Abstract
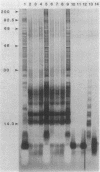
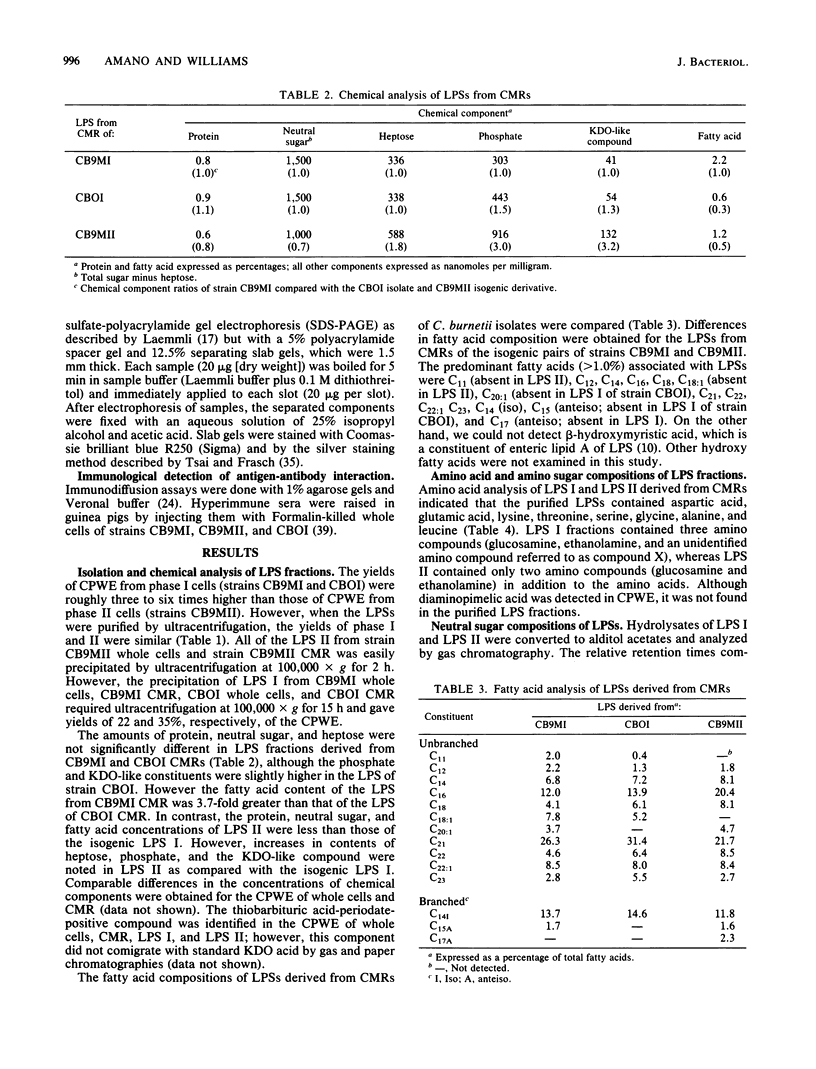
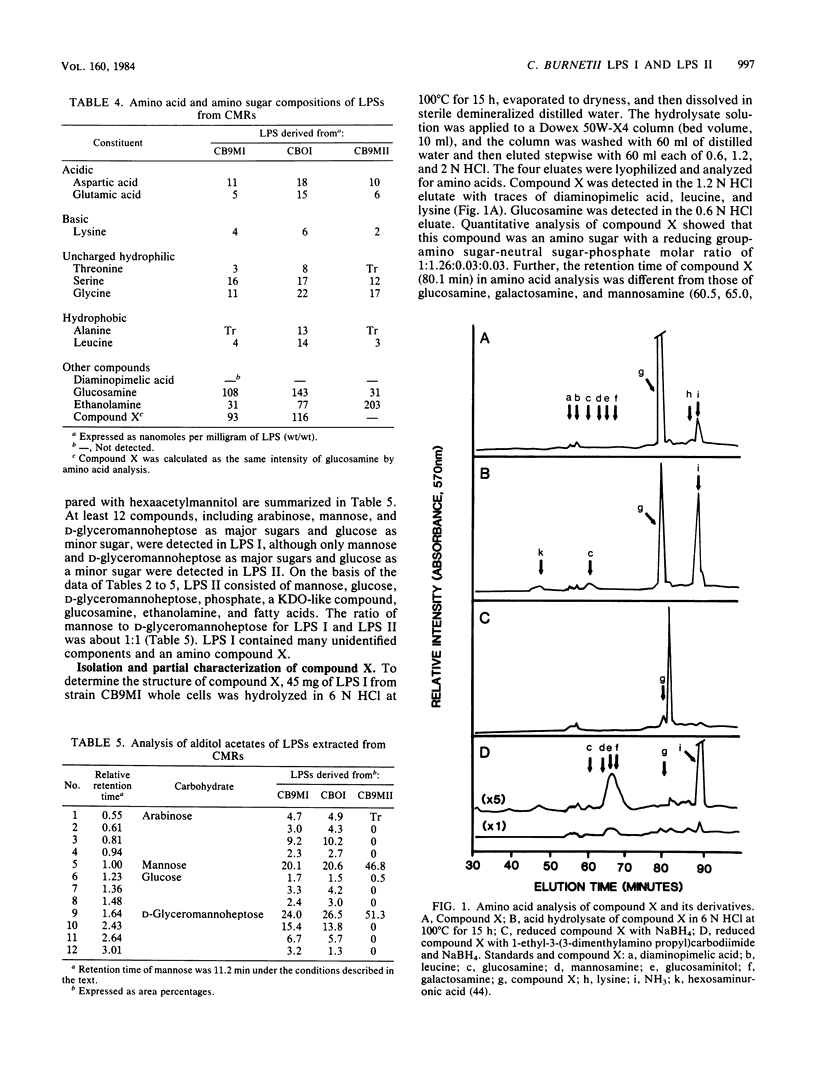
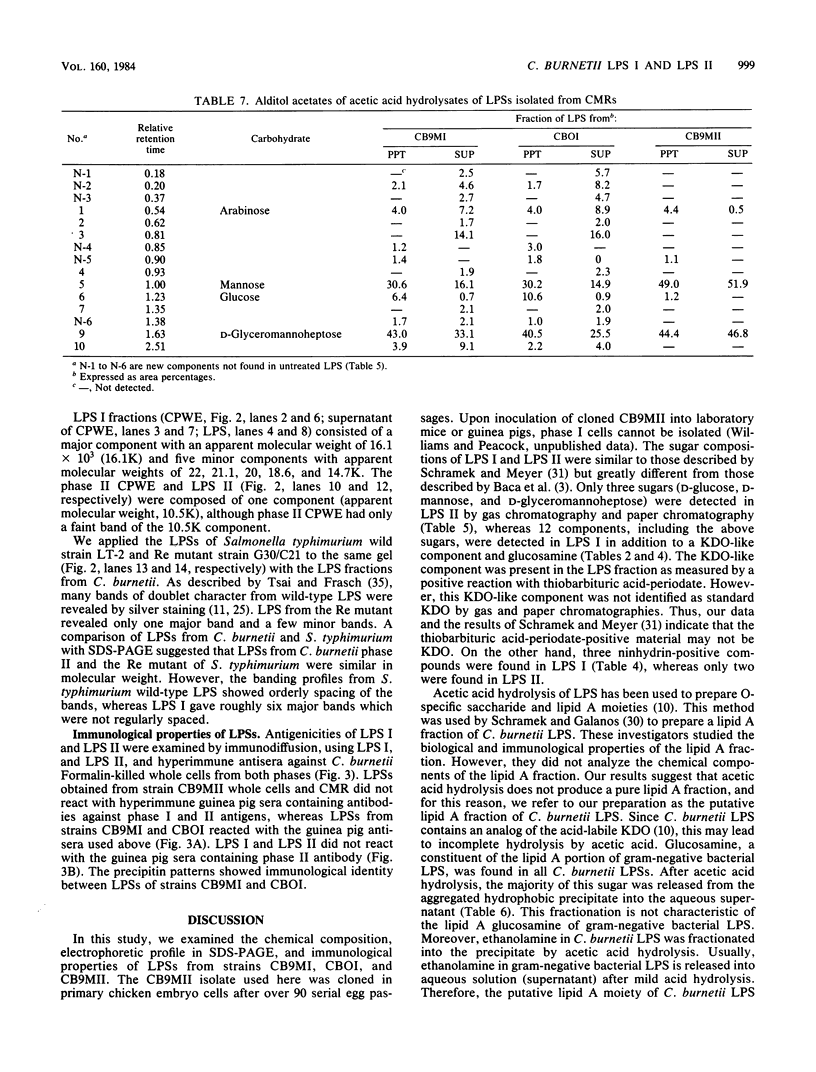
Lipopolysaccharides (LPSs) isolated from phase I and phase II Coxiella burnetii (LPS I and LPS II, respectively) were analyzed for chemical compositions, molecular heterogeneity by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, and immunological properties. The yields of crude phenol-water extracts from phase I cells were roughly three to six times higher than those from phase II cells. Purification of LPSs by ultracentrifugation gave similar yields for both LPS I and LPS II. Purified LPS I and LPS II contained roughly 0.8 and 0.6% protein, respectively. The fatty acid constituents of the LPSs were different in composition and content, with branched-chain fatty acids representing about 15% of the total. beta-Hydroxymyristic acid was not detected in either LPS I or LPS II. A thiobarbituric acid-periodate-positive compound was evident in the LPSs; however, this component was not identified as 3-deoxy-D-mannooctulosonic acid by gas and paper chromatographies. LPS II contained D-mannose, D-glucose, D-glyceromannoheptose, glucosamine, ethanolamine, 3-deoxy-D-mannooctulosonic acid-like material, phosphate, and fatty acids. LPS I contained the unique disaccharide galactosaminuronyl glucosamine and nine unidentified components in addition to the components of LPS II. The hydrophobic, putative lipid A fraction of LPS I and LPS II contained the above constituents, but the hydrophilic fraction was devoid of ethanolamine. The LPS I disaccharide galactosaminuronyl glucosamine was found in both fractions of the acetic acid hydrolysates. Analysis of LPSs by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis followed by silver staining indicated that LPS II was composed of only one band, whereas LPS I consisted of six or more bands with irregular spacing. Ouchterlony immunodiffusion tests demonstrated that LPS I reacted with phase I but not with phase II whole-cell hyperimmune antibody, and LPS II reacted neither with phase I nor phase II hyperimmune antibody. From these results, it was concluded that the chemical structures of LPSs from C. burnetii were different from those of the LPSs of gram-negative bacteria; however, the LPS structural variation in C. burnetii may be similar to the smooth-to-rough mutational variation of saccharide chain length in gram-negative bacteria.
Full text
PDF


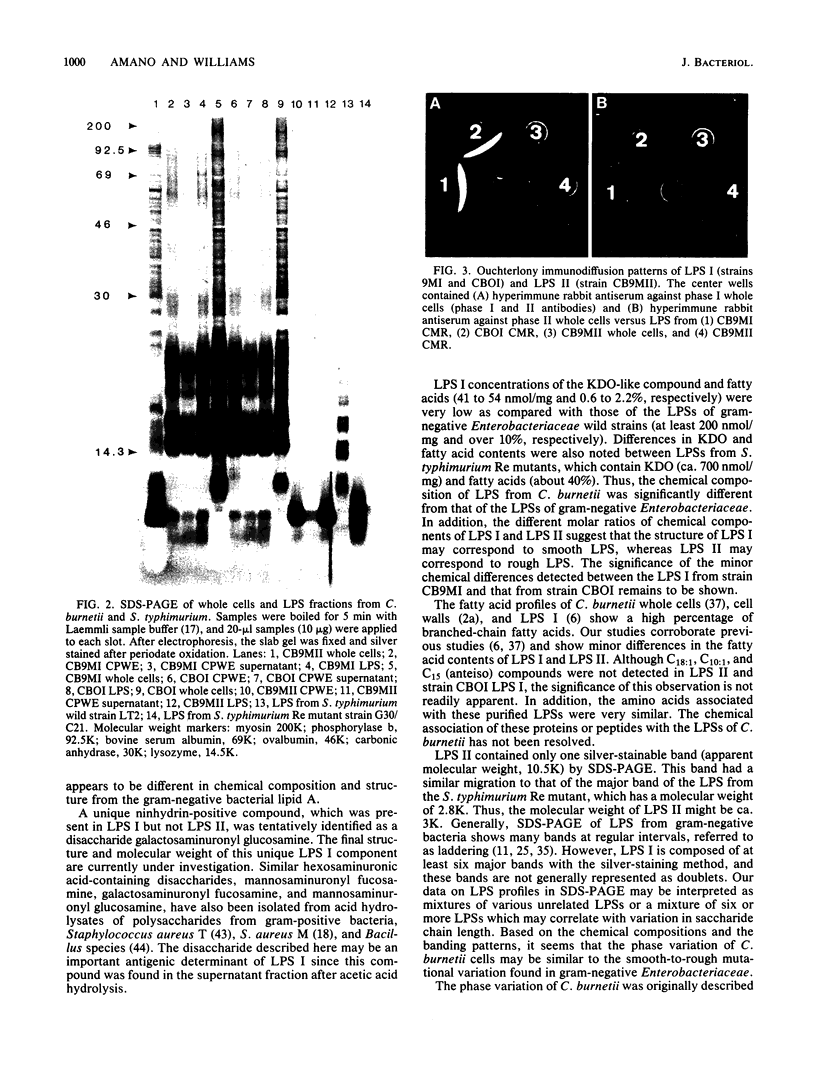


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amano K., Hayashi H., Araki Y., Ito E. The action of lysozyme on peptidoglycan with N-unsubstituted glucosamine residues. Isolation of glycan fragments and their susceptibility to lysozyme. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Jun 1;76(1):299–307. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11596.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amano K., Williams J. C., McCaul T. F., Peacock M. G. Biochemical and immunological properties of Coxiella burnetii cell wall and peptidoglycan-protein complex fractions. J Bacteriol. 1984 Dec;160(3):982–988. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.3.982-988.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amano K., Williams J. C. Peptidoglycan of Legionella pneumophila: apparent resistance to lysozyme hydrolysis correlates with a high degree of peptide cross-linking. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):520–526. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.520-526.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BREZINA R. Contribution to the study of phase variation in Coxiella burneti. Acta Virol. 1958 Apr-Jun;2(2):91–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baca O. G., Paretsky D. Some physiological and biochemical effects of a Coxiella burneti lipopolysaccharide preparation on guinea pigs. Infect Immun. 1974 May;9(5):939–945. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.5.939-945.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan M. L., McChesney J., Paretsky D. Further characterization of a lipopolysaccharide from Coxiella burneti. Infect Immun. 1976 Jun;13(6):1721–1727. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.6.1721-1727.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FISET P. Phase variation of Rickettsia (Coxiella) burneti; study of the antibody response in guinea pigs and rabbits. Can J Microbiol. 1957 Apr;3(3):435–445. doi: 10.1139/m57-046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman R. C., Leive L. Heterogeneity of antigenic-side-chain length in lipopolysaccharide from Escherichia coli 0111 and Salmonella typhimurium LT2. Eur J Biochem. 1980;107(1):145–153. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04635.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOYER B. H., ORMSBEE R. A., FISET P., LACKMAN D. B. Differentiation of Phase I and Phase II Coxiella burnetti by equilibrium density gradient sedimentation. Nature. 1963 Feb 9;197:573–574. doi: 10.1038/197573a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazár J., Skultétyová E., Brezina R. Phagocytosis of Coxiella burneti by macrophages. Acta Virol. 1975 Sep;19(5):426–431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto R. A., Walker J. S. Interaction between Coxiella burnetii and guinea pig peritoneal macrophages. Infect Immun. 1976 Aug;14(2):416–421. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.2.416-421.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krauss H., Schiefer H. G., Schmatz H. D. Ultrastructural investigations on surface structures involved in Coxiella burnetii phase variation. Infect Immun. 1977 Mar;15(3):890–896. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.3.890-896.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROBERTS N. R., LEINER K. Y., WU M. L., FARR A. L. The quantitative histochemistry of brain. I. Chemical methods. J Biol Chem. 1954 Mar;207(1):1–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liau D. F., Melly M. A., Hash J. H. Surface polysaccharide from Staphylococcus aureus M that contains taurine, D-aminogalacturonic acid, and D-fucosamine. J Bacteriol. 1974 Sep;119(3):913–922. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.3.913-922.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüderitz O., Staub A. M., Westphal O. Immunochemistry of O and R antigens of Salmonella and related Enterobacteriaceae. Bacteriol Rev. 1966 Mar;30(1):192–255. doi: 10.1128/br.30.1.192-255.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mühlradt P. F., Wray V., Lehmann V. A 31P-nuclear-magnetic-resonance study of the phosphate groups in lipopolysaccharide and lipid A from Salmonella. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Nov 15;81(1):193–203. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11941.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OSBORN M. J. STUDIES ON THE GRAM-NEGATIVE CELL WALL. I. EVIDENCE FOR THE ROLE OF 2-KETO- 3-DEOXYOCTONATE IN THE LIPOPOLYSACCHARIDE OF SALMONELLA TYPHIMURIUM. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Sep;50:499–506. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.3.499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OUCHTERLONY O. Diffusion-in-gel methods for immunological analysis. Prog Allergy. 1958;5:1–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARK J. T., JOHNSON M. J. A submicrodetermination of glucose. J Biol Chem. 1949 Nov;181(1):149–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palva E. T., Mäkelä P. H. Lipopolysaccharide heterogeneity in Salmonella typhimurium analyzed by sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Eur J Biochem. 1980;107(1):137–143. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04634.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STOKER M. G., FISET P. Phase variation of the Nine Mile and other strains of Rickettsia burneti. Can J Microbiol. 1956 May;2(3):310–321. doi: 10.1139/m56-036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schramek S., Brezina R. Characterization of an endotoxic lipopolysaccharide from Coxiella burnetii. Acta Virol. 1976 Apr;20(2):152–158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schramek S., Brezina R. Isolation of endotoxic lipopolysaccharide from phase II Coxiella burnetti. Acta Virol. 1979 Jul;23(4):349–349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schramek S., Brezina R., Kazár J., Khavkin T. N. Attempts at demonstration of lipopolysaccharide in phase II Coxiella burnetii. Acta Virol. 1978 Nov;22(6):509–511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schramek S., Galanos C. Lipid A component of lipopolysaccharides from Coxiella burnetii. Acta Virol. 1981 Jul;25(4):230–234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schramek S., Mayer H. Different sugar compositions of lipopolysaccharides isolated from phase I and pure phase II cells of Coxiella burnetii. Infect Immun. 1982 Oct;38(1):53–57. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.1.53-57.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TREVELYAN W. E., PROCTER D. P., HARRISON J. S. Detection of sugars on paper chromatograms. Nature. 1950 Sep 9;166(4219):444–445. doi: 10.1038/166444b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor R. L., Conrad H. E. Stoichiometric depolymerization of polyuronides and glycosaminoglycuronans to monosaccharides following reduction of their carbodiimide-activated carboxyl groups. Biochemistry. 1972 Apr 11;11(8):1383–1388. doi: 10.1021/bi00758a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. M., Frasch C. E. A sensitive silver stain for detecting lipopolysaccharides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90673-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuji A., Kinoshita T., Hoshino M. Analytical chemical studies on amino sugars. II. Determination of hexosamines using 3-methyl-2-benzothiazolone hydrazone hydrochloride. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 1969 Jul;17(7):1505–1510. doi: 10.1248/cpb.17.1505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzianabos T., Moss C. W., McDade J. E. Fatty acid composition of rickettsiae. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Mar;13(3):603–605. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.3.603-605.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. C., Cantrell J. L. Biological and immunological properties of Coxiella burnetii vaccines in C57BL/10ScN endotoxin-nonresponder mice. Infect Immun. 1982 Mar;35(3):1091–1102. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.3.1091-1102.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. C., Johnston M. R., Peacock M. G., Thomas L. A., Stewart S., Portis J. L. Monoclonal antibodies distinguish phase variants of Coxiella burnetii. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):421–428. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.421-428.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. C., Peacock M. G., McCaul T. F. Immunological and biological characterization of Coxiella burnetii, phases I and II, separated from host components. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):840–851. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.840-851.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu T. C., Park J. T. Chemical characterization of a new surface antigenic polysaccharide from a mutant of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1971 Nov;108(2):874–884. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.2.874-884.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoneyama T., Koike Y., Arakawa H., Yokoyama K., Sasaki Y., Kawamura T., Araki Y., Ito E., Takao S. Distribution of mannosamine and mannosaminuronic acid among cell walls of Bacillus species. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jan;149(1):15–21. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.1.15-21.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]