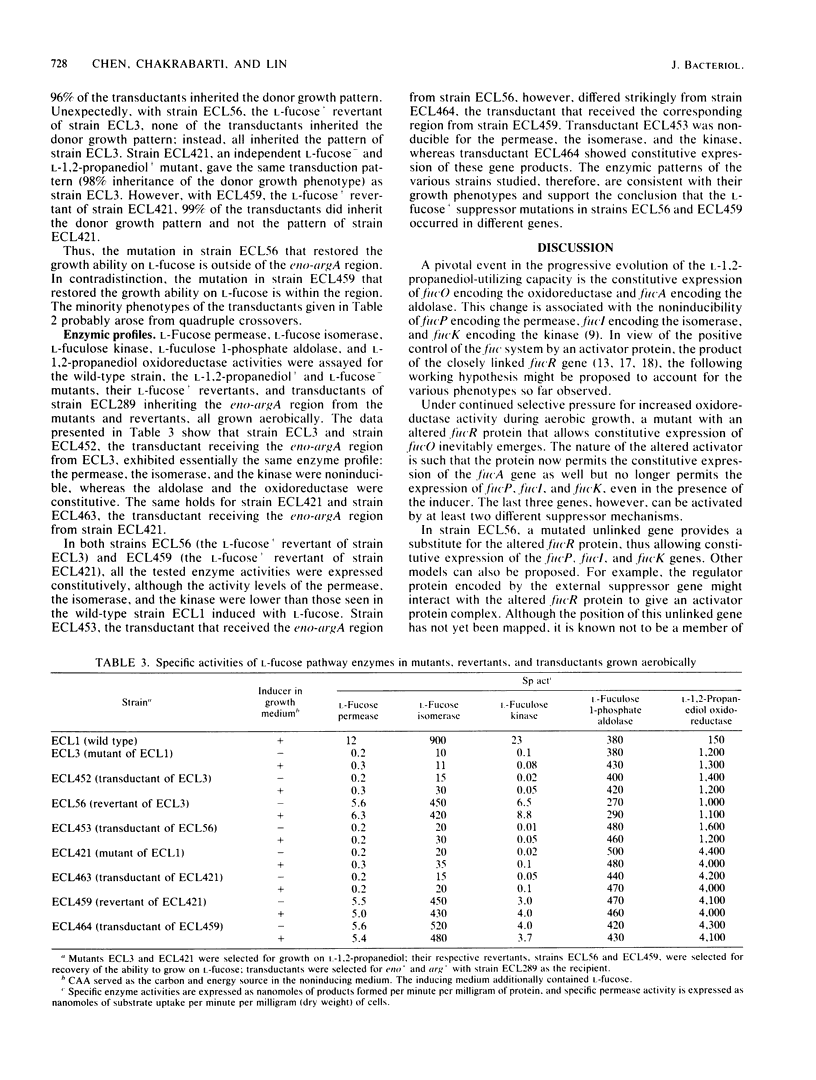
Wild-type Escherichia coli cannot grow on L-1,2-propanediol; mutants that can do so have increased basal activity of an NAD-linked L-1,2-propanediol oxidoreductase. This enzyme belongs to the L-fucose system and functions normally as L-lactaldehyde reductase during fermentation of the methylpentose. In wild-type cells, the activity of this enzyme is fully induced only anaerobically. Continued aerobic selection for mutants with an improved growth rate on L-1,2-propanediol inevitably leads to full constitutive expression of the oxidoreductase activity. When this occurs, L-fuculose 1-phosphate aldolase concomitantly becomes constitutive, whereas L-fucose permease, L-fucose isomerase, and L-fuculose kinase become noninducible. It is shown in this study that the noninducibility of the three proteins can be changed by two different kinds of suppressor mutations: one mapping external to and the other within the fuc gene cluster. Both mutations result in constitutive synthesis of the permease, the isomerase, and the kinase, without affecting synthesis of the oxidoreductase and the aldolase. Since expression of the fuc structural genes is activated by a protein specified by the regulator gene fucR, and since all the known genes of the fuc system are clustered at minute 60.2 of the chromosome, the external gene in which the suppressor mutation can occur probably has an unrelated function in the wild-type strain. The internal suppressor mutation might be either in fucR or in the promoter region of the genes encoding the permease, the isomerase, and the kinase, if these genes belong to the same operon.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chakrabarti T., Chen Y. M., Lin E. C. Clustering of genes for L-fucose dissimilation by Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1984 Mar;157(3):984–986. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.3.984-986.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. M., Lin E. C., Ros J., Aguilar J. Use of operon fusions to examine the regulation of the L-1,2-propanediol oxidoreductase gene of the fucose system in Escherichia coli K12. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Nov;129(11):3355–3362. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-11-3355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cocks G. T., Aguilar T., Lin E. C. Evolution of L-1, 2-propanediol catabolism in Escherichia coli by recruitment of enzymes for L-fucose and L-lactate metabolism. J Bacteriol. 1974 Apr;118(1):83–88. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.1.83-88.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FALKOW S., SCHNEIDER H., BARON L. S., FORMAL S. B. VIRULENCE OF ESCHERICHIA-SHIGELLA GENETIC HYBRIDS FOR THE GUINEA PIG. J Bacteriol. 1963 Dec;86:1251–1258. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.6.1251-1258.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GHALAMBOR M. A., HEATH E. C. The metabolism of L-fucose. II. The enzymatic cleavage of L-fuculose 1-phosphate. J Biol Chem. 1962 Aug;237:2427–2433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN M., COHEN S. S. Enzymatic conversion of L-fucose to L-fuculose. J Biol Chem. 1956 Apr;219(2):557–568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEATH E. C., GHALAMBOR M. A. The metabolism of L-fucose. I. The purification and properties of L-fuculose kinase. J Biol Chem. 1962 Aug;237:2423–2426. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hacking A. J., Aguilar J., Lin E. C. Evolution of propanediol utilization in Escherichia coli: mutant with improved substrate-scavenging power. J Bacteriol. 1978 Nov;136(2):522–530. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.2.522-530.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hacking A. J., Lin E. C. Disruption of the fucose pathway as a consequence of genetic adaptation to propanediol as a carbon source in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jun;126(3):1166–1172. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.3.1166-1172.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hacking A. J., Lin E. C. Regulatory changes in the fucose system associated with the evolution of a catabolic pathway for propanediol in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1977 May;130(2):832–838. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.2.832-838.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillman J. D., Fraenkel D. G. Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jun;122(3):1175–1179. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.3.1175-1179.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irani M., Maitra P. K. Isolation and characterization of Escherichia coli mutants defective in enzymes of glycolysis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Jan;56(1):127–133. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80324-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LURIA S. E., ADAMS J. N., TING R. C. Transduction of lactose-utilizing ability among strains of E. coli and S. dysenteriae and the properties of the transducing phage particles. Virology. 1960 Nov;12:348–390. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(60)90161-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeBlanc D. J., Mortlock R. P. Metabolism of D-arabinose: a new pathway in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1971 Apr;106(1):90–96. doi: 10.1128/jb.106.1.90-96.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin E. C. Glycerol dissimilation and its regulation in bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1976;30:535–578. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.30.100176.002535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saint Martin E. J., Mortlock R. P. Natural and altered induction of the L-fucose catabolic enzymes in Klebsiella aerogenes. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jul;127(1):91–97. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.1.91-97.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skjold A. C., Ezekiel D. H. Regulation of D-arabinose utilization in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1982 Oct;152(1):521–523. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.1.521-523.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sridhara S., Wu T. T., Chused T. M., Lin E. C. Ferrous-activated nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide-linked dehydrogenase from a mutant of Escherichia coli capable of growth on 1, 2-propanediol. J Bacteriol. 1969 Apr;98(1):87–95. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.1.87-95.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sridhara S., Wu T. T. Purification and properties of lactaldehyde dehydrogenase from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1969 Oct 10;244(19):5233–5238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka S., Lerner S. A., Lin E. C. Replacement of a phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent phosphotransferase by a nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide-linked dehydrogenase for the utilization of mannitol. J Bacteriol. 1967 Feb;93(2):642–648. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.2.642-648.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang C. T., Ruch F. E., Jr, Lin C. C. Purification and properties of a nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide-linked dehydrogenase that serves an Escherichia coli mutant for glycerol catabolism. J Bacteriol. 1979 Oct;140(1):182–187. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.1.182-187.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zagalak B., Frey P. A., Karabatsos G. L., Abeles R. H. The stereochemistry of the conversion of D and L 1,2-propanediols to propionaldehyde. J Biol Chem. 1966 Jul 10;241(13):3028–3035. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



