Abstract
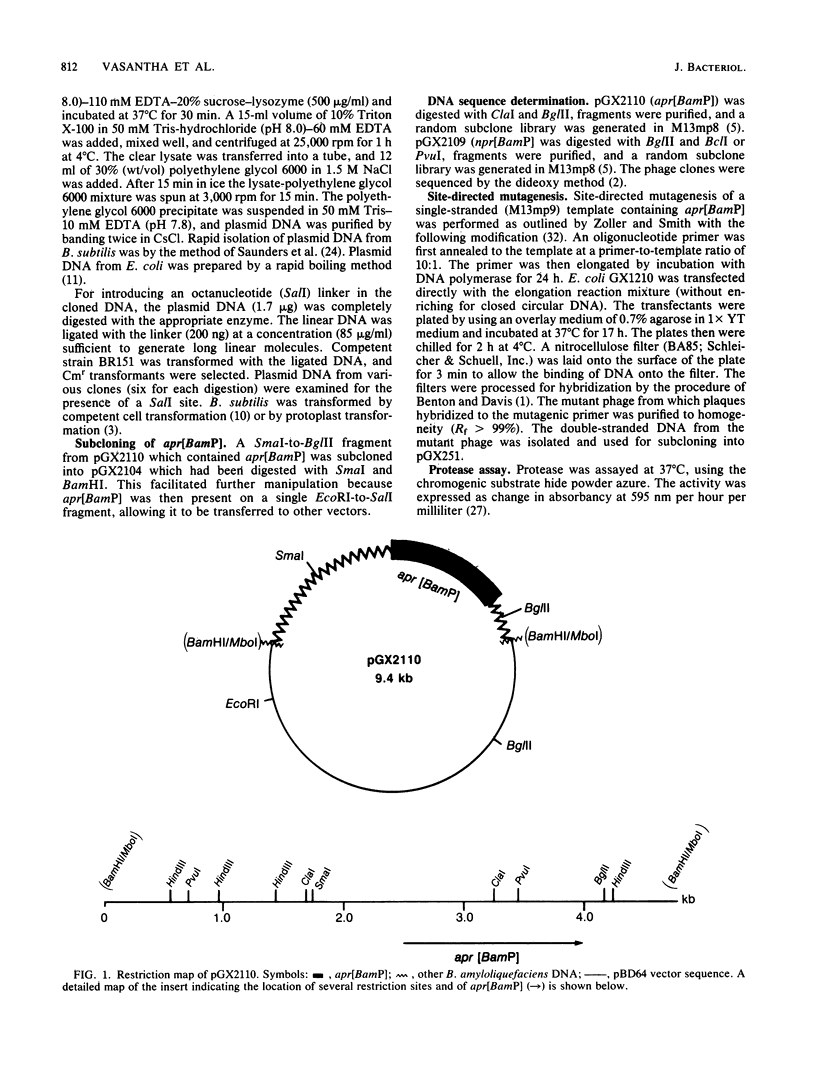
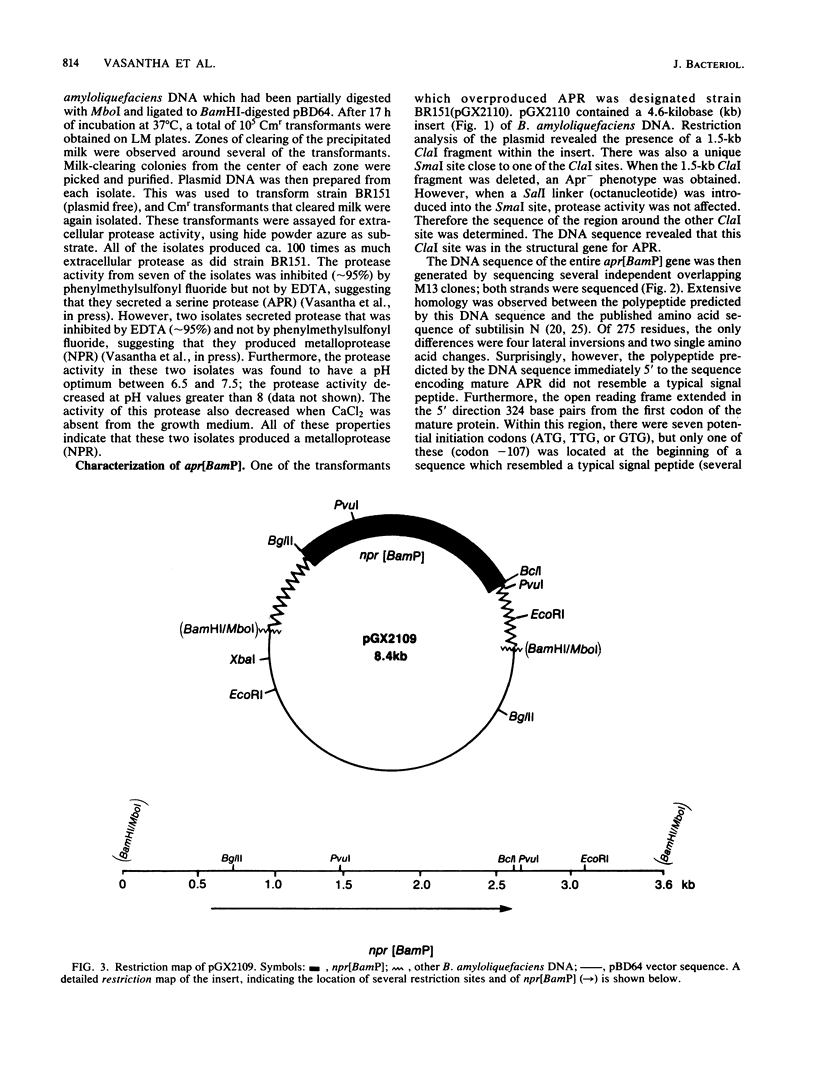
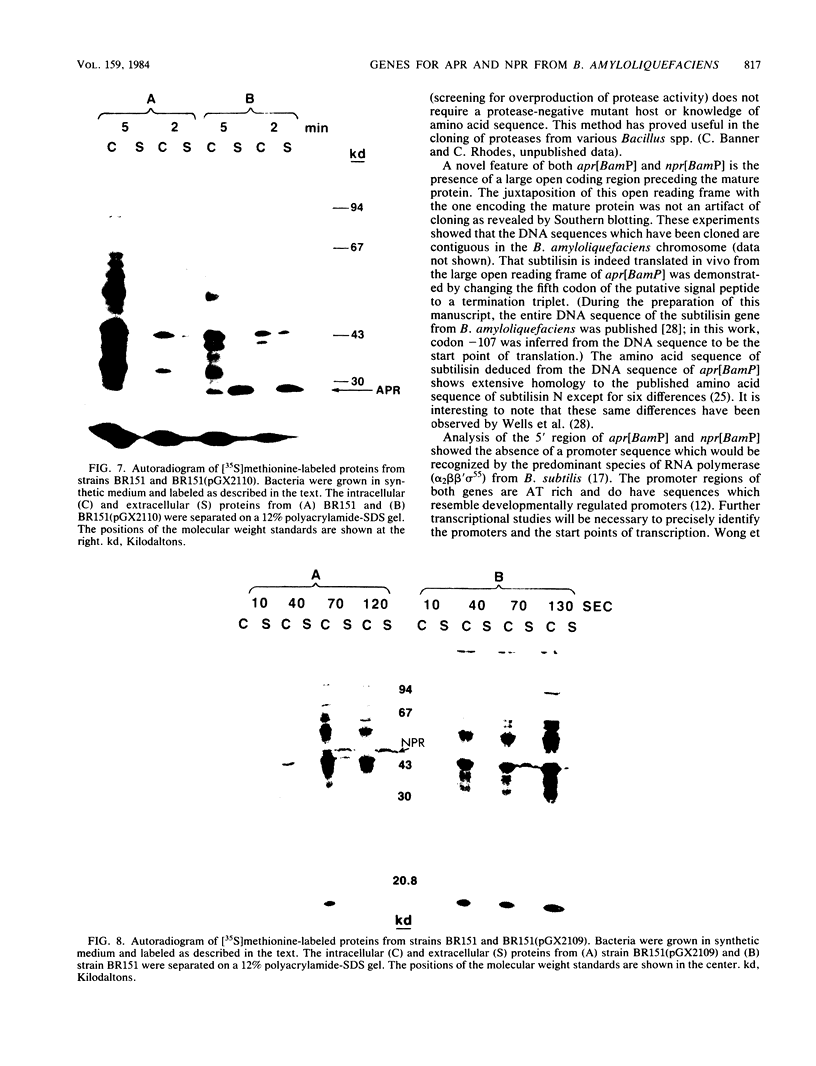
The genes for alkaline protease (apr[BamP]) and neutral protease (npr[BamP]) from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens have been isolated and expressed in Bacillus subtilis. The DNA sequences of apr[BamP] and npr[BamP] revealed, in each case, the presence of a large open reading frame. The inferred amino acid sequence of either gene contained a signal sequence and an additional polypeptide sequence ('pro' sequence) preceding the mature protein. Based on DNA sequence, the start point of translation has been identified as amino acid residue - 107 for apr[BamP] and -221 for npr[BamP]. To demonstrate that the start point of translation of apr[BamP] in vivo is probably at codon -107, codon -103 (AAA) was changed to an ochre (TAA) by site-directed mutagenesis. Alkaline protease was produced from this ochre mutant derivative of apr[BamP] only when the host strain was Su+. The presence of a pro sequence may be common to all of the secreted proteases from bacilli.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M. D., Gibson T. J., Hong G. F. Buffer gradient gels and 35S label as an aid to rapid DNA sequence determination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3963–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang S., Cohen S. N. High frequency transformation of Bacillus subtilis protoplasts by plasmid DNA. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Jan 5;168(1):111–115. doi: 10.1007/BF00267940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colman P. M., Jansonius J. N., Matthews B. W. The structure of thermolysin: an electron density map at 2-3 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1972 Oct 14;70(3):701–724. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90569-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deininger P. L. Random subcloning of sonicated DNA: application to shotgun DNA sequence analysis. Anal Biochem. 1983 Feb 15;129(1):216–223. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90072-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duvall E. J., Williams D. M., Lovett P. S., Rudolph C., Vasantha N., Guyer M. Chloramphenicol-inducible gene expression in Bacillus subtilis. Gene. 1983 Oct;24(2-3):171–177. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90077-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich S. D., Niaudet B., Michel B. Use of plasmids from Staphylococcus aureus for cloning of DNA in Bacillus subtilis. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1982;96:19–29. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-68315-2_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii M., Takagi M., Imanaka T., Aiba S. Molecular cloning of a thermostable neutral protease gene from Bacillus stearothermophilus in a vector plasmid and its expression in Bacillus stearothermophilus and Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1983 May;154(2):831–837. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.2.831-837.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gryczan T. J., Contente S., Dubnau D. Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus plasmids introduced by transformation into Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1978 Apr;134(1):318–329. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.1.318-329.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gryczan T., Contente S., Dubnau D. Molecular cloning of heterologous chromosomal DNA by recombination between a plasmid vector and a homologous resident plasmid in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Gen Genet. 1980 Feb;177(3):459–467. doi: 10.1007/BF00271485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson W. C., Moran C. P., Jr, Losick R. Two RNA polymerase sigma factors from Bacillus subtilis discriminate between overlapping promoters for a developmentally regulated gene. Nature. 1983 Apr 28;302(5911):800–804. doi: 10.1038/302800a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy P. L., Pangburn M. K., Burstein Y., Ericsson L. H., Neurath H., Walsh K. A. Evidence of homologous relationship between thermolysin and neutral protease A of Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4341–4345. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran C. P., Jr, Lang N., LeGrice S. F., Lee G., Stephens M., Sonenshein A. L., Pero J., Losick R. Nucleotide sequences that signal the initiation of transcription and translation in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;186(3):339–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00729452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen J. B., Caulfield M. P., Lampen J. O. Lipoprotein nature of Bacillus licheniformis membrane penicillinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3511–3515. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen J. B., Lampen J. O. Membrane-bound penicillinases in Gram-positive bacteria. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 25;257(8):4490–4495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman D., Halvorson H. O. A putative signal peptidase recognition site and sequence in eukaryotic and prokaryotic signal peptides. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 25;167(2):391–409. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80341-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Priest F. G. Extracellular enzyme synthesis in the genus Bacillus. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Sep;41(3):711–753. doi: 10.1128/br.41.3.711-753.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAITO H., MIURA K. I. PREPARATION OF TRANSFORMING DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID BY PHENOL TREATMENT. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Aug 20;72:619–629. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders C. W., Schmidt B. J., Mirot M. S., Thompson L. D., Guyer M. S. Use of chromosomal integration in the establishment and expression of blaZ, a Staphylococcus aureus beta-lactamase gene, in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1984 Mar;157(3):718–726. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.3.718-726.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith E. L., Markland F. S., Kasper C. B., DeLange R. J., Landon M., Evans W. H. The complete amino acid sequence of two types of subtilisin, BPN' and Carlsberg. J Biol Chem. 1966 Dec 25;241(24):5974–5976. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TSURU D., MCCONN J. D., YASUNOBU K. T. BACILLUS SUBTILIS NEUTRAL PROTEINASE. II. SOME PHYSICOCHEMICAL PROPERTIES. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jun;240:2415–2420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasantha N., Freese E. Enzyme changes during Bacillus subtilis sporulation caused by deprivation of guanine nucleotides. J Bacteriol. 1980 Dec;144(3):1119–1125. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.3.1119-1125.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells J. A., Ferrari E., Henner D. J., Estell D. A., Chen E. Y. Cloning, sequencing, and secretion of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens subtilisin in Bacillus subtilis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Nov 25;11(22):7911–7925. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.22.7911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong S. L., Price C. W., Goldfarb D. S., Doi R. H. The subtilisin E gene of Bacillus subtilis is transcribed from a sigma 37 promoter in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(4):1184–1188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.4.1184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright C. S., Alden R. A., Kraut J. Structure of subtilisin BPN' at 2.5 angström resolution. Nature. 1969 Jan 18;221(5177):235–242. doi: 10.1038/221235a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoller M. J., Smith M. Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis using M13-derived vectors: an efficient and general procedure for the production of point mutations in any fragment of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Oct 25;10(20):6487–6500. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.20.6487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]