Abstract
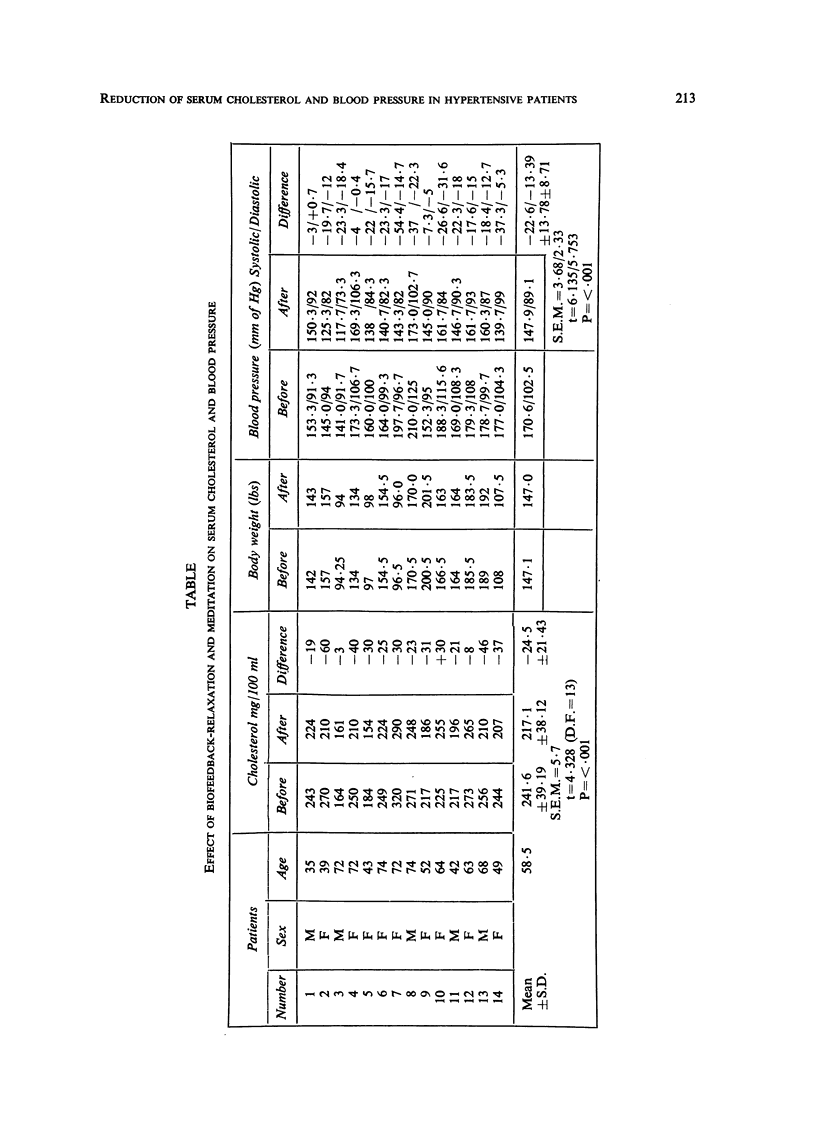
In a pilot study, 14 pharmacologically treated hypertensive patients were given training in psychophysical relaxation exercises, reinforced by biofeedback instruments, for six weeks. The patients were asked to practise twice a day and also incorporate the exercises into everyday activities. In spite of their unchanged drug schedule, their mean blood pressure (B.P.) was reduced from 170·6/102·5 to 147·9/89·14 (P = < ·001) while their mean (± S.D.) serum cholesterol level was reduced from 241·6 ± 39·19 to 217·1 ± 38·12 mg/100 ml (P = < ·001). I believe the possibility of one therapy which can reduce two risk factors at the same time should be explored further in a controlled study.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bellet S., Roman L., Kostis J. The effect of automobile driving on catecholamine and adrenocortical excretion. Am J Cardiol. 1969 Sep;24(3):365–368. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(69)90430-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breckenridge A., Dollery C. T., Parry E. H. Prognosis of treated hypertension. Changes in life expectancy and causes of death between 1952 and 1967. Q J Med. 1970 Jul;39(155):411–429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAWBER T. R., KANNEL W. B., REVOTSKIE N., KAGAN A. The epidemiology of coronary heart disease--the Framingham enquiry. Proc R Soc Med. 1962 Apr;55:265–271. doi: 10.1177/003591576205500403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunnigan M. G., Harland W. A., Fyfe T. Seasonal incidence and mortality of ischaemic heart-disease. Lancet. 1970 Oct 17;2(7677):793–797. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)91460-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELMADJIAN F., HOPE J. M., LAMSON E. T. Excretion of epinephrine and norepinephrine under stress. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1958;14:513–553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIEDMAN M., ROSENMAN R. H. Association of specific overt behavior pattern with blood and cardiovascular findings; blood cholesterol level, blood clotting time, incidence of arcus senilis, and clinical coronary artery disease. J Am Med Assoc. 1959 Mar 21;169(12):1286–1296. doi: 10.1001/jama.1959.03000290012005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIEDMAN M., ROSENMAN R. H., BYERS S. O. Deranged cholesterol metabolism and its possible relationship to human atherosclerosis: a review. J Gerontol. 1955 Jan;10(1):60–85. doi: 10.1093/geronj/10.1.60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRUNDY S. M., GRIFFIN A. C. Effects of periodic mental stress on serum cholesterol levels. Circulation. 1959 Apr;19(4):496–498. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.19.4.496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galton D. J. Hormonal control of lipolysis. Proc R Soc Med. 1974 Jun;67(7):661–662. doi: 10.1177/003591577406700736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins C. D. Psychologic and social precursors of coronary disease (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1971 Feb 4;284(5):244–255. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197102042840506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins C. D. Psychologic and social precursors of coronary disease. (II). N Engl J Med. 1971 Feb 11;284(6):307–317. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197102112840607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kissebah A. H. 'Stress' hormones and lipid metabolism. Proc R Soc Med. 1974 Jun;67(7):665–667. doi: 10.1177/003591577406700738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miettinen M., Turpeinen O., Karvonen M. J., Elosuo R., Paavilainen E. Effect of cholesterol-lowering diet on mortality from coronary heart-disease and other causes. A twelve-year clinical trial in men and women. Lancet. 1972 Oct 21;2(7782):835–838. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)92208-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel C. H. Yoga and bio-feedback in the management of hypertension. Lancet. 1973 Nov 10;2(7837):1053–1055. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)92660-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel C. 12-month follow-up of yoga and bio-feedback in the management of hypertension. Lancet. 1975 Jan 11;1(7898):62–64. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)91070-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel C., North W. R. Randomised controlled trial of yoga and bio-feedback in management of hypertension. Lancet. 1975 Jul 19;2(7925):93–95. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)90002-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raab W. Correlated cardiovascular adrenergic and adrenocortical responses to sensory and mental annoyances in man. A potential accessory cardiac risk factor. Psychosom Med. 1968 Nov-Dec;30(6):809–818. doi: 10.1097/00006842-196811000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raab W. Emotional and sensory stress factors in myocardial pathology. Neurogenic and hormonal mechanisms in pathogenesis, therapy, and prevention. Am Heart J. 1966 Oct;72(4):538–564. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(66)90112-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenman R. H., Friedman M., Straus R., Jenkins C. D., Zyzanski S. J., Wurm M. Coronary heart disease in the Western Collaborative Group Study. A follow-up experience of 4 and one-half years. J Chronic Dis. 1970 Sep;23(3):173–190. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(70)90094-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russek H. I. Role of emotional stress in the etiology of clinical coronary heart disease. Dis Chest. 1967 Jul;52(1):1–9. doi: 10.1378/chest.52.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMAS C. B., MURPHY E. A. Further studies on cholesterol levels in the Johns Hopkins medical students: the effect of stress at examinations. J Chronic Dis. 1958 Dec;8(6):661–668. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(58)90121-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taggart P., Carruthers M. Endogenous hyperlipidaemia induced by emotional stress of racing driving. Lancet. 1971 Feb 20;1(7695):363–366. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)92207-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taggart P., Parkinson P., Carruthers M. Cardiac responses to thermal, physical, and emotional stress. Br Med J. 1972 Jul 8;3(5818):71–76. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5818.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VON EULER U. S., LUNDBERG U. Effect of flying on the epinephrine excretion in air force personnel. J Appl Physiol. 1954 Mar;6(9):551–555. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1954.6.9.551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOLF S. Cardiovascular reactions to symbolic stimuli. Circulation. 1958 Aug;18(2):287–292. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.18.2.287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright B. M., Dore C. F. A random-zero sphygmomanometer. Lancet. 1970 Feb 14;1(7642):337–338. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)90709-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


