Abstract
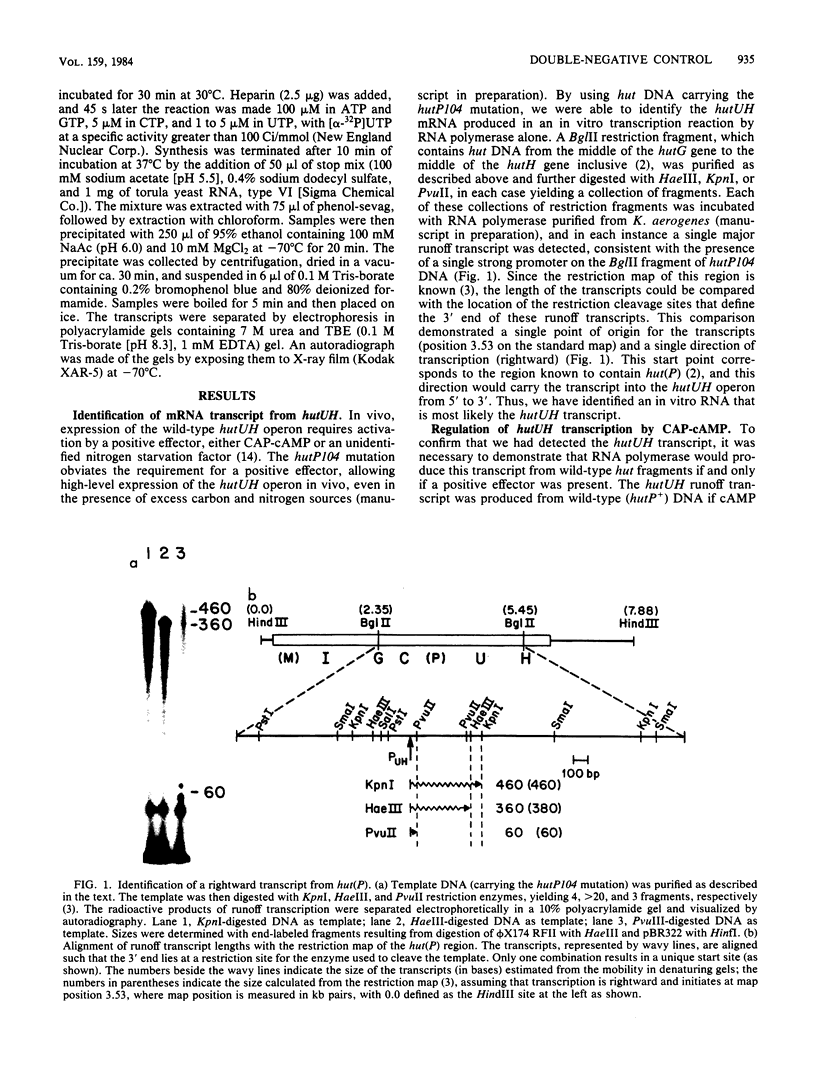
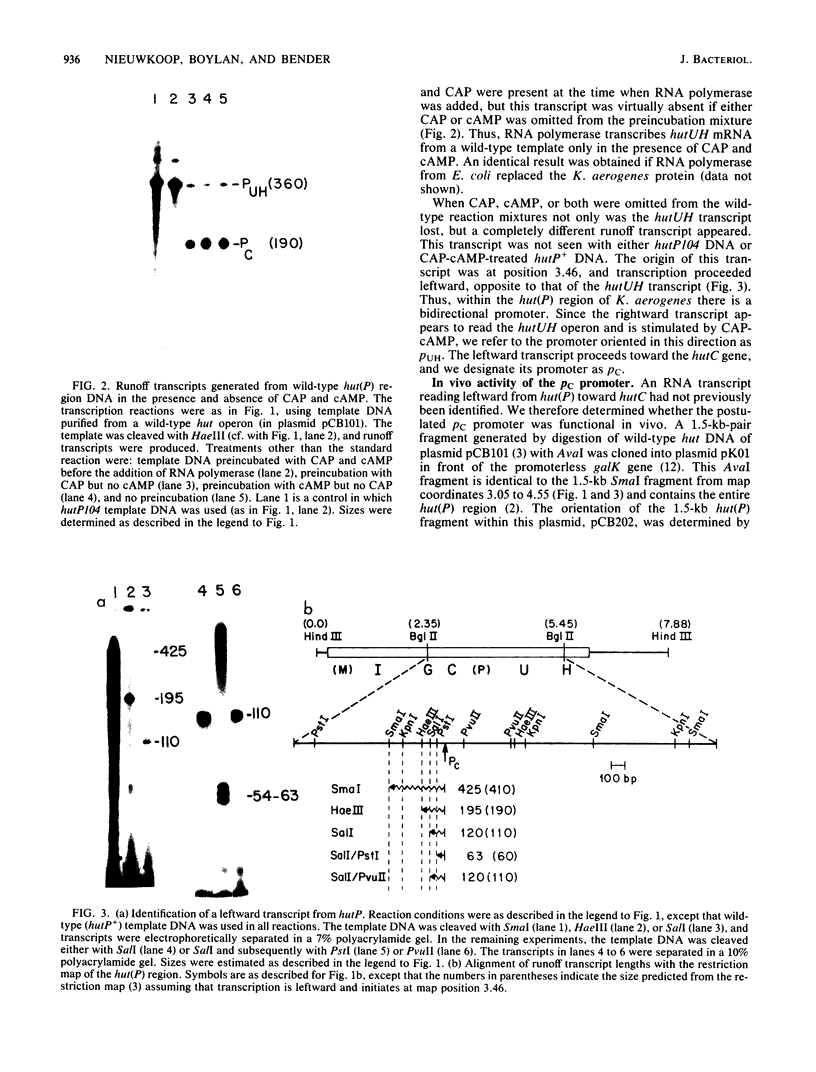
RNA polymerase transcribed the hutUH operon of Klebsiella aerogenes if the catabolite gene activator protein (CAP) and cyclic AMP (cAMP) were present or if the DNA template was derived from a promoter mutant in which hutUH expression was independent of the need for positive effectors. In the absence of CAP or cAMP, not only was hutUH transcription absent, but transcription in the opposite direction (toward hutC) was initiated at a site (pC) ca. 70 base pairs from the site (pUH) of hutUH mRNA initiation. When the pC promoter was cloned in front of a promoterless galK gene, active expression of galK was observed. Thus, the pC promoter is active in vivo as well as in vitro. Transcription from pUH and pC may be mutually exclusive, with the major effect of CAP and cAMP being to prevent transcription from pC, thus relieving the antagonistic effect on transcription from pUH. This "double-negative" control by CAP-cAMP is supported by two observations: (i) CAP-cAMP was unable to activate transcription from pUH if RNA polymerase had been previously bound to pC and (ii) a mutation that allowed transcription from pUH in the absence of positive effectors simultaneously eliminated the activity of pC. An alternative model, in which CAP-cAMP is required for pUH expression and RNA polymerase binding at pC serves to modulate this control in some unknown way, is also considered. The physiological role of the transcript from pC other than regulation of pUH is unknown.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blumenberg M., Magasanik B. A study in evolution: the histidine utilization genes of enteric bacteria. J Mol Biol. 1979 Nov 25;135(1):23–37. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90338-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boylan S. A., Bender R. A. Genetic and physical maps of Klebsiella aerogenes genes for histidine utilization (hut). Mol Gen Genet. 1984;193(1):99–103. doi: 10.1007/BF00327421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boylan S. A., Eades L. J., Janssen K. A., Lomax M. I., Bender R. A. A restriction enzyme cleavage map of the histidine utilization (hut) genes of Klebsiella aerogenes and deletions lacking regions of hut DNA. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;193(1):92–98. doi: 10.1007/BF00327420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brill W. J., Magasanik B. Genetic and metabolic control of histidase and urocanase in Salmonella typhimurium, strain 15-59. J Biol Chem. 1969 Oct 10;244(19):5392–5402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg R. B., Bloom F. R., Magasanik B. Regulation of histidase synthesis in intergeneric hybrids of enteric bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jul;127(1):114–119. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.1.114-119.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg R. B., Magasanik B. Gene order of the histidine utilization (hut) operons in Klebsiella aerogenes. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jun;122(3):1025–1031. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.3.1025-1031.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe P. A., Hager D. A., Burgess R. R. Purification and properties of the sigma subunit of Escherichia coli DNA-dependent RNA polymerase. Biochemistry. 1979 Apr 3;18(7):1344–1352. doi: 10.1021/bi00574a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maquat L. E., Reznikoff W. S. In vitro analysis of the Escherichia coli RNA polymerase interaction with wild-type and mutant lactose promoters. J Mol Biol. 1978 Nov 15;125(4):467–490. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90311-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenney K., Shimatake H., Court D., Schmeissner U., Brady C., Rosenberg M. A system to study promoter and terminator signals recognized by Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Gene Amplif Anal. 1981;2:383–415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parada J. L., Magasanik B. Expression of the hut operons of Salmonella typhimurium in Klebsiella aerogenes and in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1975 Dec;124(3):1263–1268. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.3.1263-1268.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prival M. J., Magasanik B. Resistance to catabolite repression of histidase and proline oxidase during nitrogen-limited growth of Klebsiella aerogenes. J Biol Chem. 1971 Oct 25;246(20):6288–6296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlesinger S., Scotto P., Magasanik B. Exogenous and endogenous induction of the histidine-degrading enzymes in Aerobacter aerogenes. J Biol Chem. 1965 Nov;240(11):4331–4337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. R., Magasanik B. Nature and self-regulated synthesis of the repressor of the hut operons in Salmonella typhimurium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jul;68(7):1493–1497. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.7.1493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyler B., Deleo A. B., Magasanik B. Activation of transcription of hut DNA by glutamine synthetase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jan;71(1):225–229. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.1.225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]