Abstract
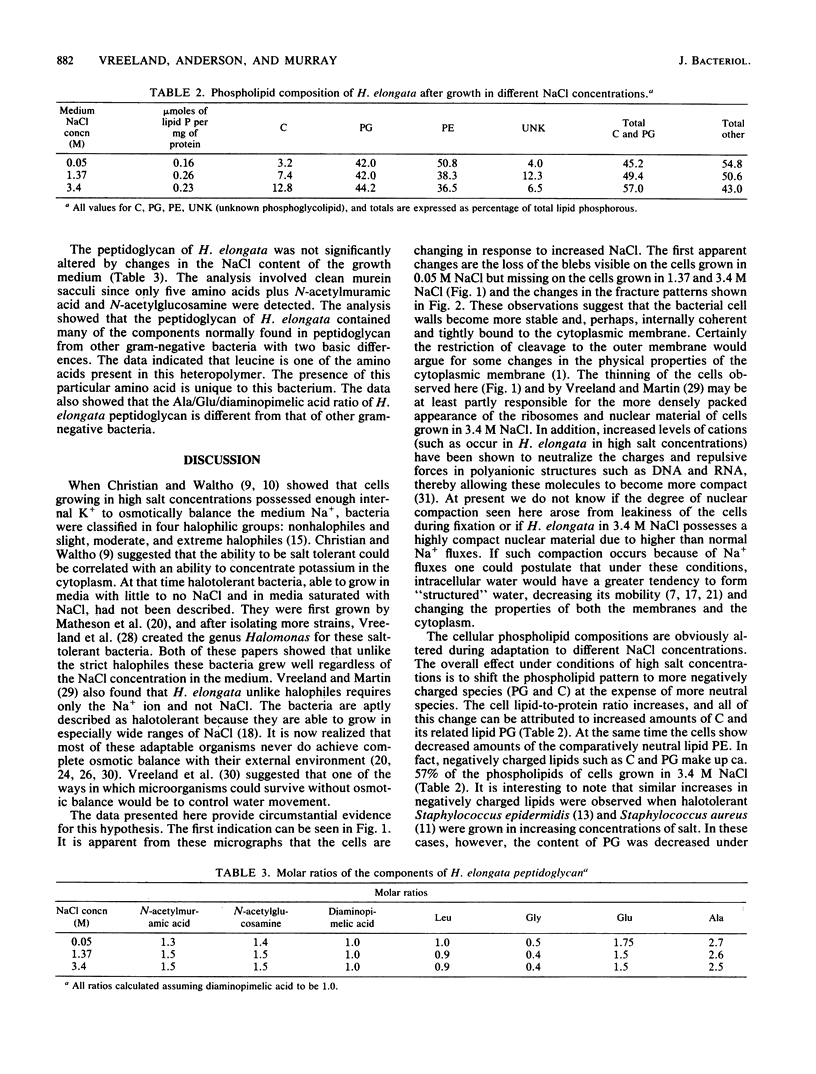
The salt-tolerant bacterium Halomonas elongata makes a variety of physiological adaptations in response to increases in the salt concentration of its growth medium. The cell walls become more compact and internally coherent. The overall lipid pattern shows an increased amount of negatively charged lipids. In addition, the peptidoglycan composition of H. elongata, although not changing in response to increased NaCl, contains the hydrophobic amino acid leucine which is unique among bacterial species. The results suggest that H. elongata is able to live in a wide variety of salt concentrations because it alters its cell physiology in ways which increase both structural integrity and the amount of less-mobile, "structured" cell water, making the cells less susceptible to NaCl-induced dehydration.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer M. E., Dolack M., Houser E. Effects of lipid phase transition of the freeze-cleaved envelope of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1977 Mar;129(3):1563–1573. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.3.1563-1573.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer M. E., Leive L. Effect of ethylenediaminetetraacetate upon the surface of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jun;130(3):1364–1381. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.3.1364-1381.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beveridge T. J., Hall M., Murray R. G. Cleavage planes in the envelope of Aquaspirillum bengal. Can J Microbiol. 1978 Feb;24(2):191–195. doi: 10.1139/m78-034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burdett I. D., Murray R. G. Septum formation in Escherichia coli: characterization of septal structure and the effects of antibiotics on cell division. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jul;119(1):303–324. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.1.303-324.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHRISTIAN J. H., WALTHO J. A. Solute concentrations within cells of halophilic and non-halophilic bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Dec 17;65:506–508. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90453-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHRISTIAN J. H., WALTHO J. A. The sodium and potassium content of non-halophilic bacteria in relation to salt tolerance. J Gen Microbiol. 1961 May;25:97–102. doi: 10.1099/00221287-25-1-97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan K. C., Leung O. C., Lee L. H. Influence of temperature on ionic sparing effect and cell-associated cations in the moderate halophile, Micrococcus varians var. halophilus. Microbios. 1979;24(96):81–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen R. F. Removal of fatty acids from serum albumin by charcoal treatment. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jan 25;242(2):173–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanemasa Y., Yoshioka T., Hayashi H. Alteration of the phospholipid composition of Staphylococcus aureus cultured in medium containing NaCl. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Nov 30;280(3):444–450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komaratat P., Kates M. The lipid composition of a halotolerant species of Staphylococcus epidermidis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Sep 19;398(3):464–484. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(75)90197-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin E. L., Duryea-Rice T., Vreeland R. H., Hilsabeck L., Davis C. Effects of NaCl on the uptake of alpha-[14C]aminoisobutyric acid by the halotolerant bacterium Halomonas elongata. Can J Microbiol. 1983 Oct;29(10):1424–1429. doi: 10.1139/m83-218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masui M., Wada S. Intracellular concentrations of Na+, K+, and cl minus of a moderately halophilic bacterium. Can J Microbiol. 1973 Oct;19(10):1181–1186. doi: 10.1139/m73-191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matheson A. T., Sprott G. D., McDonald I. J., Tessier H. Some properties of an unidentified halophile: growth characteristics, internal salt concentration, and morphology. Can J Microbiol. 1976 Jun;22(6):780–786. doi: 10.1139/m76-114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RENKONEN O. Determination of glycerol in phosphatides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Jan 29;56:367–369. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90580-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouser G., Fkeischer S., Yamamoto A. Two dimensional then layer chromatographic separation of polar lipids and determination of phospholipids by phosphorus analysis of spots. Lipids. 1970 May;5(5):494–496. doi: 10.1007/BF02531316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadler M., McAninch M., Alico R., Hochstein L. I. The intracellular Na+ and K+ composition of the moderately halophilic bacterium, Paracoccus halodenitrificans. Can J Microbiol. 1980 Apr;26(4):496–502. doi: 10.1139/m80-083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shindler D. B., Wydro R. M., Kushner D. J. Cell-bound cations of the moderately halophilic bacterium Vibrio costicola. J Bacteriol. 1977 May;130(2):698–703. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.2.698-703.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unemoto T., Hayashi M. Regulation of internal solute concentrations of marine Vibrio alginolyticus in response to external NaCl concentration. Can J Microbiol. 1979 Aug;25(8):922–926. doi: 10.1139/m79-137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITFIELD J. F., MURRAY R. G. The effects of the ionic environment on the chromatin structures of bacteria. Can J Microbiol. 1956 May;2(3):245–260. doi: 10.1139/m56-029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]